The Brouwer Route was a 17th-century route used by ships sailing from the Cape of Good Hope to the Dutch East Indies, as the eastern leg of the Cape Route. The route took ships south from the Cape (which is at 34° latitude south) into the Roaring Forties, then east across the Indian Ocean, before turning northeast for Java. Thus it took advantage of the strong westerly winds for which the Roaring Forties are named, greatly increasing travel speed.[1]
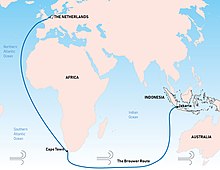
The problem with the route was lack of an accurate way, at the time, to determine longitude,[2] and thereby to know how far east a vessel had travelled. A sighting of either Amsterdam Island or Saint Paul Island was the only cue for ships to change direction and head north.[3] However, this was reliant on the captain's expertise. Consequently, many ships were damaged by or wrecked on rocks, reefs, or islands on the western continental shelf of Australia, which was virtually unknown to Europeans at the time.
The route was devised by the Dutch explorer Hendrik Brouwer in 1611, and found to halve the duration of the journey from Europe to Java, compared to the previous Arab and Portuguese monsoon route, which involved following the coast of East Africa northwards, sailing through the Mozambique Channel round Madagascar and then across the Indian Ocean, sometimes via India. By 1616 the Brouwer Route was compulsory for ship captains of the Dutch East India Company headed to Java.[2]
For the British East India Company, Captain Humphrey Fitzherbert on Royal Exchange trialled the route in 1620, which they called the Southern route, and initially thought it a great success, but the second English ship to use the route, Tryall (sometimes spelt Trial), incorrectly judged the longitude, sailed too far east before turning north, and was wrecked on Tryal Rocks off the Pilbara coast of Australia in May 1622. The English then avoided the route for the next two decades.[4]
The Brouwer Route played a major role in the European discovery of the west coast of Australia. Several ships were wrecked along the coast, including Batavia in 1629, Vergulde Draeck in 1656, Zuytdorp in 1712, and Zeewijk in 1727. In 1696 Willem de Vlamingh explored the Australian coast while looking for survivors of the Ridderschap van Holland, which had disappeared in 1694 with about 300 people on board; neither survivors nor ship were found.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ The Seynbrief, Sailing Toward Destiny, National Library of Australia.
- ^ a b Parthesius, Robert (2010). Dutch Ships in Tropical Waters: The Development of the Dutch East India Company Shipping Network in Asia 1595–1660. Amsterdam University Press. p. 114. ISBN 9053565175.
- ^ De Witt, D. (2013). The Unfortunate Dutchman. Nutmeg Publishing. ISBN 1301681180.
- ^ Lee, I. (April 1934). "The First Sighting of Australia by the English". The Geographical Journal. Royal Geographical Society.
Readings
edit- Appleyard, R. T.; Manford, T. (1979). The Beginning: European Discovery and Early Settlement of Swan River Western Australia. Nedlands: University of Western Australia Press. ISBN 0855641460.
- Henderson, J. (1993). Phantoms of the Tryall. Perth: St. George Books. ISBN 0867780533.