Townsend's warbler (Setophaga townsendi) is a small songbird of the New World warbler family.
| Townsend's warbler | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Parulidae |
| Genus: | Setophaga |
| Species: | S. townsendi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Setophaga townsendi (Townsend, 1837)
| |
| |
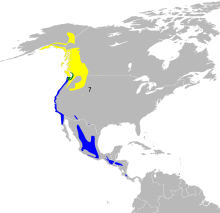
| Range of S. townsendi Breeding range Year-round range Wintering range
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Sylvia townsendi (protonym) | |
Taxonomy
editTownsend's warbler was formally described in 1837 by the American naturalist John Kirk Townsend under the binomial name Sylvia townsendi.[2] The type locality is Fort Vancouver on the Columbia River in the state of Washington.[3] After the merger of the genera Dendroica and Setophaga,[4] Townsend's warbler is now placed in the genus Setophaga that was introduced by the English naturalist William Swainson in 1827.[5][6] The species is monotypic: no subspecies are recognised.[6]
Description
editTownsend's warbler has a yellow face with a black stripe across its cheeks extending into an ear patch, a thin pointed bill, two white wing bars, olive upperparts with black streaks on their backs and flanks, and a white belly.[7] Adult males have a black cap, black throat and yellow lower breast; females have a dark cap and a yellow throat. Immature birds are similar to females with a dark green cap and cheeks.[8]
| Standard Measurements[9][8] | |
|---|---|
| length | 4.5–5 in (110–130 mm) |
| weight | 8.8 g (0.31 oz) |
| wingspan | 8 in (200 mm) |
| wing | 63.1–69.9 mm (2.48–2.75 in) |
| tail | 47.1–54 mm (1.85–2.13 in) |
| culmen | 9.9–10.8 mm (0.39–0.43 in) |
| tarsus | 18.1–19 mm (0.71–0.75 in) |
Life history
editTheir breeding habitats are coniferous forests with large trees on the northwestern coast of North America.[7] Their nests are shallow cups built with grass and lined with moss.[10] These nests are usually placed atop a branch in a conifer. The female lays 4 to 5 brown-speckled white eggs.[10]
This bird is closely related to the hermit warbler, and the two species interbreed where their ranges overlap.[8]
Birds from Haida Gwaii migrate short distances further south on the Pacific coast. Other birds winter in Mexico, Central America, and the south-western United States.[7]
They forage actively in the higher branches, often gleaning insects from foliage and sometimes hovering or catching insects in flight.[11] They mainly eat insects and spiders and seeds. Outside of the nesting season, these birds forage in mixed flocks. In winter, they also eat berries and plant nectar,[10] and honeydew directly from the anus of scale insects.[12]
The song of the male bird is a buzzed zee-zee-zee-bzz-zee or weazy weazy weazy weazy twea,[10] somewhat similar to that of its eastern relative, the black-throated green warbler.[8] The call is a sharp tup.
This bird was named after the American ornithologist, John Kirk Townsend.[2] Although Townsend is also credited with first describing this bird, he used a name chosen by Thomas Nuttall, who was travelling with him, and so sidestepped the convention against naming a species after oneself.[7]
References
edit- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Setophaga townsendi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22721683A94723311. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22721683A94723311.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ a b Townsend, John Kirk (1837). "Description of twelve new species of birds, chiefly from the vicinity of the Columbia River". Journal of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 7: 187–192 [191–192].
- ^ Paynter, Raymond A. Jr, ed. (1968). Check-List of Birds of the World. Vol. 14. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Museum of Comparative Zoology. p. 26.
- ^ Chesser, R. Terry; Banks, Richard C.; Barker, F. Keith; Cicero, Carla; Dunn, Jon L.; Kratter, Andrew W.; Lovette, Irby J.; Rasmussen, Pamela C.; Remsen, J. V.; Rising, James D.; Stotz, Douglas F.; Winker, Kevin (2011). "Fifty-Second Supplement to the American Ornithologists' Union check-list of North American Birds". The Auk. 128 (3): 600–613. doi:10.1525/auk.2011.128.3.600. S2CID 13691956.
- ^ Swainson, William John (1827). "A synopsis of the birds discovered in Mexico by W. Bullock, F.L.S. and Mr. William Bullock jun". Philosophical Magazine. New Series. 1: 364–369 [368]. doi:10.1080/14786442708674330.
- ^ a b Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (2020). "New World warblers, mitrospingid tanagers". IOC World Bird List Version 10.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ a b c d Wright, A. L.; Hayward, G. D.; Matsuoka, S. M.; Hayward, P. H. (2020-03-04). Rodewald, P. G. (ed.). "Birds of the World". Townsend's Warbler. Cornell Lab of Ornithology. doi:10.2173/bow.towwar.01. Retrieved 2022-10-21.
- ^ a b c d Sibley, David Allen (2000). The Sibley Guide to Birds. New York: Knopf. p. 438. ISBN 0-679-45122-6.
- ^ Godfrey, W. Earl (1966). The Birds of Canada. Ottawa: National Museum of Canada. p. 331.
- ^ a b c d "Townsend's Warbler". Audubon Guide to North American Birds. 2014-11-13. Retrieved 2022-10-21.
- ^ Rich, Terrell D.; Dobkin, David S. (1996). "Conservation and Management of Neotropical Migrant Landbirds in the Northern Rockies and Great Plains". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 60 (1): 209. doi:10.2307/3802059. JSTOR 3802059.
- ^ Greenberg, Russell; Caballero, Claudia Macias; Bichier, Peter (1993). "Defense of Homopteran Honeydew by Birds in the Mexican Highlands and Other Warm Temperate Forests". Oikos. 68 (3): 519. Bibcode:1993Oikos..68..519G. doi:10.2307/3544920. JSTOR 3544920.
External links
edit- "Townsend's warbler media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Townsend's warbler species account - Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Townsend's warbler - Dendroica townsendi - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- Townsend's warbler photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Townsend's warbler species account at Neotropical Birds (Cornell Lab of Ornithology)
