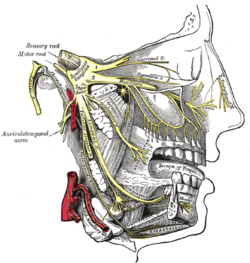
The superior dental plexus is a nerve plexus that innervates the upper/maxillary teeth and as adjacent structures.[1] It is formed by the anterior superior alveolar nerve (ASAN), middle superior alveolar nerve (MSAN), and the posterior superior alveolar nerve (PSAN).[1][2][3] It issues dental branches and gingival branches.[4]
| Superior dental plexus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus dentalis superior |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.053 |
| TA2 | 6236 |
| FMA | 77528 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
A cadaveric study found the plexus to be situated in the alveolar process of the maxilla.[5]
Anatomy
editThe PSAN forms the posterior portion of the plexus and is distributed to the upper molar teeth and adjacent gingiva as well as the mucosa of the cheek.[1]
The MSAN forms the middle portion of the plexus and is distributed to the upper premolar teeth and the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus.[1]
The ASAN forms the anterior portion of the plexus and is distributed to the canine and incisor teeth as well as the anterior portion of the maxillary sinus.[1]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c d e Morris, Alyssa L.; Tadi, Prasanna (2023), "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Teeth", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 32491475, retrieved 2023-07-19
- ^ Shafique, Shiza; M Das, Joe (2023), "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Maxillary Nerve", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 31194417, retrieved 2023-07-19
- ^ Iwanaga, Joe; Tubbs, R. Shane (2018-01-28). "Palatal Injection does not Block the Superior Alveolar Nerve Trunks: Correcting an Error Regarding the Innervation of the Maxillary Teeth". Cureus. 10 (1): e2120. doi:10.7759/cureus.2120. ISSN 2168-8184. PMC 5873831. PMID 29600124.
- ^ "superior dental plexus". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2023-07-19.
- ^ Murakami, G.; Ohtsuka, K.; Sato, I.; Moriyama, H.; Shimada, K.; Tomita, H. (March 1994). "The superior alveolar nerves: their topographical relationship and distribution to the maxillary sinus in human adults". Okajimas Folia Anatomica Japonica. 70 (6): 319–328. doi:10.2535/ofaj1936.70.6_319. ISSN 0030-154X. PMID 8041567.