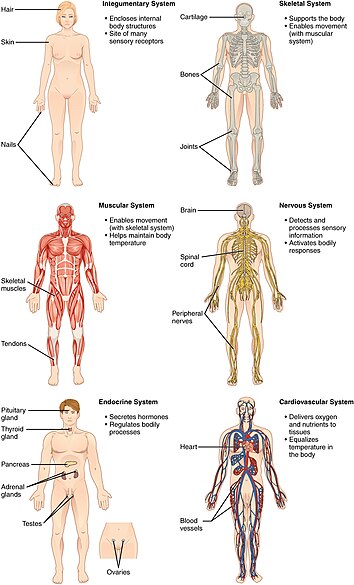
This is a list of the main organ systems in the human body.
- Clockwise from top left: integumentary system
- skeletal system
- nervous system
- cardiovascular system
- endocrine system
- (missing exocrine system)
- muscular system
Circulatory system/cardiovascular system
editCirculates blood around the body via the heart, arteries and veins, delivering oxygen and nutrients to organs and cells and carrying their waste products away, as well as keeping the body's temperature in a safe range.
Digestive system/excretory system
editAbsorbs nutrients and removes waste via the gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach and intestines.
Endocrine system
editInfluences the function of the body using hormones.
Exocrine system
editSystem that secrete substances through ducts for various functions.
Integumentary system
editThe integumentary system comprises skin and its appendages; hair, nails, sweat glands and oil glands.
Immune system/lymphatic system
editDefends the body against pathogens that may harm the body. The system contains a network of lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph.
Muscular system
editEnables the body to move using muscles.
Nervous system
editCollects and processes information from the senses via nerves and the brain and tells the muscles to contract to cause physical actions.
Reproductive system
editThe reproductive organs are required for the production of offspring.
Respiratory system
editBrings air into and out of the lungs to absorb oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
Skeletal system
editUrinary system/renal system
editThe urinary system (also known as renal system) filter blood with the help of kidneys to produce urine, and get rid of waste.