DADLE ([D-Ala2, D-Leu5]-Enkephalin) is a synthetic opioid peptide with analgesic properties. Although it is often considered a selective δ-opioid receptor agonist, it also binds to the μ1 subtype of μ-opioid receptors.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
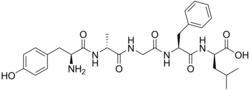
(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoic acid
| |
| Other names
• [D-Ala2, D-Leu5]-Enkephalin
• L-Tyrosyl-D-alanylglycyl-L-phenylalanyl-D-Leucine • N-(N-(N-(N-L-tyrosyl-D-alanyl)glycyl)-L-phenylalanyl)-D-Leucine • Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-D-Leu-OH | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.059.337 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H39N5O7 | |
| Molar mass | 569.659 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Treatment with DADLE results in transient depression of mean arterial blood pressure and heart rate.[1][2]
Its peptide sequence is Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-D-Leu.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Medical Dictionary Online". Archived from the original on 2007-08-28. Retrieved 2007-11-10.
- ^ Online Medical Dictionary, enkephalin, leucine-2-alanine