The hyoid apparatus is the collective term used in veterinary anatomy for the bones which suspend the tongue and larynx.[1] It consists of pairs of stylohyoid, thyrohyoid, epihyoid and ceratohyoid bones, and a single basihyoid bone.[2] The hyoid apparatus resembles the shape of a trapeze,[3] or a bent letter "H".[4] The basihyoid bone lies within the muscle at the base of the tongue.[1]
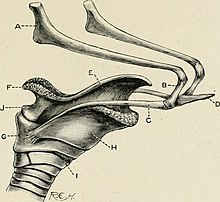

In humans, the single hyoid bone is an equivalent of the hyoid apparatus.[5]
References
edit- ^ a b König, Horst Erich; Liebich, Hans-Georg, eds. (2007). "Skeleton of the head". Veterinary anatomy of domestic mammals textbook and colour atlas (3rd ed.). Stuttgart: Schattauer. p. 71. ISBN 978-3-7945-2485-3.
- ^ Thrall, Donald E.; Robertson, Ian D. (2011). "Chapter 2. The skull". Atlas of normal radiographic anatomy & anatomic variants in the dog and cat. St. Louis: Elsevier/Saunders. p. 37. ISBN 978-1-4377-0178-4.
- ^ Aspinall, Victoria; Cappello, Melanie (2009). "Chapter 3. Skeletal system". Introduction to Veterinary Anatomy and Physiology (2nd ed.). Butterworth Heinemann. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-7020-2938-7.
- ^ Colville, Thomas P.; Bassert, Joanna M. (2016). "Chapter 7. The skeletal system". Clinical Anatomy and Physiology for Veterinary Technicians (3rd ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier. p. 188. ISBN 978-0-323-22793-3.
- ^ "Hyoid apparatus - Definition". mondofacto.com. Archived from the original on 2011-11-08. Retrieved 2012-08-04.