
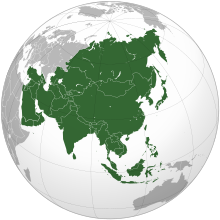
 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured article The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, ending the war. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) was incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of Japan in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be willing to mediate, the Soviets were covertly preparing to attack Japanese forces in Manchuria and Korea (in addition to South Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands) in fulfillment of promises they had secretly made to the US and the UK at the Tehran and Yalta Conferences. On 6 August 1945, at 8:15 am local time, the United States detonated an atomic bomb over the Japanese city of Hiroshima. Sixteen hours later, American President Harry S. Truman called again for Japan's surrender, warning them to "expect a rain of ruin from the air, the like of which has never been seen on this earth." Late on 8 August 1945, in accordance with the Yalta agreements, but in violation of the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact, the Soviet Union declared war on Japan, and soon after midnight on 9 August 1945, the Soviet Union invaded the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo. Hours later, the United States dropped a second atomic bomb, on the Japanese city of Nagasaki. Emperor Hirohito ordered the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War to accept the terms the Allies had set down in the Potsdam Declaration. After several more days of behind-the-scenes negotiations and a failed coup d'état, Emperor Hirohito gave a recorded radio address across the Empire on 15 August announcing the surrender of Japan to the Allies. (Full article...)Selected Country Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of 1,564,116 square kilometres (603,909 square miles), with a population of just 3.3 million, making it the world's most sparsely populated sovereign state. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border a closed sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population. The territory of modern-day Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the First Turkic Khaganate, the Second Turkic Khaganate, the Uyghur Khaganate and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous land empire in history. His grandson Kublai Khan conquered China proper and established the Yuan dynasty. After the collapse of the Yuan, the Mongols retreated to Mongolia and resumed their earlier pattern of factional conflict, except during the era of Dayan Khan and Tumen Zasagt Khan. In the 16th century, Tibetan Buddhism spread to Mongolia, being further led by the Manchu-founded Qing dynasty, which absorbed the country in the 17th century. By the early 20th century, almost one-third of the adult male population were Buddhist monks. After the collapse of the Qing dynasty in 1911, Mongolia declared independence, and achieved actual independence from the Republic of China in 1921. Shortly thereafter, the country became a satellite state of the Soviet Union. In 1924, the Mongolian People's Republic was founded as a socialist state. After the anti-communist revolutions of 1989, Mongolia conducted its own peaceful democratic revolution in early 1990. This led to a multi-party system, a new constitution of 1992, and transition to a market economy. (Full article...)Featured biographySeptimia Zenobia (Palmyrene Aramaic: 𐡡𐡶𐡦𐡡𐡩, Bat-Zabbai; c. 240 – c. 274) was a third-century queen of the Palmyrene Empire in Syria. Many legends surround her ancestry; she was probably not a commoner and she married the ruler of the city, Odaenathus. Her husband became king in 260, elevating Palmyra to supreme power in the Near East by defeating the Sasanian Empire of Persia and stabilizing the Roman East. After Odaenathus' assassination, Zenobia became the regent of her son Vaballathus and held de facto power throughout his reign. In 270, Zenobia launched an invasion that brought most of the Roman East under her sway and culminated with the annexation of Egypt. By mid-271 her realm extended from Ancyra, central Anatolia, to Upper Egypt, although she remained nominally subordinate to Rome. However, in reaction to the campaign of the Roman emperor Aurelian in 272, Zenobia declared her son emperor and assumed the title of empress, thus declaring Palmyra's secession from Rome. The Romans were victorious after heavy fighting; the empress was besieged in her capital and captured by Aurelian, who exiled her to Rome, where she spent the remainder of her life. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureThe Qianlong Emperor was the sixth emperor of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China. The fourth son of the Yongzheng Emperor, his reign officially began 11 October 1735, lasting for 60 years. Named Hongli, he chose the era name Qianlong, meaning "heavenly prosperity". Although his early years saw the continuation of an era of prosperity and great military success in China, his final years saw troubles at home and abroad converge on the Qing Empire. Qianlong abdicated the throne at the age of 85, to his son, the Jiaqing Emperor, fulfilling his promise not to reign longer than his grandfather, the Kangxi Emperor.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
The Hajj is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims, and a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetime by all adult Muslims who are physically and financially capable of undertaking the journey, and can support their family during their absence. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |





























































































