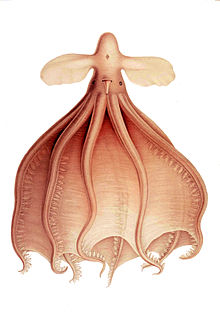
Cirrothauma murrayi, the blind cirrate octopus,[2] is a nearly blind octopus whose eyes can sense light, but not form images. It has been found worldwide, usually 1,500 to 4,500 metres (4,900 to 14,800 ft) beneath the ocean's surface.[3][4] Like other cirrates, it has an internal shell, muscular fins for swimming, and a web connecting the arms.[5]
| Cirrothauma murrayi | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Cephalopoda |
| Order: | Octopoda |
| Family: | Cirroteuthidae |
| Genus: | Cirrothauma |
| Species: | C. murrayi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cirrothauma murrayi Chun, 1911
| |
The species was first caught by an expedition led by Sir John Murray in 1910,[6] and it was later named in honor of Murray. It was described by German marine biologist Carl Chun in 1911.[4]
The large buccal mass, esophagus, and stomach of the Cirrothauma Murrayi strongly suggest whole organisms, especially crustaceans, are part of its diet. The enzymatic action of salivary excretions separates the crustacean's musculoskeletal attachments and allows for the tissue to be removed, leaving the exoskeleton of the crustacean undamaged.[7]
Description
editEye structure
editThe eye structure is very different from other octopods. Their eyes are small, lens-less and almost non-functional, as the eyes also lack irises and ciliary bodies.[8] The nearly sightless eyes are embedded deep in the gelatinous tissue of their head.[8]
Suckers
editCirrothauma murrayi has about six strong sessile suckers which help them swim as well as hunt fish.[8]
References
edit- ^ Lyons, G.; Allcock, L. (2014). "Cirrothauma murrayi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2014: e.T163011A963624. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-3.RLTS.T163011A963624.en. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ^ "Cirrothauma murrayi Chun, 1911". World Register of Marine Species. MolluscaBase.
- ^ "Cirrothauma murrayi". tolweb.org. Retrieved 2018-09-14.
- ^ a b Vecchione, Michael; Young, Richard. "Cirrothauma murrayi". Tree of Life Web Project. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- ^ Mangold, Katharina; Vecchione, Michael; Young, Richard. "Cirrata". Tree of Life Web Project. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- ^ Aldred, Nixon & Young 1983, p. 4.
- ^ Aldred, Nixon & Young 1983.
- ^ a b c "Cirrothauma murrayi". tolweb.org. Retrieved 2018-09-14.
Bibliography
edit- Aldred, R. G.; Nixon, M.; Young, J. Z. (26 April 1983). "Cirrothauma Murrayi Chun, A Finned Octopod". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 301 (1103): 1–54. Bibcode:1983RSPTB.301....1A. doi:10.1098/rstb.1983.0021. JSTOR 2396064.
