An Azmari (Amharic: አዝማሪ) is an entertainer who sings and plays traditional string instruments of the Ethiopian Highlands. Its comparable to medieval European minstrels or bard or West African griots. [1]
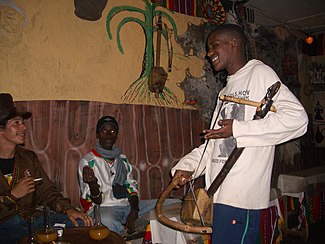
Azmari, who may be either male or female, are skilled at singing extemporized verses, accompanying themselves on either a masenqo (one-stringed fiddle) or krar (lyre).
Etymology edit
Azmari means (to sing or singer) in Amharic. Amharas tend to call all musicians Azmari simply because there's no other word in the language denoting a person who plays a musical instrument.[2]
History edit
The earliest documented mention of the Azmaris goes back to the mid-15th century, and they presumably go back much further.[3]
Role in society edit
Azmaris once played an important role as social critics by improvising sophisticated texts of praise or criticism.[4] Azmaris would mock people in high places, and even Emperors were not spared if they were found to be unpopular with the public. Azmaris were the first to convey scandals in high places.[5]
Female Azmaris flourished in feudal Ethiopia. They were just like their male counterparts poet-musicians. The female musicians are usually wives or lovers of male Azmaris who gradually learned the repertory of their male counterparts.[6]
Between 1841-1843, the English traveller Major William Cornwallis Harris captured the prevailing political atmosphere and attitudes of Sahle Selassie's court towards his enemies in a song of praise played by one of his female chorist (azmari).
In stature like the lance he bears,
His godlike mien the prince declares;
And famed for virtue through the land,
All bow to Saloo's just command.
The sabre feels the royal grasp,
And Pagans writhe in death's cold clasp;
The Galla taste the captive fare,
And dread the vengeance which they dare.— A memorable observation by Major William Cornwallis Harris, of a female Azmari praise of king Sahle Selassie court, in " Misgana (translated from Amharic) praise song", [7]
Today edit
Azmaris have continued perform in various settings ranging from wedding ceremonies, to hotels, and in drinking establishments called tejbeit, which specialise in the serving of tej (mead). The Azmaris introduced the popular Tizita ballad form.[8][9]
Notable Azmari edit
References edit
- ^ Kebede, Ashenafi (January 1975). "The "Azmari", Poet-Musician of Ethiopia". The Musical Quarterly. 61 (1): 47–57. doi:10.1093/mq/lxi.1.47.
- ^ May, Elizabeth (1983). Musics of many cultures : an introduction. Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 234. OCLC 10960729.
- ^ Shelemay, Kay Kaufman (2021). SING AND SING ON : sentinel musicians and the making of the ethiopian american diaspora. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 316. OCLC 1241245393.
- ^ Uhlig, Siegbert (2017). Ethiopia : history, culture and challenges. Munster, East Lansing: Michigan State University Press. p. 207. OCLC 978295392.
- ^ Milkias, Paulos (2011). Ethiopia. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. pp. 344–345. OCLC 728097838.
- ^ Milkias, Paulos (2011). Ethiopia. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. pp. 344–345. OCLC 728097838.
- ^ The Highlands of Ethiopia (London, 1844) vol.3 page 288
- ^ Dag Woubshet (2008). "Tizita: A New World Interpretation" (PDF). English at Cornell: A newsletter from the Department of English. Cornell University. Retrieved 2010-02-05.
- ^ Uhlig, Siegbert (2017). Ethiopia : history, culture and challenges. Munster, East Lansing: Michigan State University Press. p. 207. OCLC 978295392.
See also edit