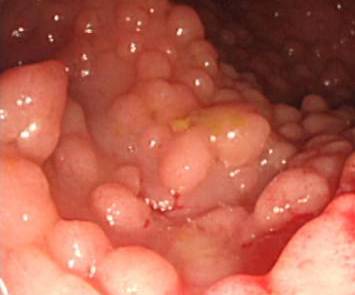
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) is a inherited genetic disease in which multiple polyps arise in the colon, usually numbering more than 100. Accumulation of a polyps this severe ultimately leads to colorectal cancer if the diagnosis is made late, of unchecked. Similar disease to FAPare Gardner Syndrome, and Turcoat Syndrome As the name would imply, there are a numerous amount of polyps, but they are not limited to the colon and be found in other areas of the digestive tract.
Genetics edit
Fap is a autosomal dominant inherited disease. Individuals afflicted with this disease only need one gene to be mutated to inherit the disease. The mutated gene that encodes for polyposis is the APC known as Adenomatous polyposis coli.
Symtpoms edit
Individuals who have FAP start to develop polyps in their teens, and are unaware of the disease until symptoms occur. Symptoms would include, bloody bowel movements, diarrhea, and constipation.
Diagnosis edit
Once symptoms are present the premiere recomended procedure to find the cause of the symptoms would be to have a colonoscopy; a procedure in which a fiber optic camera is inserted into the colon to actively search for any abnormalities. Upon inspection of the colon if there are polyps that are greater than 100 in total, the individual would have a diagnosis of FAP. After the colonoscopy, if the patients chooses they could undergo further genetic testing to verify the diagnosis.
Treatment edit
Unfortunately there is no cure for FAP. Treatment of FAP include annuals colonoscopes to determine if the patient has a high rick of developing cancer in the area of polyposis. FAP is usually diagnosed late and either a colon resection or colectomy is the only chance for survival. Patients that have advanced stages of FAP may have an extreme procdure called a total colectomy, in which the entire colon is removed and the small intestine is surgically attached to the rectum.

