1938 United States Senate elections
The 1938 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Franklin D. Roosevelt's second term. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans gained eight seats from the Democrats, though this occurred after multiple Democratic gains since the 1932 election, leading to the Democrats retaining a commanding lead over the Republicans with more than two-thirds of the legislative chamber.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
35 of the 96 seats in the United States Senate 49 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
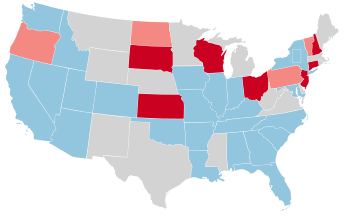 Results of the elections: Democratic hold Republican gain Republican hold No election | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A contemporary account[1] cited a number of reasons for the losses suffered by the Democrats. The Recession of 1937 had continued into the first half of 1938, and had arguably weakened public confidence in the administration's New Deal economic policies, along with controversy over the Judicial Procedures Reform Bill of 1937 (Roosevelt's "court-packing" plan).
There were, in addition, strains between the more liberal New Deal supporters and the conservative wing of the Democratic party centered in the Southern states, which were exacerbated by an effort led by President Roosevelt to target certain conservative senators for defeat in Democratic primaries, including Walter George of Georgia, Millard Tydings of Maryland, Robert Rice Reynolds of North Carolina, and Ellison Smith of South Carolina. While a number of New Deal supporters won primary elections, such as Alben Barkley in Kentucky, who defeated Governor Happy Chandler, James P. Pope of Idaho, a prominent New Deal supporter, lost his bid for re-nomination, as did California's William McAdoo — though McAdoo's Democratic opponent, Sheridan Downey, had campaigned as a liberal New Dealer on many issues who would also do more to improve pension plans.[2]
President Franklin D. Roosevelt had faced opposition from conservative Democrats and the Republicans in Congress since the beginning of his presidency. Josiah Bailey, Edward R. Burke, Harry F. Byrd, James F. Byrnes, Walter F. George, Peter G. Gerry, Carter Glass, Pat Harrison, Rush Holt Sr., Kenneth McKellar, and Ellison D. Smith were the conservative Democratic senators that opposed Roosevelt's policies although Harrison, Burke, Byrnes, and McKellar had initially supported the First New Deal. Vice President John Nance Garner pushed for Roosevelt to support more conservative policies. The Republicans gained eight seats in the Senate while the Democrats maintained their majority. However, there were around twenty unreliable Democratic votes for Roosevelt which allowed conservatives to block some of his policies.[3]
Gains, losses, and holds
editRetirements
editOne Democrat retired instead of seeking re-election, one Democrat retired instead of seeking election to finish the unexpired term and one Democrat retired instead of seeking election to finish the unexpired term and election to a full term.
| State | Senator | Replaced by |
|---|---|---|
| Illinois | William H. Dieterich | Scott W. Lucas |
| Oregon (special) | Alfred E. Reames | Alexander G. Barry |
| Oregon | Alfred E. Reames | Rufus C. Holman |
| South Dakota (special) |
Defeats
editSeven Democrats sought re-election but lost in the primary or general election. One Democrat sought election to a full term but lost in the primary election and one Democrat sought election to finish the unexpired term but lost in the primary election.
Death
editOne Democrat died on June 17, 1938, and his seat remained vacant until the election.
| State | Senator | Replaced by |
|---|---|---|
| New York (special) | Royal S. Copeland | James M. Mead |
Post-election changes
editChange in composition
editBefore the elections
edit| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | ||
| D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 |
| D19 | D20 | D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 |
| D38 | D37 | D36 | D35 | D34 | D33 | D32 | D31 | D30 | D29 |
| D39 | D40 | D41 | D42 | D43 | D44 | D45 | D46 Ala. (reg) Ala. (sp) Ran[a] |
D47 Ariz. Ran |
D48 Ark. Ran |
| Majority → | D49 Calif. Ran | ||||||||
| D58 Kan. Ran |
D57 Iowa Ran |
D56 Ind. Ran |
D55 Ill. Retired |
D54 Idaho Ran |
D53 Ga. Ran |
D52 Fla. Ran |
D51 Conn. Ran |
D50 Colo. Ran | |
| D59 Ky. Ran |
D60 La. Ran |
D61 Md. Ran |
D62 Mo. Ran |
D63 Nev. Ran |
D64 N.H. Ran |
D65 N.J. (sp) Retired |
D66 N.Y. (reg) Ran |
D67 N.Y. (sp) Died |
D68 N.C. Ran |
| FL2 | D77 Wisc. Ran |
D76 Wash. Ran |
D75 Utah Ran |
D74 Tenn. (sp) Ran |
D73 S.D. (reg) Ran S.D. (sp) Retired |
D72 S.C. Ran |
D71 Ore. (reg) Ore. (sp) Retired |
D70 Okla. Ran |
D69 Ohio Ran |
| FL1 | I1 | P1 | R15 Vt. Ran |
R14 Pa. Ran |
R13 N.D. Ran |
R12 | R11 | R10 | R9 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | ||
Result of the elections
edit| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | ||
| D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 |
| D19 | D20 | D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 |
| D38 | D37 | D36 | D35 | D34 | D33 | D32 | D31 | D30 | D29 |
| D39 | D40 | D41 | D42 | D43 | D44 | D45 | D46 Ala. (sp) Elected[b][a] Ala. (reg) Re-elected[a] |
D47 Ariz. Re-elected |
D48 Ark. Re-elected |
| Majority → | D49 Calif. Hold | ||||||||
| D58 La. Re-elected |
D57 Ky. Re-elected |
D56 Iowa Re-elected |
D55 Ind. Re-elected |
D54 Ill. Hold |
D53 Idaho Hold |
D52 Ga. Re-elected |
D51 Fla. Re-elected |
D50 Colo. Re-elected | |
| D59 Md. Re-elected |
D60 Mo. Re-elected |
D61 Nev. Re-elected |
D62 N.Y. (reg) Re-elected |
D63 N.Y. (sp) Hold |
D64 N.C. Re-elected |
D65 Okla. Re-elected |
D66 S.C. Re-elected |
D67 Tenn. (sp) Hold |
D68 Utah Re-elected |
| R19 N.J. (sp) Gain |
R20 Ohio Gain |
R21 Ore. (reg) Ore. (sp) Gain |
R22 S.D. (reg) S.D. (sp) Gain |
R23 Wisc. Gain |
P1 | I1 | FL1 | FL2 | D69 Wash. Re-elected |
| R18 N.H. Gain |
R17 Kan. Gain |
R16 Conn. Gain |
R15 Vt. Re-elected |
R14 Pa. Re-elected |
R13 N.D. Re-elected |
R12 | R11 | R10 | R9 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | ||
| Key: |
|
|---|
Race summaries
editSpecial elections during the 75th Congress
editIn these special elections, the winner was seated during 1938 or before January 3, 1939; ordered by election date.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Alabama (Class 3) |
J. Lister Hill | Democratic | 1938 (Appointed) | Interim appointee elected April 26, 1938. |
|
| New Jersey (Class 1) |
John Milton | Democratic | 1938 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. Winner elected November 8, 1938. Republican gain. |
|
| New York (Class 1) |
Royal S. Copeland | Democratic | 1922 1928 1934 |
Incumbent died June 17, 1938. Winner elected November 8, 1938. Democratic hold. |
|
| Oregon (Class 3) |
Alfred E. Reames | Democratic | 1938 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. Winner elected November 8, 1938. Republican gain. Winner did not run for the next term, however; see below. |
|
| South Dakota (Class 3) |
Herbert E. Hitchcock | Democratic | 1936 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. Winner elected November 8, 1938. Republican gain. Winner did not run for the next term, however; see below. |
|
| Tennessee (Class 2) |
George L. Berry | Democratic | 1937 (Appointed) | Interim appointee lost nomination to finish the term. Winner elected November 8, 1938. Democratic hold. Winner delayed his term until January 16, 1939, to finish his term as district attorney. |
|
Races leading to the 76th Congress
editIn these general elections, the winners were elected for the term beginning January 3, 1939; ordered by state.
All of the elections involved the Class 3 seats.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Alabama | J. Lister Hill | Democratic | 1938 (Appointed) 1938 (special) |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Arizona | Carl Hayden | Democratic | 1926 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Arkansas | Hattie Caraway | Democratic | 1931 (Appointed) 1932 (special) |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| California | William Gibbs McAdoo | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent lost renomination. New senator elected. Democratic hold. Incumbent then resigned and Thomas M. Storke (D) was appointed to finish the term. |
|
| Colorado | Alva B. Adams | Democratic | 1923 (Appointed) 1924 (Retired) 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Connecticut | Augustine Lonergan | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Florida | Claude Pepper | Democratic | 1936 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Georgia | Walter F. George | Democratic | 1922 (special) 1926 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Idaho | James P. Pope | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent lost renomination. New senator elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| Illinois | William H. Dieterich | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent retired. New senator elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| Indiana | Frederick Van Nuys | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent re-elected. |
Others
|
| Iowa | Guy Gillette | Democratic | 1936 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kansas | George McGill | Democratic | 1930 (special) 1932 |
Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Kentucky | Alben W. Barkley | Democratic | 1926 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Louisiana | John H. Overton | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Maryland | Millard Tydings | Democratic | 1926 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Missouri | Bennett Champ Clark | Democratic | 1932 1933 (Appointed) |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Nevada | Pat McCarran | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New Hampshire | Fred H. Brown | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
| New York | Robert F. Wagner | Democratic | 1926 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina | Robert R. Reynolds | Democratic | 1932 (special) 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Dakota | Gerald Nye | Republican | 1925 (Appointed) 1926 (special) 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Ohio | Robert J. Bulkley | Democratic | 1930 (special) 1932 |
Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Oklahoma | Elmer Thomas | Democratic | 1926 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Oregon | Alfred E. Reames | Democratic | 1938 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Pennsylvania | James J. Davis | Republican | 1930 (special) 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Carolina | Ellison D. Smith | Democratic | 1909 1914 1920 1926 1932 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Dakota | Herbert E. Hitchcock | Democratic | 1936 (Appointed) | Interim appointee lost nomination to next term. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Utah | Elbert D. Thomas | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Vermont | Ernest W. Gibson | Republican | 1933 (Appointed) 1934 (special) |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Washington | Homer Bone | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Wisconsin | F. Ryan Duffy | Democratic | 1932 | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
Closest races
editThirteen races had a margin of victory under 10%:
| State | Party of winner | Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Indiana | Democratic | 0.3% |
| Iowa | Democratic | 0.3% |
| Connecticut | Republican (flip) | 2.9% |
| Illinois | Democratic | 3.0% |
| South Dakota | Republican (flip) | 5.0% |
| Ohio | Republican (flip) | 7.2% |
| New Jersey | Republican (flip) | 7.3% |
| North Dakota | Democratic | 7.5% |
| New Hampshire | Republican (flip) | 8.4% |
| New York | Democratic | 9.5% |
| California | Democratic | 9.7% |
| Idaho | Democratic | 9.8% |
| Oregon | Republican (flip) | 9.8% |
There is no tipping point state.
Alabama
editThere were 2 elections due to the August 19, 1937, resignation of two-term Democrat Hugo Black. Democrat Dixie Bibb Graves was appointed August 20, 1937 (by her husband, the governor) to finish Black's term.
Alabama (special)
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Hill: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% Heflin: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Lister Hill | 90,601 | 61.81% | ||
| Democratic | James Thomas Heflin | 50,189 | 34.24% | ||
| Democratic | Charles W. Williams | 5,783 | 3.95% | ||
| Turnout | 1.87% | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
| Majority | 40,412 | 27.57% | |||
After congressman J. Lister Hill won the January 4, 1938, Democratic primary, Graves resigned and Hill was appointed to continue the term until the April 26, 1938, special election, which he won unopposed.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Lister Hill (Incumbent) | 49,429 | 100.00% | ||
| Turnout | 1.87% | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Hill was then easily re-elected in November to the next term.
Alabama (regular)
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Hill: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% 90-100% Heflin: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Lister Hill (Incumbent) | 113,413 | 86.38% | ||
| Republican | J. M. Pennington | 17,885 | 13.62% | ||
| None | Scattering | 1 | 0.00% | ||
| Majority | 95,528 | 72.76% | |||
| Turnout | 131,299 | 4.96% | |||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Arizona
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Hayden: 70–80% 80–90% >90% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Democrat Carl Hayden was re-elected to a third term, defeating Republican nominee Burt H. Clingan, chairman of the Arizona Industrial Commission, in the general election.
In contrast to previous elections, Hayden was easily reelected, receiving only token opposition from a relatively unknown Republican challenger.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Carl T. Hayden (Incumbent) | 68,328 | 65.48% | |
| Democratic | Robert E. Miller | 22,154 | 21.23% | |
| Democratic | Whit I. Hughes | 13,867 | 13.29% | |
| Total votes | 104,349 | 100.00 | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Carl T. Hayden (Incumbent) | 82,714 | 76.52% | |
| Republican | Burt H. Clingan | 25,378 | 23.48% | |
| Majority | 57,336 | 53.04% | ||
| Turnout | 108,092 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Arkansas
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Caraway: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Hattie Wyatt Caraway (Incumbent) | 122,883 | 89.58% | |
| Republican | C. T. Atkinson | 14,290 | 10.42% | |
| Majority | 108,593 | 79.16% | ||
| Turnout | 137,173 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
California
edit| | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
County results Downey: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Bancroft: 40–50% 50–60% 70–80% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Sheridan Downey | 1,372,314 | 54.41% | |
| Republican | Philip Bancroft | 1,126,240 | 44.65% | |
| Socialist | Lillian Symes Clements | 22,569 | 0.89% | |
| None | Scattering | 1,019 | 0.04% | |
| Majority | 246,074 | 9.76% | ||
| Turnout | 2,522,142 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Colorado
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Results by county Adams: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Lee: 40–50% 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Alva B. Adams (Incumbent) | 262,786 | 58.24% | |
| Republican | Archibald A. Lee | 181,297 | 40.18% | |
| Socialist | Carle Whitehead | 3,604 | 0.80% | |
| Independent Progressive | James Allander | 3,522 | 0.78% | |
| Majority | 81,489 | 18.06% | ||
| Turnout | 451,209 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Connecticut
edit| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Danaher: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Lonergan: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Trombley: 40–50% Tie: 30–40% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | John A. Danaher | 270,413 | 42.89% | |
| Democratic | Augustine Lonergan (Incumbent) | 252,426 | 40.04% | |
| Socialist | Bellani Trombley | 99,282 | 15.75% | |
| Socialist Labor | Joseph Mackey | 6,931 | 1.10% | |
| American Labor | Philip Brainard | 766 | 0.12% | |
| Communist | Michael A. Russo | 615 | 0.10% | |
| Majority | 17,987 | 2.85% | ||
| Turnout | 630,433 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Florida
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Pepper: 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% 90-100% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Claude Pepper (Incumbent) | 145,757 | 82.45% | |
| Republican | Thomas E. Swanson | 31,035 | 17.55% | |
| Majority | 114,722 | 64.90% | ||
| Turnout | 176,792 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Georgia
edit| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
County results George: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Talmadge: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Camp: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Walter F. George (Incumbent) | 66,987 | 95.09% | |
| Independent | Charles A. Jiles | 3,442 | 4.89% | |
| Independent | Eugene Talmadge | 14 | 0.02% | |
| Majority | 63,545 | 90.20% | ||
| Turnout | 70,443 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Idaho
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Clark: 50–60% 60–70% Callahan: 50-60% 60-70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | David Worth Clark | 99,801 | 54.66% | |
| Republican | Donald A. Callahan | 81,939 | 44.88% | |
| Progressive | V. A. Verhei | 845 | 0.46% | |
| Majority | 17,862 | 9.78% | ||
| Turnout | 182,585 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Illinois
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Lucas: 50–60% 60–70% Lyons: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Democrat William H. Dieterich retired, making this an open-seat.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Scott W. Lucas | 1,638,162 | 51.32% | |
| Republican | Richard J. Lyons | 1,542,574 | 48.33% | |
| Prohibition | Enoch A. Holtwick | 10,707 | 0.34% | |
| None | Scattering | 569 | 0.02% | |
| Majority | 95,588 | 2.99% | ||
| Turnout | 3,192,012 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Indiana
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Van Nuys: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Willis: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Frederick Van Nuys (Incumbent) | 788,386 | 49.85% | |
| Republican | Raymond E. Willis | 783,189 | 49.52% | |
| Prohibition | Herman L. Seeger | 6,905 | 0.44% | |
| Socialist | Louis E. Roebuck | 2,026 | 0.13% | |
| Communist | Miles Blansett | 984 | 0.06% | |
| Majority | 5,197 | 0.33% | ||
| Turnout | 1,581,490 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Iowa
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Gillette: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Dickinson: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Guy Gillette (Incumbent) | 413,788 | 49.74% | |
| Republican | Lester J. Dickinson | 410,983 | 49.41% | |
| Farmer–Labor | George F. Buresch | 4,723 | 0.57% | |
| Progressive | Raymond E. Hanke | 1,525 | 0.18% | |
| Prohibition | G. W. Bauseman | 820 | 0.10% | |
| Majority | 2,805 | 0.33% | ||
| Turnout | 831,839 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Kansas
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Reed: 50–60% 60–70% McGill: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This is the last time that a Senator from Kansas lost re-election. Republicans have not lost a Senate election in the state since.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Clyde M. Reed | 419,532 | 56.21% | |
| Democratic | George McGill (Incumbent) | 326,774 | 43.78% | |
| Independent | Joe Corpstein | 99 | 0.01% | |
| Majority | 92,758 | 12.43% | ||
| Turnout | 746,405 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Kentucky
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Barkley: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% Haswell: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Alben W. Barkley (Incumbent) | 346,735 | 62.03% | |
| Republican | John P. Haswell | 212,266 | 37.97% | |
| Democratic | Happy Chandler (write-in) | 20 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 134,469 | 22.06% | ||
| Turnout | 559,021 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Louisiana
edit| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | John H. Overton (Incumbent) | 151,582 | 99.84% | |
| Independent | Maurice E. Clark | 250 | 0.16% | |
| Majority | 151,332 | 99.68% | ||
| Turnout | 151,832 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Maryland
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Tydings: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Millard Tydings (Incumbent) | 357,245 | 68.28% | |
| Republican | Oscar Lesser | 153,253 | 29.29% | |
| Union | George W. Hunt | 5,784 | 1.11% | |
| Socialist | Elisabeth Gilman | 3,311 | 0.63% | |
| American Labor | Frank N. H. Lang | 2,330 | 0.45% | |
| Communist | Harry Straw | 1,301 | 0.25% | |
| Majority | 203,992 | 38.99% | ||
| Turnout | 523,238 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Missouri
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Clark: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Caulfield: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Bennett Champ Clark (Incumbent) | 757,587 | 60.69% | |
| Republican | Henry S. Caulfield | 488,687 | 39.15% | |
| Socialist | J. G. Hodges | 1,712 | 0.14% | |
| Socialist Labor | Karl L. Oberhue | 292 | 0.02% | |
| Majority | 268,900 | 21.54% | ||
| Turnout | 1,248,278 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Nevada
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results McCarran: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Oddie: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Pat McCarran (Incumbent) | 27,406 | 58.96% | |
| Republican | Tasker Oddie | 19,078 | 41.04% | |
| Majority | 8,328 | 17.92% | ||
| Turnout | 46,484 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
New Hampshire
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Tobey: 50-60% 60-70% Brown: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Charles W. Tobey | 100,633 | 54.23% | |
| Democratic | Fred H. Brown (Incumbent) | 84,920 | 45.77% | |
| Majority | 15,713 | 8.46% | ||
| Turnout | 185,553 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
New Jersey (special)
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Barbour: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Ely: 50–60% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | William Warren Barbour | 816,667 | 52.98% | |
| Democratic | William H. J. Ely | 704,159 | 45.68% | |
| Prohibition | Louis H. Kelley | 8,201 | 0.53% | |
| Socialist | John Palangio | 3,671 | 0.24% | |
| Townsend | Fred Turner | 3,521 | 0.23% | |
| Communist | William Norman | 3,515 | 0.23% | |
| Socialist Labor | John C. Butterworth | 1,873 | 0.12% | |
| Majority | 112,508 | 7.30% | ||
| Turnout | 1,541,607 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
New York
editThere were 2 elections due to the June 17, 1938, death of three-term Democrat Royal S. Copeland.
New York (regular)
edit| | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
County Results Wagner: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% O'Brian: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
New York Republicans nominated John Lord O'Brian for the U.S. Senate.[10] Democrats re-nominated the incumbent Wagner.[11] The American Labor Party endorsed Wagner.[12]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Robert F. Wagner (Incumbent) | 2,098,919 | 45.80% | |
| American Labor | Robert F. Wagner (Incumbent) | 398,410 | 8.69% | |
| Total | Robert F. Wagner (Incumbent) | 2,497,029 | 54.48% | |
| Republican | John Lord O'Brian | 2,046,794 | 44.66% | |
| Independent Progressive | John Lord O'Brian | 11,821 | 0.26% | |
| 'Total' | John Lord O'Brian | 2,058,615 | 44.92% | |
| Socialist | Herman J. Hahn[c] | 23,553 | 0.51% | |
| Socialist Labor | O. Martin Olson[d] | 3,851 | 0.08% | |
| Total votes | 4,583,048 | 100.00% | ||
New York (special)
edit| | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Mead: 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% Corsi: 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
New York Republicans nominated Edward Corsi for the short term to fill the vacancy caused by the death of Royal S. Copeland.[10] Democrats nominated James M. Mead.[11] The American Labor party endorsed Mead.[12]
| Democratic ticket | Republican ticket | American Labor ticket | Socialist ticket | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| James M. Mead | 2,060,876 | Edward F. Corsi | 2,083,666 | James M. Mead | 378,028 | Harry W. Laidler | 27,161 |
North Carolina
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Results by county Reynolds: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% Jonas: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Robert Rice Reynolds (Incumbent) | 316,685 | 63.80% | |
| Republican | Charles A. Jonas | 179,650 | 36.20% | |
| Majority | 137,035 | 27.60% | ||
| Turnout | 496,335 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
North Dakota
edit| | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
County results Nye: 40-50% 50-60% 60-70% Langer: 40-50% 50-60% 60-70% | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Gerald Nye (Incumbent) | 131,907 | 50.12% | |
| Independent | William Langer | 112,007 | 42.56% | |
| Democratic | J. J. Nygard | 19,244 | 7.31% | |
| Majority | 19,900 | 7.56% | ||
| Turnout | 263,158 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
Ohio
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Taft: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Bulkley: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Robert A. Taft | 1,255,414 | 53.62% | |
| Democratic | Robert J. Bulkley (Incumbent) | 1,085,792 | 46.38% | |
| Majority | 169,622 | 7.24% | ||
| Turnout | 2,341,206 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Oklahoma
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Thomas: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Glasser: 40–50% 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Elmer Thomas (Incumbent) | 307,936 | 65.37% | |
| Republican | Harry G. Glasser | 159,734 | 33.91% | |
| Prohibition | P. C. Nelson | 2,220 | 0.47% | |
| Independent | Raymond B. Clark | 603 | 0.13% | |
| Independent | Herndon J. Thompson | 573 | 0.12% | |
| Majority | 148,202 | 31.46% | ||
| Turnout | 471,066 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Oregon
editThere were 2 elections for the same seat, due to the January 31, 1938, resignation of two-term Republican Frederick Steiwer. Democratic businessman Alfred E. Reames was appointed February 1, 1938, to continue the term, pending a special election, but he did not run in either the special or the general elections.
Oregon (special)
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Barry: 50-60% 60-70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Republican Alexander G. Barry was elected to finish the term, but was not a candidate for the next term.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Alexander G. Barry | 180,815 | 54.20% | |
| Democratic | Robert A. Miller | 152,773 | 45.80% | |
| None | Scattering | 3 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 28,042 | 8.40% | ||
| Turnout | 333,591 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Oregon (regular)
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Holman: 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Rufus C. Holman | 203,120 | 54.86% | |
| Democratic | Willis Mahoney | 167,135 | 45.14% | |
| None | Scattering | 6 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 35,985 | 9.72% | ||
| Turnout | 370,261 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Pennsylvania
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County Results: Davis: 40-50% 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% Earle: 50-60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | James J. Davis (incumbent) | 2,086,931 | 54.70% | |
| Democratic | George H. Earle | 1,694,367 | 44.41% | |
| Socialist | David H. H. Felix | 20,155 | 0.53% | |
| Prohibition | Forest S. Van Valin | 9,327 | 0.24% | |
| Pathfinders | Reginald B. Naugle | 2,508 | 0.07% | |
| Communist | Pat Toohey | 1,530 | 0.04% | |
| None | Scattering | 104 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 392,564 | 10.29% | ||
| Turnout | 3,814,922 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
South Carolina
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Smith: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Johnston: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Ellison D. Smith (Incumbent) | 45,351 | 98.89% | |
| Republican | J. D. E. Meyer | 508 | 1.11% | |
| None | Scattering | 2 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 44,843 | 97.78% | ||
| Turnout | 45,861 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
South Dakota
editThere were 2 elections for the same seat due to the December 20, 1936, death of three-term Republican Peter Norbeck. Democrat Herbert Hitchcock was appointed December 29, 1936, to continue the term, pending a special election.
South Dakota (special)
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Pyle: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% McCullen: 50–60% Tie: 50% No Vote: | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Gladys Pyle | 155,292 | 58.06% | |
| Democratic | John T. McCullen | 112,177 | 41.94% | |
| Majority | 43,115 | 16.12% | ||
| Turnout | 267,469 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
South Dakota (regular)
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Gurney: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Berry: 50–60% 60–70% No Vote: | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Hitchcock lost the Democratic May 3, 1938, primary for the next term to Governor of South Dakota Tom Berry.[14]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | John Chandler Gurney[15] | 146,813 | 52.46% | |
| Democratic | Tom Berry | 133,064 | 47.54% | |
| Majority | 13,749 | 4.92% | ||
| Turnout | 279,877 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Tennessee (special)
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Tom Stewart | 194,028 | 70.50% | |
| Republican | Harley G. Fowler | 72,098 | 26.20% | |
| Independent | John Randolph Neal Jr. | 9,106 | 3.31% | |
| Majority | 21,930 | 44.30% | ||
| Turnout | 275,232 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Utah
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
County results Thomas: 50–60% 60–70% Harris: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Elbert D. Thomas (Incumbent) | 102,353 | 55.80% | |
| Republican | Franklin S. Harris | 81,071 | 44.20% | |
| Majority | 21,282 | 11.60% | ||
| Turnout | 183,424 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Vermont
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Ernest Willard Gibson (Incumbent) | 73,990 | 65.58% | |
| Democratic | John McGrath | 38,673 | 34.28% | |
| None | Scattering | 161 | 0.14% | |
| Majority | 35,317 | 31.30% | ||
| Turnout | 112,824 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
Washington
edit| | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Results by county Bone: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Colvin: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Homer Bone (Incumbent) | 371,535 | 62.62% | |
| Republican | Ewing D. Colvin | 220,204 | 37.12% | |
| Socialist Labor | Eugene Solie | 1,553 | 0.26% | |
| Majority | 151,331 | 25.50% | ||
| Turnout | 593,292 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Wisconsin
edit| | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
County results Wiley: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Ekern: 40–50% Duffy: 30–40% 40–50% | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Alexander Wiley | 416,770 | 45.92% | |
| Progressive | Herman Ekern | 249,209 | 27.46% | |
| Democratic | F. Ryan Duffy (Incumbent) | 231,976 | 25.56% | |
| Townsend | John B. Chapple | 7,251 | 0.80% | |
| Independent Communist | Fred Basset Blair | 1,283 | 0.14% | |
| Independent Socialist Labor Party (United States) | Joseph Erhardt | 1,014 | 0.11% | |
| None | Scattering | 31 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 167,561 | 18.46% | ||
| Turnout | 907,534 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Further reading
edit- Dunn, Susan. Roosevelt's Purge: How FDR Fought to Change the Democratic Party (2010) excerpt and text search
- Hixson, Walter L. "The 1938 Kentucky Senate Election: Alben W. Barkley, "Happy" Chandler, and The New Deal." Register of the Kentucky Historical Society (1982): 309–329. in JSTOR
- Plesur, Milton. "The Republican Congressional Comeback of 1938", Review of Politics Vol. 24, No. 4 (October 1962), pp. 525–562 in JSTOR
- Official New York result: LEHMAN PLURALITY OFFICIALLY 64,394; State Board Puts His Vote Finally at 2,391,286, With 2,326,892 for Dewey LABOR'S POLL AT 419,979 Blank, Void and Scattered Ballots Totaled 75,047; Poletti Won by 229,361 in NYT on December 8, 1938 (subscription required)
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ a b c On the day of the special election, the interim appointee, Dixie Bibb Graves had resigned and been replaced by a new interim appointee — J. Lister Hill — who then won the special election ("Hold") and was re-elected in November ("Re-elected").
- ^ Appointee elected
- ^ Rev. Herman J. Hahn, of Buffalo, ran also for Lieutenant Governor in 1928 and 1936.
- ^ O. Martin Olson, of Jamestown, ran also for Comptroller in 1934
References
edit- ^ 1939 Britannica Book of the Year, "Democratic Party". pp. 205–206.
- ^ LIFE. Time Inc. 1994. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-88682-602-4. ISSN 0024-3019. Retrieved October 5, 2014.
- ^ Murphy, Paul (1974). Political Parties In American History, Volume 3, 1890-present. G. P. Putnam's Sons.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - AL US Senate - Special D Primary Race - Jan 04, 1938". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved July 17, 2020.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - AL US Senate - Special Election Race - Apr 26, 1938". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved July 17, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag "Statistics of the Congressional Election of November 8, 1938" (PDF). Clerk.house.gov. Retrieved July 14, 2019.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - AL US Senate Race - Nov 08, 1938". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved July 17, 2020.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - AZ US Senate - D Primary Race - Sep 13, 1938". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved July 16, 2019.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - AZ US Senate Race - Nov 08, 1938". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved July 15, 2019.
- ^ a b Hagerty, James A. (September 30, 1938). "DEWEY NOMINATED BY REPUBLICANS; ATTACKES TAMMANY; CHOICE BY ACCLAMATION Dewey Defends Decision to Run Points to Prosecuting Staff HAILED IN OVATION Prosecutor Promises to Rid State of 'Corruption' in 'Bigger Job' O'Brian and Corsi Nominated for Senate--A. V. McDermott for Attorney General DEWEY NOMINATED BY REPUBLICANS Republican Mayor Gets Bid to Inauguration Delay in Completing Ticket Criticizes Farm Legislation Politics the Biggest Racket". The New York Times. Retrieved July 15, 2019.
- ^ a b Warren Moscow (October 1, 1938). "LEHMAN IS DRAFTED FOR FOURTH TERM; HE ATTACKS DEWEY; POLETTI ON TICKET Yielding to Pleas to Run, Governor Insists on Justice as Aide CALLS RIVAL UNQUALIFIED Rochester Platform Hits Republican's Crime Issue--Wagner, Mead Are Nominated Calls Dewey Inexperienced Dewey Crime Speech a Factor LEHMAN DRAFTED FOR FOURTH TERM Platform Strong for New Deal La Guardia a Meed Champion Farley Predicts a Big Victory Hailed as". The New York Times. Retrieved July 16, 2019.
- ^ a b Hagerty, James A. (October 4, 1938). "LABORITES NAME LEHMAN WAGNER; ADOPT PLATFORM; OVATION FOR BOTH Governor, Accepting, Stresses Policy of Law Enforcement POLETTI ALSO NOMINATED Endorsement Efforts Fall Wagner Cites Record La Guardia is Acclaimed as He Urges Candidates Friendly to Roosevelt LABORITIES NAME LEHMAN, WAGNER Yields to Dubinsky Lehman Is Acclaimed Hillman Offers Wagner's Name Vladeck in Seconding Speech". The New York Times. Retrieved July 16, 2019.
- ^ "NY US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - SD US Senate - D Primary Race - May 03, 1938". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved July 17, 2020.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - SD US Senate - R Primary Race - May 03, 1938". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved July 17, 2020.

