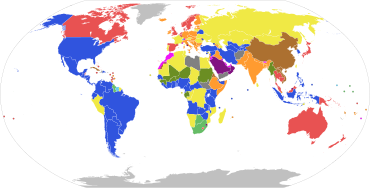
Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature
Constitutional monarchy with a ceremonial monarch
Parliamentary republic with a ceremonial president
Presidential system: Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature
Presidential republic
Hybrid systems:
Semi-presidential republic: Executive president is independent of the legislature; head of government is appointed by the president and is accountable to the legislature
Assembly-independent republic: Head of government (president or directory) is elected by the legislature, but is not accountable to it
Semi-constitutional monarchy: Monarch holds significant executive or legislative power
Absolute monarchy: Monarch has unlimited power
One-party state: Power is constitutionally linked to a single political party
Military junta: Committee of military leaders controls the government; constitutional provisions are suspended
Provisional government: No constitutionally defined basis to current regime
Dependent territories and places without governments
Note: this chart represent de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.[citation needed]
Constitutional monarchies in which the monarch personally exercises power, often alongside a weak parliament
States that do not fit in any of the above listed systems
