This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2020) |
The Idel-Ural State (Tatar: Идел-Урал өлкәсе,[citation needed] İdel-Ural ölkäse, ادیل-اورال اولكسی, also İdel-Ural berlege İdel-Ural ştatı), also known as the Volga-Ural State or Idel-Ural Republic,[3] was an unsuccessful attempt of the autonomy of Tatar peoples that claimed to unite Tatars, Bashkirs, and the Chuvash in the turmoil of the Russian Civil War. The republic was proclaimed on 1 March 1918, by a Congress of Muslims from Russia's interior and Siberia, but defeated by Bolsheviks the same month.[4] Idel-Ural means "Volga-Ural" in the Tatar language.
Idel-Ural State ادیل-اورال Идел-Урал | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–28 March 1918 | |||||||||||||||
|
Flag | |||||||||||||||
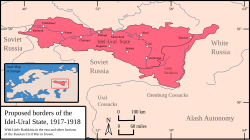 Claimed borders of Idel-Ural | |||||||||||||||
| Capital | Ufa | ||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Tatar, Russian | ||||||||||||||
| Government | Republic[1] | ||||||||||||||
| President | |||||||||||||||
• 1918 | Sadrí Maqsudí Arsal[2] | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Russian Civil War | ||||||||||||||
• Proclamation | 1 March 1918 | ||||||||||||||
• Government in-exile | 1918 | ||||||||||||||
• Defeat by Red Army | 28 March 1918 | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
History
editDuring the Russian Revolution, various regional political leaders convened in June 1917 in Kazan. The group declared the autonomy of "Muslim Turk-Tatars of Inner Russia and Siberia". Later on, in Ufa, a parliament named the Millät Mäclese (National Council) was created, in which a draft for the creation of the state would be pushed through and accepted on 29 November 1917 following the Second All-Russia Muslim Congress. However, the Idel-Ural State was met with opposition from Zeki Velidi Togan, a Bashkir revolutionary, who declared the autonomy of Bashkiria, as well as from the Bolsheviks, who had initially supported the creation of Idel-Ural but two months after denounced it as bourgeois nationalism[6][7]: 105 and declared the creation of the Tatar-Bashkir Soviet Republic, with around the same borders as Idel-Ural. This struggle between three different movements weakened the Idel-Ural State.[8]
Members of the Tatar-Bashkir Committee of Idel-Ural based outside of Russia such as Ayaz İshaki participated in an anti-Bolshevik propaganda war. Some also joined the Prometey group, a circle of anti-Soviet Muslim intellectuals based in Warsaw.[7]: 100 The idea of Idel-Ural by its supporting nationalists included the territory of modern-day Tatarstan, Bashkortostan, and most of Orenburg Oblast. The nationalists also wished for expansion towards the Caspian Sea. In January 1918, the Millät Mäclese adopted a constitution written by Galimzian Sharaf, Ilias and Jangir Alkin, Osman Tokumbetov and Y. Muzaffarov.
The Millät Mäclese looked to declare the creation of Idel-Ural on 1 March 1918, a plan which never came to fruition due to Bolshevik arrests of deputies of the Millät Mäclese and their official declaration of the Tatar-Bashkir Soviet Socialist Republic.[7]: 105 After the arrested deputies were freed, they reconvened in the Tatar part of Kazan beyond the Bolaq stream (hence in Soviet historiography it was called "Transbolaq Republic" (Забулачная республика)[9]). The Republic, which in reality included only some sections of Kazan and Ufa, was defeated by the Red Army on 28 March 1918.[9][10][11] Its parliament disbanded in April.[8]
The president of Idel-Ural, Sadrí Maqsudí Arsal, escaped to Finland in 1918. He was well received by the Finnish foreign minister Carl Enckell, who remembered his valiant defence of the national self-determination and constitutional rights of Finland in the Russian Duma.[citation needed] The president-in-exile also met officials from Estonia before continuing in 1919 to Sweden, Germany and France, in a quest for Western support. Idel-Ural was listed among the "Captive Nations" in the Cold War-era public law (1959) of the United States.[12]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Рожденный революцией. Татарскому парламенту исполнилось 100 лет". RFE/RL. 30 November 2017.
- ^ "Почему не удалось построить Идель-Уральскую республику". RFE/RL. 4 August 2018.
- ^ "Почему не удалось построить Идель-Уральскую республику". RFE/RL (in Russian). 4 August 2018. Retrieved 2020-12-25.
- ^ "Почему не удалось построить Идель-Уральскую республику". RFE/RL (in Russian). 4 August 2018. Retrieved 2020-12-25.
- ^ "Милләт Мәҗлесен ачу тантанасы". Азатлык Радиосы (in Tatar). 9 January 2012. Retrieved 2022-07-25.
- ^ IZMAIL I. SHARIFZHANOV (2007). "The parliament of Tatarstan, 1990–2005: vain hopes, or the Russian way towards parliamentary democracy in a regional dimension." Parliaments, Estates and Representation, 27:1, 239–250, DOI: 10.1080/02606755.2"007.9522264
- ^ a b c Yemelianova G.M. (2002) "Muslims under Soviet Rule: 1917–91." In: Russia and Islam. Studies in Russian and East European History and Society. Palgrave Macmillan, London. https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230288102_4
- ^ a b Devlet, Nadir. "A struggle for independence in the Russian Federation: the case of the Tatars." In: CEMOTI, n°16, 1993. Istanbul – Oulan Bator: autonomisation, mouvements identitaires et construction du politique. pp. 63–82. Accessed 13 April 2021. https://doi.org/10.3406/cemot.1993.1052
- ^ a b "Забулачная республика – взгляд через 85 лет". Казанские истории (in Russian). Retrieved 2020-12-25.
- ^ Commissar and Mullah: Soviet-Muslim Policy from 1917 to 1924, Glenn L. Roberts, Universal-Publishers, 2007, p.178
- ^ The New Central Asia: The Creation of Nations, Olivier Roy, I.B.Tauris, 2000, p.44
- ^ Campbell, John Coert (1965). American Policy Toward Communist Eastern Europe: the Choices Ahead. University of Minnesota Press. p. 116. ISBN 0-8166-0345-6.
Further reading
edit- Indus Tagirov:
- «Очерки истории Татарстана и татарского народа», Tatar Book Publishers, 1999
- «История национальной государственности татарского народа и Татарстана», Tatar Book Publishers 2008
- Alter Litvin, «Казань: время гражданской войны», 1991
