Styphelia exolasia, commonly known as Woronora beard-heath,[1] is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to a small area of New South Wales. It is an erect shrub with oblong or elliptic leaves, and drooping, white, tube-shaped flowers.
| Styphelia exolasia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Styphelia |
| Species: | S. exolasia
|
| Binomial name | |
| Styphelia exolasia | |

| |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Leucopogon exolasius (F.Muell.) Benth. | |
Description
editStyphelia exolasia is an erect shrub that typically grows to a height of 1 m (3 ft 3 in) and has softly-hairy branchlets. Its leaves are oblong to elliptic, 5.2–14.3 mm (0.20–0.56 in) long and 1.2–2.4 mm (0.047–0.094 in) wide on a petiole 0.3–0.5 mm (0.012–0.020 in) long. The edges of the leaves are turned down or rolled under, the upper surface convex and the lower surface striated. The flowers are arranged singly or in groups of up to three in leaf axils on peduncles 2.5–5.3 mm (0.098–0.209 in) long, and are pendent, with bracteoles 1.6–1.9 mm (0.063–0.075 in) long at the base. The sepals are 4.2–5.2 mm (0.17–0.20 in) long, the petals white and joined at the base to form a tube 3.1–3.6 mm (0.12–0.14 in) long. The petal tube is covered with tiny hairs on the outside, the lobes 4.0–5.4 mm (0.16–0.21 in) long and shaggy-hairy on the inside.[1][3][4]
Taxonomy
editWoronora beard-heath was first formally described in 1867 by Ferdinand von Mueller in his Fragmenta Phytographiae Australiae from specimens collected by Ludwig Leichhardt near the village of Camden.[5][6] The specific epithet (exolasia) means "hairy on the outside", referring to the floral tube.[7]
Distribution and habitat
editStyphelia exolasia is only known from a few locations in the Sydney region and on the Central Coast of New South Wales, including along the Georges River, in Heathcote National Park and along the Grose River. It grows in woodland, often on sandstone hillsides along creek banks.[3][4][8]
Conservation status
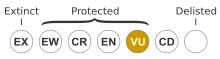
editStyphelia exolasia is listed as "vulnerable" under the Australian Government Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 and the New South Wales Government Biodiversity Conservation Act 2016. The threats to the species include its small population size, habitat loss, weed invasion and inappropriate fire regimes.[1][3][4]
References
edit- ^ a b c d "Woronora beard-heath - profile". New South Wales Government Office of Environment and Heritage. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ a b "Styphelia exolasia". Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ^ a b c Powell, Jocely M. "Leucopogon exolasius". Royal Botanic Garden Sydney. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ^ a b c "Approved Conservation Advice for Leucopogon exolasius" (PDF). Australian Government Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ "Styphelia exolasia". APNI. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ von Mueller, Ferdinand (1867). Fragmenta Phytographiae Australiae. Melbourne: Victorian Government Printer. pp. 34–35. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ Robinson, Les (1991). Field guide to the native plants of Sydney. Kenthurst, NSW: Kangaroo Press. p. 109. ISBN 0864171927.
- ^ Benson, Doug; McDougall, Lyn (1995). "Ecology of Sydney Plant Species". Cunninghamia. 4 (2): 369. Retrieved 19 October 2022.