 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fosamax, Binosto, others |
| Other names | Alendronate, alendronate sodium |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601011 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Bisphosphonate[2] |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 0.6% |
| Metabolism | excreted unchanged |
| Elimination half-life | 126 months |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
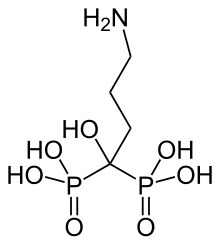
| Formula | C4H13NO7P2 |
| Molar mass | 249.097 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Alendronic acid, sold under the brand name Fosamax among others, is a bisphosphonate medication used to treat osteoporosis and Paget's disease of bone.[2] It is taken by mouth.[2] Use is often recommended together with vitamin D, calcium supplementation, and lifestyle changes.[2]
Common side effects include constipation, abdominal pain, nausea, and acid reflux.[2] Serious side effects may include esophageal problems, osteonecrosis of the jaw, and femur fractures.[2] Use is not recommended during pregnancy or in those with poor kidney function.[4] Alendronic acid works by decreasing the activity of cells that break down bone.[2]
Alendronic acid was first described in 1978 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1995.[2][5] It is available as a generic medication.[4] In the United Kingdom, a month of medication costs the NHS about 0.41 pounds as of 2019.[4] In the United States, the wholesale cost is about US$1.16 per month.[6] In 2017, it was the 90th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than eight million prescriptions.[7][8]
References edit
- ^ a b "Alendronate Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 22 August 2019. Archived from the original on 1 December 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Fosamax Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2 February 2019. Retrieved 2 February 2019.
- ^ "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ^ a b c British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 710–711. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 523. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2021-03-18. Retrieved 2020-06-03.
- ^ "NADAC as of 2019-01-30". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 2019-03-27. Retrieved 2 February 2019.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ "Alendronate Sodium - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 8 July 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.