The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Polio, also called poliomyelitis or infantile paralysis, was one of the most feared childhood diseases of the 20th century. Poliovirus, the causative agent, only naturally infects humans and spreads via the faecal–oral route. Most infections cause no or minor symptoms. In around 1% of cases, the virus enters the central nervous system, causing aseptic meningitis. There it can preferentially infect and destroy motor neurons, leading in 0.1–0.5% of cases to muscle weakness and acute flaccid paralysis. Spinal polio accounts for nearly 80% of paralytic cases, with asymmetric paralysis of the legs being typical; in a quarter of these cases permanent severe disability results. Bulbar involvement is rare, but in severe cases the virus can prevent breathing by affecting the phrenic nerve, so that patients require mechanical ventilation with an iron lung or similar device.
Depictions in ancient art show that the disease has existed for thousands of years. The virus was an endemic pathogen until the 1880s, when major epidemics began to occur in Europe and later the United States. Polio vaccines were developed in the 1950s and a global eradication campaign started in 1988. The annual incidence of wild-type disease fell from many hundreds of thousands to 22 in 2017, but has since resurged to a few hundreds.
Selected image
The first immortal human cell line, HeLa cells were derived from a cervical cancer biopsy and carry human papillomavirus 18 DNA. The cells have been growing since 1951.
Credit: Gerry Shaw (8 March 2012)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
Viruses and viral infections have affected human history. Epidemics caused by viruses began when human behaviour changed during the Neolithic period, around 12,000 years ago. Previously hunter-gatherers, humans developed more densely populated agricultural communities, which allowed viruses to spread rapidly and subsequently to become endemic. Viruses of plants and livestock also increased, and as humans became dependent on agriculture and farming, diseases such as potyviruses of potatoes and rinderpest of cattle had devastating consequences. Smallpox and measles viruses are among the oldest that infect humans. They first appeared in humans in Europe and North Africa thousands of years ago, having evolved from viruses that infected other animals. Influenza pandemics have been recorded since 1580.
There are an estimated 1031 viruses on Earth. Although scientific interest in them arose because of the diseases they cause, most viruses are beneficial. They drive evolution by transferring genes across species, play important roles in ecosystems, and are essential to life.
Selected outbreak
The 2009 flu pandemic was an influenza pandemic first recognised in Mexico City in March 2009 and declared over in August 2010. It involved a novel strain of H1N1 influenza virus with genes from five different viruses, which resulted when a previous triple reassortment of avian, swine and human influenza viruses further combined with a Eurasian swine influenza virus, leading to the term "swine flu" being used for the pandemic. It was the second pandemic to involve an H1N1 strain, the first being the 1918 "Spanish flu" pandemic.
The global infection rate was estimated as 11–21%. This pandemic strain was less lethal than previous ones, killing about 0.01–0.03% of those infected, compared with 2–3% for Spanish flu. Most experts agree that at least 284,500 people died, mainly in Africa and Southeast Asia – comparable with the normal seasonal influenza fatalities of 290,000–650,000 – leading to claims that the World Health Organization had exaggerated the danger.
Selected quotation
| “ | Viruses are living chemicals... | ” |
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
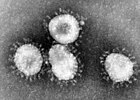
Coronaviruses are a subfamily of RNA viruses in the Nidovirales order which infect mammals and birds. They are spherical enveloped viruses, generally around 80–120 nm in diameter, containing a helical nucleocapsid. Their positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kb in size, one of the largest among RNA viruses. Around 74 characteristic club-shaped spikes project from the envelope, which in electron micrographs resemble the solar corona, from which their name derives. Infectious bronchitis virus was isolated in 1933 from chickens; two mice coronaviruses causing hepatitis and encephalomyelitis were discovered in the 1940s.
Coronaviruses predominantly infect epithelial cells, with the viral spike protein determining tissue tropism and host range. Animal coronaviruses often infect the gastrointestinal tract, causing diarrhoea in cows and pigs, and are transmitted by the faecal–oral route. Human and bird coronaviruses infect the respiratory tract, are transmitted via aerosols and droplets; they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include around 15% of common cold cases, while more lethal coronaviruses cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19. Many human coronaviruses have evolved from viruses of bats.
Did you know?
- ...that the largest in-flight transmission of SARS virus (coronavirus pictured) took place on an Air China flight in March 2003?
- ...that computational biologist Bette Korber describes her development of a mosaic antigen vaccine against HIV as creating "little Frankenstein proteins"?
- ...that although measles was declared eradicated from the United States in 2000, more than 500 people there had been diagnosed with the disease in January–May 2019?
- ...that Barrie Marmion spearheaded the development of the first vaccine against Q fever?
- ...that Michael Osterholm and Mark Olshaker's book Deadliest Enemy provides a nine-point plan to defeat "killer germs"?
Selected biography
Edward Jenner (1749–1823) was an English physician and scientist who pioneered the smallpox vaccine, the world's first vaccine. Noting the common observation that milkmaids were generally immune to smallpox, Jenner postulated that the pus in the blisters that milkmaids received from cowpox (a similar but much less virulent disease) protected them from smallpox. In 1796, Jenner tested his hypothesis by inoculating an eight-year-old boy with pus from an infected milkmaid. He subsequently repeatedly challenged the boy with variolous material, then the standard method of immunisation, without inducing disease. He published a paper including 23 cases in 1798. Although several others had previously inoculated subjects with cowpox, Jenner was the first to show that the procedure induced immunity to smallpox. He later successfully popularised cowpox vaccination.
Jenner is often called "the father of immunology", and his work is said to have saved more lives than that of any other individual.
In this month
5 June 1981: First report of HIV/AIDS (symbol pictured) appeared in medical literature
6 June 1997: Gene silencing in plants shown to be a viral defence mechanism
7–13 June 1962: Donald Caspar and Aaron Klug proposed the quasi-equivalence principle of virus structure
7–13 June 1962: André Lwoff proposed a viral classification scheme based on nature of genome, type of symmetry and presence of envelope
7–13 June 1962: George Hirst proposed that the influenza virus genome is segmented
9 June 1981: The American Society for Virology was founded
13 June 2012: First case of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) occurred in Saudi Arabia
18 June 1981: A vaccine against foot-and-mouth disease was the first genetically engineered vaccine
21 June 1996: Nevirapine approved, first NNRTI for HIV/AIDS
26 June 1993: Clinical trial of hepatitis B virus drug fialuridine terminated; the drug caused several fatalities due to lactic acidosis
28 June 2011: FAO declared rinderpest eradicated
30 June 1985: Ryan White was denied re-admittance to his school after an AIDS diagnosis, in a case that changed public perceptions of the disease
Selected intervention
The first Ebola vaccine was approved in 2019. Developed by the Public Health Agency of Canada, rVSV-ZEBOV is based on an attenuated recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus, genetically modified to express a surface glycoprotein of Zaire ebolavirus, and is estimated to be 97.5% effective. In the Kivu Ebola epidemic of 2018–20, a ring vaccination strategy was employed to protect direct and indirect contacts of infected people, as well as health workers, and around 300,000 people were vaccinated with rVSV-ZEBOV. A second vaccine was approved in 2020; this uses two different doses – a vector based on human adenovirus serotype 26 used to prime, boosted around eight weeks later by modified vaccinia Ankara (based on a heavily attenuated vaccinia virus) – and is not suitable for response to an outbreak. The efficacy is unknown. Multiple other vaccine candidates are in development to prevent Ebola, including replication-deficient adenovirus vectors, replication-competent human parainfluenza 3 vectors, and virus-like nanoparticle preparations.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus