| Acessory saphenous vein | |
|---|---|
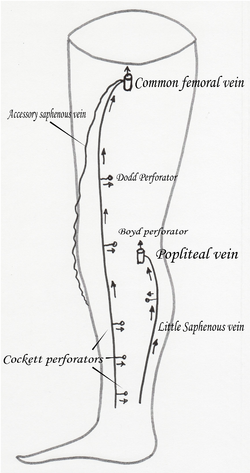 Accessory saphenous vein | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Drains to | great saphenous vein |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The accessory saphenous vein is a special anterior tributary of the great saphenous vein (GSV), draining the antero-lateral face of the tigh.
It becomes very often insufficient, causing important varicous veins with an autonomous course and often is the only insufficient vein present on a patient.
Usually it joins GSV very near the saphenous-femoral junction at the saphenous arch or can drain directly in the femoral vein. Sometimes it can drain below the saphenous arch or in a GSV tributary. Sometimes it can drain in the external pudendal vein (wich sometimes communicates with an ovarian vein) and be the reason of a varicose disease of the thigh secondary to pelvic varicose disease.[1]
In contrast with others tributaries, its wall is histologically saphenous-type with a thick media, running parallel and extern to the GSV.[1]
When treated properly the patient can be considered cured from his disease because this vein is just a collateral one, and most of the time is the only sick vein over all the superficial venous system.
At the superior 1/3 of the thigh it is located under the superficial fascia, like the GSV, but becomes very superficial below this level.[2]
We can identify it near the saphenous ostium by a typical ultrasonographic image the so-called Mickey mouse sign (the 2 ears will be the GSV and the ASV, the head is the common femoral vein).
When the ultrasonography is performed, we can see it running across the anterior face of the thigh in a plan outside the femoral vessels, the GSV being at the inside of those vessels.[2]
When insufficient, usually it tries to drain in the superior peroneal perforator at the external face of the knee, but it can reach the leg at its lower 1/3 and, drain in the lower peroneal perforator.
The importance of this vein is the frequent confusion between it and the GSV made at ultrasonographic examination. This confusion can allow to a medical error and finishes on a stripping of the real GSV. So its presence is described as a reason for stripping postoperative recurrences.[1]
 |
 |
 |
References
edit- ^ a b c "The saphenofemoral junction - Accessory saphenous veins". Retrieved 02-08-2013.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ a b Franceschi, C. (2009). Principles of Venous Hemodynamics. Nova biomedical Books. pp. 14–15. ISBN 978-60692-485-3.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: length (help); Unknown parameter|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)