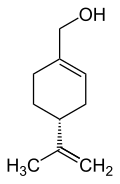
Perillyl alcohol and its precursor limonene are naturally occurring monocyclic terpenes derived from the mevalonate pathway in plants. Perillyl alcohol can be found in the essential oils of various plants, such as lavender, lemongrass, sage, and peppermint.[1] It has a number of manufacturing, household, and medical applications. For example, perillyl alcohol may be used as an ingredient in cleaning products and cosmetics.[2]
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4-Isopropenyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)methanol
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.856 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H16O | |||
| Molar mass | 152.237 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Perillyl alcohol has shown some antitumor activity in laboratory and animal studies.[3] Perillyl Alcohol decrease production of proangiogenic growth factors VEGF and interleukin-8 (IL-8) in vitro.[4]
Mammals possess enzymes (P450, liver) to convert limonene to Perillyl alcohol.[4] Limonene is formed from geranyl pyrophosphate in the mevalonate pathway. Conversion of limonene to perillyl alcohol is done via hydroxylation by enzymes that belong to the superfamily of cytochrome P450 proteins. Perillyl alcohol can be further converted to perillaldehyde (perillyl aldehyde) and perillic acid.[5]
The name comes from the herb perilla.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Crowell PL, Elson CE (2001). Isoprenoids, Health and Disease. In: Wildman REC, editors. Neutraceuticals and Functional Foods. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, LLC. pp. 31–53.
- ^ Laszlo P (2007). Citrus: A History. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- ^ "Perillyl Alcohol". Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
- ^ a b Chen TC, Da Fonseca CO, Schönthal AH (2015). "Preclinical development and clinical use of perillyl alcohol for chemoprevention and cancer therapy". American Journal of Cancer Research. 5 (5): 1580–93. PMC 4497427. PMID 26175929.
- ^ Mann, J. C.; Hobbs, J. B.; Banthorpe, D. V.; Harborne, J. B. (1994). Natural products: their chemistry and biological significance. Harlow, Essex, England: Longman Scientific & Technical. pp. 308–9. ISBN 0-582-06009-5.