| Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis | |
|---|---|
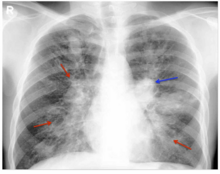 | |
| Chest Xray of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis showing left-sided perihilar opacity (blue arrow) along with non-homogeneous infiltrates (transient pulmonary infiltrates indicated by red arrows) in all zones of both lung fields | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Wheezing, cough including coughing up blood, fever, tiredness, weight loss[1] |
| Complications | Bronchiectasis[2] |
| Causes | Aspergillus exposure[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood tests[2][3] |
| Differential diagnosis | Pneumonia, Churg-Strauss syndrome[2] |
| Treatment | Antifungal medication, corticosteroids[1] |
| Frequency | 2% of people with asthma[2] |
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is an allergic reaction to the fungus Aspergillus, after it has been inhaled.[1][4] Symptoms may include wheezing, cough including coughing up blood, fever, tiredness, and weight loss.[1] Complications may include bronchiectasis—a condition marked by abnormally dilated airways.[2]
Most people breathe in Aspergillus spores without getting sick.[5] Risk factors include asthma, cystic fibrosis, and being immunocompromised.[3] The underlying mechanism involves inflammation due to an abnormal immune response which results in increased mucus production.[2] The diagnosis may be supported by chest X-ray, CT scan, increased eosinophils, IgE levels of greater than 1,000 IU/mL, or a positive skin allergy test to A. fumigatus.[2] It is a type of aspergillosis.[5]
Treatment is generally with the antifungal medication itraconazole and corticosteroids such as prednisone.[1] Other agents used may include amphotericin B and omalizumab.[2] In about half of people the disease recurs and repeated treatment is requires.[1] ABPA affects about 1 to 4 million people.[4] It occurs in about 2% of people with asthma and up to 15% of people with cystic fibrosis.[2]
References edit
- ^ a b c d e f g "Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 19 November 2021. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Orphanet: Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 23 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ^ a b Sisodia, Jitendra; Bajaj, Tushar (2022). "Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- ^ a b "Aspergillosis". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). Archived from the original on 21 March 2021. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ^ a b "About Aspergillosis | Aspergillosis | Types of Fungal Diseases | Fungal Diseases | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 2 February 2021. Archived from the original on 27 June 2021. Retrieved 23 January 2022.