The 833 cents scale is a musical tuning and scale proposed by Heinz Bohlen[clarification needed] based on combination tones, an interval of 833.09 cents, and, coincidentally, the Fibonacci sequence.[1] The golden ratio is , which as a musical interval is 833.09 cents (). In the 833 cents scale this interval is taken as an alternative to the octave as the interval of repetition,[2] however the golden ratio is not regarded as an equivalent interval (notes 833.09 cents apart are not "the same" in the 833 cents scale the way notes 1200 cents apart are in traditional tunings). Other music theorists such as Walter O'Connell, in his 1993 "The Tonality of the Golden Section",[3] and Lorne Temes in 1970,[4] appear to have also created this scale prior to Bohlen's discovery of it.

Derivation
editStarting with any interval, take the interval produced by the highest original tone and the closest combination tone. Then do the same for that interval. These intervals "converge to a value close to 833 cents. That means nothing else than that for instance for an interval of 144:89 (833.11 cents) both the summation and the difference tone appear...again 833 cents distance from this interval".[1]
| Base interval | Closest combination tone (ratio) |
Closest combination tone (cents) |
|---|---|---|
| 2:1 | 3:2 | |
| 3:2 | 5:3 | |
| 5:3 | 8:5 | |
| 8:5 | 13:8 | |
| 13:8 | 21:13 | 830.253 |
| 21:13 | 34:21 | 834.175 |
| 34:21 | 55:34 | 832.676 |
| 55:34 | 89:55 | 833.248 |
| 89:55 | 144:89 | 833.030 |
| 144:89 | 233:144 | 833.113 |
| 233:144 | 377:233 | 833.081 |
| 377:233 | 610:377 | 833.094 |
| ... | ||
For example, 220 Hz and 220 Hz (unison) produce combination tones at 0 and 440 Hz. 440 Hz is an octave above 220 Hz. 220 Hz and 440 Hz produce combination tones at 220 Hz and 660 Hz. 660 Hz is a perfect fifth (3:2) above 440 Hz, and produce combination tones at 220 Hz and 1,100 Hz. 1,100 Hz is a major sixth (5:3) above 660 Hz, and produce combination tones at 440 Hz and 1,760 Hz. 1100 Hz and 1760 Hz are a minor sixth (8:5), and so on. "It is by the way unimportant which interval we choose as a starting point for the above exercise; the result is always 833 cent."[1]
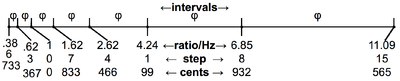
Once the interval of 833.09 cents is determined, a stack of them is produced:
| Tone | −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cents | 634.55 | 267.64 | 1100.73 | 733.82 | 366.91 | 0 | 833.09 | 466.18 | 99.27 | 932.36 | 565.45 |
| Ratio | 1.443 | 1.167 | 1.889 | 1.528 | 1.236 | 1.000 | 1.618 | 1.309 | 1.059 | 1.713 | 1.386 |
| Scale step | 6 | 3 | 0 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 15 |
Two stacks are also produced on 3:2 and its inverse 4:3 to provide steps 2 and 5, creating a two dimensional lattice. Given that the golden ratio is an irrational number there are three infinite stacks of possible golden ratios which never return exactly back to the unison or octave. Scale step 5 is 597.32 cents and scale step -5 is 602.68 cents (5.37 cents apart).
Scale
editBohlen describes a symmetrical seven tone scale, with the pitches of steps 0, 1, 3, 4, & 6 derived from the stack of golden ratio intervals.
| Scale step | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ... | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cents | 00.00 | 99.27 | 235.77 | 366.91 | 466.18 | 597.32 | 733.82 | 833.09 | ... | |||||||||
| Step width | 99.27 | 136.5 | 131.14 | 99.27 | 131.14 | 136.5 | 99.27 | ... | ||||||||||
| Stacked tone | 0 | 3 | −1 | 2 | −2 | 1 | ... | |||||||||||
This is comparable to the derivation of the major scale from a stack of perfect fifths (FCGDAEB = CDEFGAB). See: Generated collection.
The scale "contains a network of harmonic relationships with the property to match harmonic interval cycles of 833 cents."[5] Steps 2 and 5 were presumably chosen to fill in the gaps between what become steps 1 and 3 and 4 and 6 (267.64 cents). The value of step 2 (235.77) was chosen to create a perfect twelfth (compound perfect fifth) between steps 16 (235.77+833.09+833.09) and step 0, and once chosen determined the value of step 5 due to the symmetry of the scale. Step 10 and 0 form an octave. All notes 7 steps apart form the golden ratio with each other, for example 16 & 9 and 10 & 3.
The repetition of frequencies and the coincidence of higher steps with consonances such as the perfect fifth and octave may be seen (the step number of intervals that coincide with the stack of golden ratios are in bold, while the ratios of repeated intervals are in bold):
| Step | Ratio | Ratio (dec.) |
Ratio (cents) |
Width (cents) |
Audio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ⁄ | 1.0000 | 0 | ||
| 99.27 | |||||
| 1 | 4⁄4 | 1.0590 | 99.27 | ||
| 136.50 | |||||
| 2 | 3 ⁄ 3 | 1.1459 | 235.77 | ||
| 131.14 | |||||
| 3 | 2 ⁄ 2 | 1.2361 | 366.91 | ||
| 99.27 | |||||
| 4 | 3⁄2 | 1.3090 | 466.18 | ||
| 131.14 | |||||
| 5 | ⁄3 / 3 | 1.4120 | 597.32 | ||
| 136.50 | |||||
| 6 | 4 ⁄ 3 | 1.5279 | 733.82 | ||
| 99.27 | |||||
| 7 (0) | 2⁄ | 1.6180 | 833.09 | ||
| 99.27 | |||||
| 8 (1) | 5⁄4 | 1.7135 | 932.36 | ||
| 136.50 | |||||
| 9 (2) | 3 ⁄ 2 | 1.8541 | 1,068.86 | ||
| 131.14 | |||||
| 10 (3) | ⁄ | 1.0000 | 0 | ||
| 99.27 | |||||
| 11 (4) | 4⁄4 | 1.0590 | 99.27 | ||
| 131.14 | |||||
| 12 (5) | ⁄6 / 4 | 1.1424 | 230.41 | ||
| 136.50 | |||||
| 13 (6) | 2 ⁄ 2 | 1.2361 | 366.91 | ||
| 99.27 | |||||
| 14 (0) | 3⁄2 | 1.3090 | 466.18 | ||
| 99.27 | |||||
| 15 (1) | 6⁄8 | 1.3863 | 565.45 | ||
| 136.50 | |||||
| 16 (2) | 3 ⁄2 | 1.5 | 701.96 | ||
| ... | |||||
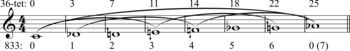
The scale contains .83333 × 12 steps per octave (≈10).[5] While ideally untempered, the scale may be approximated by 36 equal temperament, one advantage being that 36-TET includes traditional 12-TET.[2]
See
editSources
edit- ^ a b c Bohlen, Heinz (last updated 2012). "An 833 Cents Scale: An experiment on harmony", Huygens-Fokker.org.
- ^ a b c d e "833 Cent Golden Scale (Bohlen)", Xenharmonic Wiki.
- ^ O'Connell, Walter (1993). "The Tonality of the Golden Section", Anaphoria.com.
- ^ Temes, Lorne, "Golden Tones", University of Toronto, 1970. Anaphoria.com
- ^ a b Pareyon, Gabriel (2011). On Musical Self-Similarity, p.398. ISBN 9789525431322.
External links
edit- "Fun with Emulator X: Bohlen 833 cents scale and harmonics", CatSynth.
- "Golden Ratio", Xenharmonic Wiki.
