 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Neo-rx, others |
| Other names | Neomycin sulfate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Systemic: Monograph Topical: Monograph Eye and ear: Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682274 |
| Routes of administration | Topical, by mouth |
| Drug class | Aminoglycoside[1] |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | None |
| Protein binding | N/A |
| Metabolism | N/A |
| Elimination half-life | 2 to 3 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
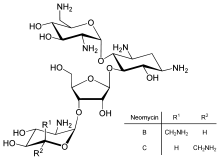
| Formula | C23H46N6O13 |
| Molar mass | 614.650 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Neomycin is an antibiotic.[1] Applied to the skin it is used to treat superficial bacterial skin infections.[1] By mouth it is used to sterilize the bowel before surgery and to treat hepatic encephalopathy.[2][3] As an eye drop it is used for conjunctivitis and as an ear drop it is used for otitis externa.[4]
Common side affects when applied to the skin include contact dermatitis.[1] Common side effects when taken by mouth include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.[3] Other side effects when taken by mouth may include hearing problems, balance problems, kidney problems, and seizures.[3] While it is unclear if applying it to the skin is safe in pregnancy, taking it by mouth may harm the baby.[1][3] It is in the aminoglycoside class.[1]
Neomycin was discovered in 1949 and approval for medical use in 1952.[5][6] It is available as a generic medication.[2] The cream is available in combination with polymyxin B, bacitracin, or hydrocortisone and over the counter.[1] In the United States 100 tablets of 500 mg cost about 86 USD as of 2021.[7] In the United Kingdom combination products applied externally are generally inexpensive.[2]
References edit
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Neomycin (Topical) Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 21 January 2021. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 547. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ^ a b c d e f "Neomycin (Systemic) Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 29 April 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ a b "Neomycin (EENT) Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 28 January 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ Ricci, Alfredo (25 June 2008). Amino Group Chemistry: From Synthesis to the Life Sciences. John Wiley & Sons. p. 306. ISBN 978-3-527-62127-9. Archived from the original on 13 November 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 507. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2020-08-01. Retrieved 2020-05-25.
- ^ "Neomycin Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 29 April 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2021.