Dinitolmide (or zoalene) is a fodder additive for poultry, used to prevent coccidiosis infections.[2] It is sold under trade names such as Coccidine A, Coccidot, and Zoamix.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
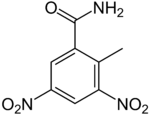
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methyl-3,5-dinitrobenzamide | |
| Other names
3,5-Dinitro-o-toluamide
Zoalene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.189 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H7N3O5 | |
| Molar mass | 225.16 g/mol |
| Melting point | 177 °C; 351 °F; 450 K[1] |
| Pharmacology | |
| QP51AX12 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | noncombustible[1] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 5 mg/m3[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dinitolmide is usually added to feed in doses of 125 ppm (preventive) or 250 ppm (curative). It is a broad-spectrum anticoccidial drug,[2] preventing seven main strains of Eimeria coccidium. It leaves no residues in tissues.[citation needed] It can be also used to prevent coccidiosis of domestic rabbits.
References
edit- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0230". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b Gerhold, R. W.; Fuller, A. L.; Lollis, L.; Parr, C.; McDougald, L. R. (2011). "The Efficacy of Anticoccidial Products against Eimeria spp. in Northern Bobwhites". Avian Diseases. 55 (1): 59–64. doi:10.1637/9572-101310-Reg.1. PMID 21500637. S2CID 30943649.