Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.[1] It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system.[2][3] The Mycenaeans were mainland Greek peoples who were likely stimulated by their contact with insular Minoan Crete and other Mediterranean cultures to develop a more sophisticated sociopolitical culture of their own.[4] The most prominent site was Mycenae, after which the culture of this era is named. Other centers of power that emerged included Pylos, Tiryns, and Midea in the Peloponnese, Orchomenos, Thebes, and Athens in Central Greece, and Iolcos in Thessaly. Mycenaean settlements also appeared in Epirus,[5] Macedonia,[6] on islands in the Aegean Sea,[7] on the south-west coast of Asia Minor, [7] and on Cyprus,[8] while Mycenaean-influenced settlements appeared in the Levant[9] and Italy.[10]
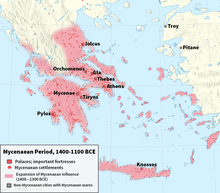 | |
| Alternative names | Mycenaean civilization |
|---|---|
| Geographical range | Mainland Greece, Aegean islands and Western Anatolia |
| Period | Bronze Age |
| Dates | c. 1750 – c. 1050 BC |
| Type site | Mycenae |
| Major sites | Pylos, Tiryns, Midea, Orchomenos, Iolcos |
| Characteristics |
|
| Preceded by | Minoan civilization, Korakou culture, Tiryns culture |
| Followed by | Greek Dark Ages |
The Mycenaean Greeks introduced several innovations in the fields of engineering, architecture and military infrastructure, while trade over vast areas of the Mediterranean was essential for the Mycenaean economy. Their syllabic script, Linear B, offers the first written records of the Greek language, and their religion already included several deities that can also be found in the Olympic pantheon. Mycenaean Greece was dominated by a warrior elite society and consisted of a network of palace-centered states that developed rigid hierarchical, political, social, and economic systems. At the head of this society was the king, known as a wanax.
Mycenaean Greece perished with the collapse of Bronze Age culture in the eastern Mediterranean, to be followed by the Greek Dark Ages, a recordless transitional period leading to Archaic Greece where significant shifts occurred from palace-centralized to decentralized forms of socio-economic organization (including the extensive use of iron).[11] Various theories have been proposed for the end of this civilization, among them the Dorian invasion or activities connected to the "Sea Peoples". Additional theories such as natural disasters and climatic changes have also been suggested. The Mycenaean period became the historical setting of much ancient Greek literature and mythology, including the Trojan Epic Cycle.[12]
Chronology
editThe Bronze Age in mainland Greece is generally termed as the "Helladic period" by modern archaeologists, after Hellas, the Greek name for Greece. This period is divided into three subperiods: The Early Helladic (EH) period (c. 3200–2000 BC)[13] was a time of prosperity with the use of metals and a growth in technology, economy and social organization. The Middle Helladic (MH) period (c. 2000–1700/1675 BC[1]) faced a slower pace of development, as well as the evolution of megaron-type dwellings and cist grave burials.[3] The last phase of Middle Helladic, the Middle Helladic III (c. 1750–1675 BC), along with the Late Helladic (LH) period (c. 1700/1675–1050 BC) roughly coincide with Mycenaean Greece.[1]
The Late Helladic period is further divided into LHI and LHII, both of which coincide with the middle phase of Mycenaean Greece (c. 1700/1675–1420 BC), and LHIII (c. 1420–1050 BC), the period of expansion, and decline of the Mycenaean civilization.[1] The transition period from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age in Greece is known as Sub-Mycenaean (c. 1050–1000 BC).[3]
Based on recent research, Alex Knodell (2021) considers the beginning of Mycenaean occupation in Peloponnese in Middle Helladic III (c. 1750–1675 BC), and divides the whole Mycenaean time into three cultural periods: Early Mycenaean (c. 1750–1400 BC), Palatial Bronze Age (c. 1400–1200 BC), and Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1200–1050 BC).[1]
| Ceramic period | Dates BC |
|---|---|
| Middle Helladic III | 1750/1720–1700/1675 |
| Late Helladic I | 1700/1675–1635/1600 |
| Late Helladic IIA | 1635/1600–1480/1470 |
| Late Helladic IIB | 1480/1470–1420/1410 |
| Ceramic period | Dates BC |
|---|---|
| Late Helladic IIIA1 | 1420/1410–1390/1370 |
| Late Helladic IIIA2 | 1390/1370–1330/1315 |
| Late Helladic IIIB | 1330/1315–1210/1200 |
| Ceramic period | Dates BC |
|---|---|
| Late Helladic IIIC (Early) | 1210/1200–1170/1160 |
| Late Helladic IIIC (Middle) | 1170/1160–1100 |
| Late Helladic IIIC (Late) | 1100–1070/1040 |
Identity
editThe decipherment of the Mycenaean Linear B script, a writing system adapted for the use of the (Indo-European) Greek language of the Late Bronze Age,[14] demonstrated the continuity of Greek speech from the second millennium BC into the eighth century BC when a new Phoenician-derived alphabetic script emerged.[15] Moreover, it revealed that the bearers of Mycenaean culture were ethnically connected with the populations that resided in the Greek peninsula after the end of this cultural period.[16] Lastly, the decipherment marked the advent of an Indo-European language in the Aegean region in contrast to unrelated prior languages spoken in adjoining areas.[17] Various collective terms for the inhabitants of Mycenaean Greece were used by Homer in his 8th-century BC epic the Iliad in reference to the Trojan War.[18]
Homer interchangeably used the ethnonyms Achaeans, Danaans, and Argives to refer to the besiegers,[18] and these names appear to have passed down from the time they were in use to the time when Homer applied them as collective terms in his Iliad.[19] There is an isolated reference to a-ka-wi-ja-de in the Linear B records in Knossos, Crete dated to c. 1400 BC, which presumably refers to a Mycenaean (Achaean) state on the Greek mainland.[20]
Egyptian records mention a T(D)-n-j or Danaya (Tanaju) land for the first time c. 1437 BC, during the reign of Pharaoh Thutmoses III (r. 1479–1425 BC). This land is geographically defined in an inscription from the reign of Amenhotep III (r. c. 1390–1352 BC), where a number of Danaya cities are mentioned, which cover the largest part of southern mainland Greece.[21] Among them, cities such as Mycenae, Nauplion, and Thebes have been identified with certainty. Danaya has been equated with the ethnonym Danaoi (Greek: Δαναοί), the name of the mythical dynasty that ruled in the region of Argos, also used as an ethnonym for the Greek people by Homer.[21][22]
In the official records of another Bronze Age empire, that of the Hittites in Anatolia, various references from c. 1400 BC to 1220 BC mention a country named Ahhiyawa.[23][24] Recent scholarship, based on textual evidence, new interpretations of the Hittite inscriptions, and recent surveys of archaeological evidence about Mycenaean–Anatolian contacts during this period, concludes that the term Ahhiyawa must have been used in reference to the Mycenaean world (land of the Achaeans), or at least to a part of it.[25][26] This term may have also had broader connotations in some texts, possibly referring to all regions settled by Mycenaeans or regions under direct Mycenaean political control.[23] Another similar ethnonym, Ekwesh, in twelfth century BC Egyptian inscriptions has been commonly identified with the Ahhiyawans. These Ekwesh were mentioned as a group of the Sea People.[27]
History
editEarly Mycenaean period and Shaft Grave era (c. 1750–1400 BC)
editScholars have proposed different theories on the origins of the Mycenaeans.[2] According to one theory, Mycenaean civilization reflected the exogenous imposition of archaic Indo-Europeans from the Eurasian steppe onto the pre-Mycenaean local population.[2] An issue with this theory, however, is the very tenuous material and cultural relationship between Aegean and northern steppe populations during the Bronze Age.[2] Another theory proposes that Mycenaean culture in Greece dates back to circa 3000 BC with Indo-European migrants entering a mainly-depopulated area; other hypotheses argue for a date as early as the seventh millennium BC (with the spread of agriculture) and as late as 1600 BC (with the spread of chariot technology).[2] In a 2017 genetic study conducted by Lazaridis et al., "the Minoans and Mycenaeans were genetically similar, [but] the Mycenaeans differed from Minoans in deriving additional ancestry from an ultimate source related to the hunter–gatherers of eastern Europe and Siberia, introduced via a proximal source related to the inhabitants of either the Eurasian steppe or Armenia."[2] However, Lazaridis et al. admit that their research "does not settle th[e] debate" on Mycenaean origins.[2] Historian Bernard Sergent notes that archaeology alone is not able to solve the issue and that the majority of Hellenists believed Mycenaeans spoke a non-Indo-European Minoan language before Linear B was deciphered in 1952.[29]
Notwithstanding the above academic disputes, the mainstream consensus among modern Mycenologists is that Mycenaean civilization began around 1750 BC,[1] earlier than the Shaft Graves,[30] originating and evolving from the local socio-cultural landscape of the Early and Middle Bronze Age in mainland Greece with influences from Minoan Crete.[31][32] Towards the end of the Middle Bronze Age (c. 1700/1675 BC),[1] a significant increase in the population and the number of settlements occurred.[33] A number of centers of power emerged in southern mainland Greece dominated by a warrior elite society;[3][31] while the typical dwellings of that era were an early type of megaron buildings, some more complex structures are classified as forerunners of the later palaces. In a number of sites, defensive walls were also erected.[34]
Meanwhile, new types of burials and more imposing ones have been unearthed, which display a great variety of luxurious objects.[33][35] Among the various burial types, the shaft grave became the most common form of elite burial, a feature that gave the name to the early period of Mycenaean Greece.[33] Among the Mycenaean elite, deceased men were usually laid to rest in gold masks and funerary armor, and women in gold crowns and clothes gleaming with gold ornaments.[36] The royal shaft graves next to the acropolis of Mycenae, in particular the Grave Circles A and B, signified the elevation of a native Greek-speaking royal dynasty whose economic power depended on long-distance sea trade.[37]
During this period, the Mycenaean centers witnessed increased contact with the outside world, especially with the Cyclades and the Minoan centers on the island of Crete.[3][33] Mycenaean presence appears to be also depicted in a fresco at Akrotiri, on Thera island, which possibly displays many warriors in boar's tusk helmets, a feature typical of Mycenaean warfare.[38] In the early 15th century BC, commerce intensified with Mycenaean pottery reaching the western coast of Asia Minor, including Miletus and Troy, Cyprus, Lebanon, Palestine and Egypt.[39]
Early Mycenaean civilization from the Shaft Grave period generally showcases heavy influence from Minoan Crete in regards to e.g. art, infrastructure and symbols, while also maintaining some Helladic elements as well as some innovations, and some West Asian influences. A difference between Mycenaean and Minoan civilizations is complexity and monumentality; Mycenaean craftmanship and architecture are more simplified versions of Minoan ones, but are more monumental in size. Later phases of the Mycenaean civilization showcase more sophistication, eventually coming to surpass Minoan Crete after a few centuries.[40]
At the end of the Shaft Grave era, a new and more imposing type of elite burial emerged, the tholos: large circular burial chambers with high vaulted roofs and a straight entry passage lined with stone.[41]
Koine era or Palatial Bronze Age (c. 1400–1200 BC)
editStarting in the 15th century BC, the Mycenaeans began to spread their influence throughout the Aegean and Western Anatolia. By c. 1450 BC, the palace of Knossos was ruled by a Mycenaean elite who formed a hybrid Minoan-Mycenaean culture. Mycenaeans also colonized several other Aegean islands, reaching as far as Rhodes.[42][43] Thus the Mycenaeans became the dominant power of the region, marking the beginning of the Mycenaean 'Koine' era (from Greek: Κοινή, common), a highly uniform culture that spread in mainland Greece and the Aegean.[44]
From the early 14th century BC, Mycenaean trade began to take advantage of the new commercial opportunities in the Mediterranean after the Minoan collapse.[43] The trade routes were expanded further, reaching Cyprus, Amman in the Near East, Apulia in Italy and Spain.[43] From that time period (c. 1400 BC), the palace of Knossos has yielded the earliest records of the Greek Linear B script, based on the previous Linear A of the Minoans. The use of the new script spread in mainland Greece and offers valuable insight into the administrative network of the palatial centers. However, the unearthed records are too fragmentary for a political reconstruction of Bronze Age Greece.[45]
Excavations at Miletus, southwest Asia Minor, indicate the existence of a Mycenaean settlement there already from c. 1450 BC, replacing the previous Minoan installations.[46] This site became a sizable and prosperous Mycenaean center until the 12th century BC.[47] Apart from the archaeological evidence, this is also attested in Hittite records, which indicate that Miletos (Milawata in Hittite) was the most important base for Mycenaean activity in Asia Minor.[48] Mycenaean presence also reached the adjacent sites of Iasus and Ephesus.[49]
Meanwhile, imposing palaces were built in the main Mycenaean centers of the mainland. The earliest palace structures were megaron-type buildings, such as the Menelaion in Sparta, Lakonia.[50] Palaces proper are datable from c. 1400 BC, when Cyclopean fortifications were erected at Mycenae and nearby Tiryns.[3] Additional palaces were built in Midea and Pylos in Peloponnese, Athens, Eleusis, Thebes and Orchomenos in Central Greece and Iolcos, in Thessaly, the latter being the northernmost Mycenaean center. Knossos in Crete also became a Mycenaean center, where the former Minoan complex underwent a number of adjustments, including the addition of a throne room.[51] These centers were based on a rigid network of bureaucracy where administrative competencies were classified into various sections and offices according to specialization of work and trades. At the head of this society was the king, known as wanax (Linear B: wa-na-ka) in Mycenaean Greek. All powers were vested in him, as the main landlord and spiritual and military leader. At the same time he was an entrepreneur and trader and was aided by a network of high officials.[52]
Involvement in Asia Minor
editThe presence of Ahhiyawa in western Anatolia is mentioned in various Hittite accounts from c. 1400 to c. 1220 BC.[48] Ahhiyawa is generally accepted as a Hittite term for Mycenaean Greece (Achaeans in Homeric Greek), but a precise geographical definition of the term cannot be drawn from the texts.[53] During this time, the kings of Ahhiyawa were evidently capable of dealing with their Hittite counterparts both on a diplomatic and military level.[54] Moreover, Ahhiyawa achieved considerable political influence in parts of Western Anatolia, typically by encouraging anti-Hittite uprisings and collaborating with local vassal rulers.[55]
In c. 1400 BC, Hittite records mention the military activities of an Ahhiyawan warlord, Attarsiya, possibly related to the mythic character of Atreus. Attarsiya attacked Hittite vassals in western Anatolia including Madduwatta.[56] Later, in c. 1315 BC, an anti-Hittite rebellion headed by Arzawa, a Hittite vassal state, received support from Ahhiyawa.[57] Meanwhile, Ahhiyawa appears to be in control of a number of islands in the Aegean, an impression also supported by archaeological evidence.[58] During the reign of the Hittite king Hattusili III (c. 1267–1237 BC), the king of Ahhiyawa is recognized as a "Great King" and of equal status with the other contemporary great Bronze Age rulers: the kings of Egypt, Babylonia and Assyria.[59] At that time, another anti-Hittite movement, led by Piyama-Radu, broke out and was supported by the king of Ahhiyawa.[60] Piyama-Radu caused major unrest which may have extended to the region of Wilusa, and later invaded the island of Lesbos, which then passed into Ahhiyawan control.[61]
Scholars have speculated that the mythic tradition of the Trojan War could have a historical basis in the political turmoil of this era.[62] As a result of this instability, the Hittite king initiated correspondence in order to convince his Ahhiyawan counterpart to restore peace in the region. The Hittite record mentions a certain Tawagalawa, a possible Hittite rendering of the Greek name Eteocles, as brother of the king of Ahhiyawa.[61][63]
Collapse or Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1200–1050 BC)
editInitial decline and revival
editIn c. 1250 BC, the first wave of destruction apparently occurred in various centres of mainland Greece for reasons that cannot be identified by archaeologists. In Boeotia, Thebes was burned to the ground, around that year or slightly later.[64] Nearby Orchomenos was not destroyed at this time but was abandoned, while the Boeotian fortifications of Gla displays evidence for a targeted destruction as only the four gates and the monumental building, called the Melathron, were burned before the site was abandoned.[65] In the Peloponnese, a number of buildings surrounding the citadel of Mycenae were attacked and burned.[66]
These incidents appear to have prompted the massive strengthening and expansion of the fortifications in various sites. In some cases, arrangements were also made for the creation of subterranean passages which led to underground cisterns. Tiryns, Midea and Athens expanded their defences with new cyclopean-style walls.[67] The extension program in Mycenae almost doubled the fortified area of the citadel. To this phase of extension belongs the impressive Lion Gate, the main entrance into the Mycenaean acropolis.[67]
It appears that after this first wave of destruction a short-lived revival of Mycenaean culture followed.[68] Mycenaean Greece continues to be mentioned in international affairs, particularly in Hittite records. In c. 1220 BC, the king of Ahhiyawa is again reported to have been involved in an anti-Hittite uprising in western Anatolia.[69] Another contemporary Hittite account reports that Ahhiyawan ships should avoid Assyrian-controlled harbors, as part of a trade embargo imposed on Assyria.[70] In general, in the second half of 13th century BC, trade was in decline in the Eastern Mediterranean, most probably due to the unstable political environment there.[71]
Final collapse and differing trajectories
editNone of the defence measures appear to have prevented the final destruction and collapse of the Mycenaean states. A second destruction struck Mycenae in c. 1190 BC or shortly thereafter. This event marked the end of Mycenae as a major power. The site was then reoccupied, but on a smaller scale.[66] A recent study suggests that neither of the palaces at Tiryns or Midea were destroyed by an earthquake,[72] and further studies have shown that upwards of fifty arrowheads were found scattered in the destruction debris at Midea perhaps indicating that the destruction was caused by an assault.[73] The palace of Pylos, in the southwestern Peloponnese, was destroyed in c. 1180 BC.[74][75] The Linear B archives found there, preserved by the heat of the fire that destroyed the palace, mention hasty defence preparations due to an imminent attack without giving any detail about the attacking force.[68]
As a result of this turmoil, specific regions in mainland Greece witnessed a dramatic population decrease, especially Boeotia, Argolis and Messenia.[68] Mycenaean refugees migrated to Cyprus and the Levantine coast.[75] Nevertheless, other regions on the edge of the Mycenaean world prospered, such as the Ionian islands, the northwestern Peloponnese, parts of Attica and a number of Aegean islands.[68] The acropolis of Athens, oddly, appears to have avoided destruction.[68]
Athens and the eastern coast of Attica were still occupied in the 12th century BC, and were not destroyed or abandoned; this points to the existence of new decentralized coastal and maritime networks there. It is attested by the cemetery of Perati that lasted a century and showed imports from Cyclades, Dodecanese, Crete, Cyprus, Egypt and Syria, as well as by the Late Helladic IIIC (c. 1210–1040 BC) cemetery of Drivlia at Porto Rafti; located 2 km west of Perati. This indicates that Attica participated in long-distance trade, and was also incorporated in a mainland-looking network.[76]
The site of Mycenae experienced a gradual loss of political and economic status, while Tiryns, also in the Argolid region, expanded its settlement and became the largest local center during the post-palatial period, in Late Helladic IIIC, c. 1200–1050 BC.[77]
Hypotheses for the collapse
editThe reasons for the end of the Mycenaean culture have been hotly debated among scholars. At present, there is no satisfactory explanation for the collapse of the Mycenaean palace systems. The two most common theories are population movement and internal conflict. The first attributes the destruction of Mycenaean sites to invaders.[78]
The hypothesis of a Dorian invasion, known as such in Ancient Greek tradition, that led to the end of Mycenaean Greece, is supported by sporadic archaeological evidence such as new types of burials, in particular cist graves, and the use of a new dialect of Greek, the Doric one. It appears that the Dorians moved southward gradually over a number of years and devastated the territory, until they managed to establish themselves in the Mycenaean centers.[79] A new type of ceramic also appeared, called "Barbarian Ware" because it was attributed to invaders from the north.[68] On the other hand, the collapse of Mycenaean Greece coincides with the activity of the Sea Peoples in the Eastern Mediterranean. They caused widespread destruction in Anatolia and the Levant and were finally defeated by Pharaoh Ramesses III in c. 1175 BC. One of the ethnic groups that comprised these people were the Eqwesh, a name that appears to be linked with the Ahhiyawa of the Hittite inscriptions.[80]
Alternative scenarios propose that the fall of Mycenaean Greece was a result of internal disturbances which led to internecine warfare among the Mycenaean states or civil unrest in a number of states, as a result of the strict hierarchical social system and the ideology of the wanax.[81] In general, due to the obscure archaeological picture in 12th–11th century BC Greece, there is a continuing controversy among scholars over whether the impoverished societies that succeeded the Mycenaean palatial states were newcomers or populations that already resided in Mycenaean Greece. Recent archaeological findings tend to favor the latter scenario.[68] Additional theories, concerning natural factors, such as climate change, droughts, or earthquakes have also been proposed.[81] Another theory considers the decline of the Mycenaean civilization as a manifestation of a common pattern for the decline of many ancient civilizations: the Minoan, the Harappan and the Western Roman Empire; the reason for the decline is migration due to overpopulation.[82] The period following the end of Mycenaean Greece, c. 1100–800 BC, is generally termed the "Greek Dark Ages".[83]
Political organization
editPalatial states
editMycenaean palatial states, or centrally organized palace-operating polities, are recorded in ancient Greek literature and mythology (e.g., Iliad, Catalogue of Ships) and confirmed by discoveries made by modern archaeologists such as Heinrich Schliemann. Each Mycenaean kingdom was governed from the palace, which exercised control over most, if not all, industries within its realm. The palatial territory was divided into several sub-regions, each headed by its provincial center. Each province was further divided in smaller districts, the damoi.[84] A number of palaces and fortifications appear to be part of a wider kingdom. For instance, Gla, located in the region of Boeotia, belonged to the state of nearby Orchomenos.[64] Moreover, the palace of Mycenae appeared to have ruled over a territory two to three times the size of the other palatial states in Bronze Age Greece. Its territory would have also included adjacent centers, including Tiryns and Nauplion, which could plausibly be ruled by a member of Mycenae's ruling dynasty.[85]
The unearthed Linear B texts are too fragmentary for the reconstruction of the political landscape in Mycenaean Greece and they do not support nor deny the existence of a larger Mycenaean state.[53][86] On the other hand, contemporary Hittite and Egyptian records suggest the presence of a single state under a "Great King".[87] Alternatively, based on archaeological data, some sort of confederation among a number of palatial states appears to be possible.[53] If some kind of united political entity existed, the dominant center was probably located in Thebes or in Mycenae, with the latter state being the most probable center of power.[88]
Society and administration
editThe Neolithic agrarian village (6000 BC) constituted the foundation of Bronze Age political culture in Greece.[89] The vast majority of the preserved Linear B records deal with administrative issues and give the impression that Mycenaean palatial administration was highly systematized, featuring thoroughly consistent language, terminology, tax calculations, and distribution logistics.[45][84] Considering this sense of uniformity, the Pylos archive, which is the best preserved one in the Mycenaean world, is generally taken as a representative one.[45]
The state was ruled by a king, the wanax (ϝάναξ), whose role was religious and perhaps also military and judicial.[90] The wanax oversaw virtually all aspects of palatial life, from religious feasting and offerings to the distribution of goods, craftsmen and troops.[91] Under him was the lāwāgetas ("the leader of the people"), whose role appears mainly religious. His activities possibly overlap with the wanax and is usually seen as the second-in-command.[91] Both wanax and lāwāgetas were at the head of a military aristocracy known as the eqeta ("companions" or "followers").[90][92] The land possessed by the wanax is usually the témenos (te-me-no). There is also at least one instance of a person, Enkhelyawon, at Pylos, who appears titleless in the written record but whom modern scholars regard as probably a king.[93]
A number of local officials positioned by the wanax appear to be in charge of the districts, such as ko-re-te (koreter, '"governor"), po-ro-ko-re-te (prokoreter, "deputy") and the da-mo-ko-ro (damokoros, "one who takes care of a damos"), the latter probably being appointed to take charge of the commune. A council of elders was chaired, the ke-ro-si-ja (cf. γερουσία, gerousía). The basileus, who in later Greek society was the name of the king, refers to communal officials.[90]
In general, Mycenaean society appears to have been divided into two groups of free men: the king's entourage, who conducted administrative duties at the palace, and the people, da-mo.[94] These last were watched over by royal agents and were obliged to perform duties for and pay taxes to the palace.[90] Among those who could be found in the palace were well-to-do high officials, who probably lived in the vast residences found in proximity to Mycenaean palaces, but also others, tied by their work to the palace and not necessarily better off than the members of the da-mo, such as craftsmen, farmers, and perhaps merchants. Occupying a lower rung of the social ladder were the slaves, do-e-ro, (cf. δοῦλος, doúlos).[95] These are recorded in the texts as working either for the palace or for specific deities.[90]
Economy
editOrganization
editThe Mycenaean economy, given its pre-monetary nature, was a palace economy, focusing on the redistribution of goods, commodities and labor by a central administration. The preserved Linear B records in Pylos and Knossos indicate that the palaces were closely monitoring a variety of industries and commodities, the organization of land management and the rations given to the dependent personnel.[96][97] The Mycenaean palaces maintained extensive control of the nondomestic areas of production through careful control and acquisition and distribution in the palace industries, and the tallying of produced goods.[98][99] For instance, the Knossos tablets record c. 80,000–100,000 sheep grazing in central Crete, and the quantity of the expected wool from these sheep and their offspring, as well as how this wool was allocated.[99] The archives of Pylos display a specialized workforce, where each worker belonged to a precise category and was assigned to a specific task in the stages of production, notably in textiles.[100]
Nevertheless, palatial control over resources appears to have been highly selective in spatial terms and in terms of how different industries were managed.[101] Thus, sectors like the production of perfumed oil and bronze materials were directly monitored from the palace, but the production of ceramics was only indirectly monitored.[102] Regional transactions between the palaces are also recorded on a few occasions.[103]
Large-scale infrastructure
editThe palatial centers organized their workforce and resources for the construction of large scale projects in the fields of agriculture and industry.[97] The magnitude of some projects indicates that this was the result of combined efforts from multiple palatial centers. Most notable of them are the drainage system of the Kopais basin in Boeotia, the building of a large dam outside Tiryns, and the drainage of the swamp in the Nemea valley.[104] Also noticeable is the construction of harbors, such as the harbor of Pylos, that were capable of accommodating large Bronze Age era vessels like the one found at Uluburun.[104] The Mycenaean economy also featured large-scale manufacturing as testified by the extent of workshop complexes that have been discovered, the largest known to date being the recent ceramic and hydraulic installations found in Euonymeia, next to Athens, that produced tableware, textiles, sails, and ropes for export and shipbuilding.[105]
The most famous project of the Mycenaean era was the network of roads in the Peloponnese.[104] This appears to have facilitated the speedy deployment of troops—for example, the remnants of a Mycenaean road, along with what appears to have been a Mycenaean defensive wall on the Isthmus of Corinth. The Mycenaean era saw the zenith of infrastructure engineering in Greece, and this appears not to have been limited to the Argive plain.[106]
Trade
editTrade over vast areas of the Mediterranean was essential for the economy of Mycenaean Greece. The Mycenaean palaces imported raw materials, such as metals, ivory and glass, and exported processed commodities and objects made from these materials, in addition to local products: oil, perfume, wine, wool and pottery.[97] International trade of that time was not only conducted by palatial emissaries but also by independent merchants.[107]
Based on archaeological findings in the Middle East, in particular physical artifacts, textual references, inscriptions and wall paintings, it appears that Mycenaean Greeks achieved strong commercial and cultural interaction with most of the Bronze Age people living in this region: Canaanites, Kassites, Mitanni, Assyrians, and Egyptians.[107][108][109] The 14th century BC Uluburun shipwreck, off the coast of southern Anatolia, displays the established trade routes that supplied the Mycenaeans with all the raw materials and items that the economy of Mycenaean Greece needed, such as copper and tin for the production of bronze products.[110] A chief export of the Mycenaeans was olive oil, which was a multi-purpose product.[111]
Cyprus appears to be the principal intermediary station between Mycenaean Greece and the Middle East, based on the considerable greater quantities of Mycenaean goods found there.[112] On the other hand, trade with the Hittite lands in central Anatolia appears to have been limited.[107][113] Trade with Troy is also well attested, while Mycenaean trade routes expanded further to the Bosphorus and the shores of the Black Sea.[114] Mycenaean swords have been found as far away as Georgia in the eastern Black Sea coast.[115]
Commercial interaction was also intense with the Italian peninsula and the western Mediterranean. Mycenaean products, especially pottery, were exported to southern Italy, Sicily and the Aeolian Islands. Mycenaean products also penetrated further into Sardinia,[116][117] as well as southern Spain.[118]
Sporadic objects of Mycenaean manufacture were found in various distant locations, like in Central Europe,[119] such as in Bavaria, Germany, where an amber object inscribed with Linear B symbols has been unearthed.[120] Mycenaean bronze double axes and other objects dating from the 13th century BC have been found in Ireland and in Wessex and Cornwall in England.[121][122]
Anthropologists have found traces of opium in Mycenaean ceramic vases.[123] The drug trade in Mycenaean Greece is traced as early as 1650–1350 BC, with opium poppies being traded in the eastern Mediterranean.[124][125]
Religion
editTemples and shrines are strangely rare in the Mycenaean archaeological sites. Monumental cultic structures are absent at all the palatial centers, with the exception of Mycenae. However, the cultic center of Mycenae seems to have been a later (13th century BC) development.[126] Small shrines have been identified in Asine, Berbati, Malthi and Pylos,[127] while a number of sacred enclosures have been located near Mycenae, Delphi and Amyclae.[128] Linear B records mention a number of sanctuaries dedicated to a variety of deities, at least in Pylos and Knossos. They also indicate that there were various religious festivities including offerings.[129] Written Mycenaean records mention various priests and priestesses who were responsible for specific shrines and temples.[130] The latter were prominent figures in society, and the role of Mycenaean women in religious festivities was also important, just as in Minoan Crete.[131]
The Mycenaean pantheon already included many divinities that were subsequently encountered in Classical Greece,[132] although it is difficult to determine whether these deities had the characteristics and responsibilities that would be attributed to them in later periods.[133] In general, the same divinities were worshipped throughout the Mycenaean palatial world. There may be some indications for local deities at various sites, in particular in Crete. The uniformity of Mycenaean religion is also reflected in archaeological evidence with the phi- and psi-figurines that have been found all over Late Bronze Age Greece.[126]
Poseidon (Linear B: Po-se-da-o) seems to have occupied a place of privilege. He was a chthonic deity, connected with earthquakes (E-ne-si-da-o-ne: Earth-shaker), but it seems that he also represented the river spirit of the underworld.[134] Paean (Pa-ja-wo) is probably the precursor of the Greek physician of the gods in Homer's Iliad. He was the personification of the magic-song which was supposed to "heal" the patient.[135] A number of divinities have been identified in the Mycenaean scripts only by their epithets used during later antiquity. For example, Qo-wi-ja ("cow-eyed") is a standard Homeric epithet of Hera.[136] Ares appeared under the name Enyalios (assuming that Enyalios is not a separate god).[137] Additional divinities that can be also found in later periods include Hephaestus, Erinya, Artemis (a-te-mi-to and a-ti-mi-te) and Dionysos (Di-wo-nu-so).[138][139][140][141] Zeus also appears in the Mycenaean pantheon, but he was certainly not the chief deity.[133]
A collection of "ladies" or "mistresses", Po-ti-ni-ja (Potnia) are named in the Mycenaean scripts. As such, Athena (A-ta-na) appears in an inscription at Knossos as mistress Athena, similar to a later Homeric expression, but in the Pylos tablets she is mentioned without any accompanying word.[142] Si-to po-ti-ni-ja appears to be an agricultural goddess, possibly related to Demeter of later antiquity,[136] while in Knossos there is the "mistress of the Labyrinth".[143] The "two queens and the king" (wa-na-ssoi, wa-na-ka-te) are mentioned in Pylos.[144][145] Goddess Pe-re-swa mentioned may be related to Persephone.[136][142] A number of Mycenaean divinities seem to have no later equivalents, such as Marineus, Diwia and Komawenteia.[133]
Women
editDaily life
editBy observing Mycenaean wall paintings, scholars have deduced that women during this time often wore long dresses, their hair long, and wore jewelry, most notably beads.[146] Mycenaean beads have long been an aspect of Mycenaean culture that is shrouded in a significant amount of mystery. It is not known for certain why they (men, women, and children) wore them, or why they appear to have been significant to the culture, but beads made of carnelian, lapis lazuli, etc., were known to have been worn by women on bracelets, necklaces, and buttons on cloaks, and were often buried with the deceased.[147]
In later periods of Greek history, seclusion of females from males was common in the household, though scholars have found no evidence of seclusion during Mycenaean times, and believe that males and females worked with and around each other on a regular basis. Not much is known about women's duties in the home or whether they differed from the duties of men. And though men were involved in warfare and hunting, there is no evidence that suggests women ever took part in either of the two, though whether women took part in hunting has been up for debate amongst some historians. There is evidence that, in this patriarchal society, men and women were, in some respects, viewed equally. Mycenae practiced a system of rationing food to citizens, and evidence shows that women received the same amount of rations as men.[146]
If women were not officials in the cult or married to high-ranking male officers, they were likely low-ranking laborers. Linear B details specialized groups of female laborers called "workgroups". These women labored with other women as well as their children, and usually were located close to the palace. Women who belonged to workgroups did not belong to independent households, but were managed and fed by palace scribes. All of the women in a workgroup would serve the same occupation, such as textiles. Women in workgroups are not believed to have been able to acquire land holdings or have had economic independence of any kind, and are believed by some to have been slaves, though there are some conflicting debates among scholars concerning this. Though scholars are unsure if ordinary women could obtain land and exert economic power, there is evidence that women could obtain positions of power, such as the title of priestess, which allowed them to have land holdings, have elite connections, and high social status. Mycenaean society is believed to have been largely patriarchal, but women could exert social and economic power through titles and positions of power, like that of a priestess, though religion was not the only place that a woman could gain social authority.[150] Women with special talents or skills, such as being a skilled midwife or craftswomen, could gain social authority in their villages, but are not believed to have been able to receive land holdings. Elite women (those who were married to male elites) were afforded benefits fitting their high social standing, but even the wife of elites could not own land and had no economic independence.[151] Some scholars believe that Knossos was probably more equal in relation to gender than Pylos, though the evidence for this is little and is highly disputed.[152]
Religion
editMen and women alike were involved in cult activity. Some women could be elevated to becoming legally independent by becoming priestesses, which appears to be hereditary through both the male and female line. No woman in Mycenae is believed to have been able to "own" land at this time, but priestesses were women who could legally procure land. Through the cult, land was "leased" to them, rather than given to them in ownership. Along with land holding benefits, priestesses often had ties with the upper-class elites, and were usually wealthy themselves.[150] Only a small number of women could become priestesses in Mycenae, but there were other cultic titles that women could aspire to obtain, such as that of Key-bearer. Key-bearers appear to be women who had authority over the sacred treasury of a particular deity, and were able to dispense it in times of need. Though scholars do not have enough evidence to suggest that all Key-bearers could own land and had high status, there is a written record in Linear B of a Key-bearer with elite ties who owned land, so it is possible that they had similar benefits to priestesses. Other religious roles filled by women were the three types of sacred slaves: slave of the God, slave of the Priestess, and slave of the Key-bearer. Though not as grand a title as that of Priestess of Key-Bearer, the sacred slaves were allotted certain benefits fitting their positions in the cult. One other documented position women filled in the cult was called ki-ri-te-wi-ja. Though documented, scholars are not certain exactly what the duties of this role entailed, or what type of women would have filled it. What they do know, however, is that these religious roles afforded the women who occupied them a certain amount of economic autonomy.[151]
Architecture
editPalaces
editThe palatial structures at Mycenae, Tiryns and Pylos were erected on the summits of hills or rocky outcrops, dominating the immediate surroundings.[153] The best preserved are found in Pylos and Tiryns, while Mycenae and the Menelaion are only partially preserved. In Central Greece, Thebes and Orchomenos have been only partially exposed. On the other hand, the palace built at the acropolis of Athens has been almost completely destroyed. A substantial building at Dimini in Thessaly, possibly ancient Iolcos,[154] is believed by a number of archaeologists to be a palace.[153] A Mycenaean palace has been also unearthed in Laconia, near the modern village of Xirokambi.[155]
The palatial structures of mainland Greece share a number of common features.[156] The focal point of the socio-political aspect of a Mycenaean palace was the megaron, the throne room.[153] It was laid out around a circular hearth surrounded by four columns. The throne was generally found on the right-hand side upon entering the room, while the interior of the megaron was lavishly decorated, flaunting images designed intentionally to demonstrate the political and religious power of the ruler.[157] Access to the megaron was provided through a court, which was reached from a propylon.[156] The iconography of the palatial chambers is remarkably uniform throughout Greece. For instance, in Pylos and Tiryns the paintings are focused on marine motifs, providing depictions of octopodes, fish and dolphins.[158] Around the megaron a group of courtyards each opened upon several rooms of different dimensions, such as storerooms and workshops, as well as reception halls and living quarters.[156] In general Mycenaean palaces have yielded a wealth of artifacts and fragmentary frescoes.[156]
Additional common features are shared by the palaces of Pylos, Mycenae and Tiryns;[156] a large court with colonnades lies directly in front of the central megaron,[159] while a second, but smaller, megaron is also found inside these structures.[156] The staircases in the palace of Pylos indicate that the palaces had two stories.[160] The private quarters of the members of the royal family were presumably located on the first floor.[161]
Fortifications
editThe construction of defensive structures was closely linked to the establishment of the palaces in mainland Greece. The principal Mycenaean centers were well-fortified and usually situated on an elevated terrain, like on the Acropolis of Athens, Tiryns and Mycenae or on coastal plains, in the case of Gla.[162] Mycenaean Greeks in general appreciated the symbolism of war as expressed in defensive architecture, reflected by the visual impressiveness of their fortifications.[162]
Cyclopean is the term normally applied to the masonry characteristics of Mycenaean fortification systems and describes walls built of large, unworked boulders more than 8 m (26 ft) thick and weighing several metric tonnes.[163] They were roughly fitted together without the use of mortar or clay to bind them, though smaller hunks of limestone fill the interstices. Their placement formed a polygonal pattern giving the curtain wall an irregular but imposing appearance. At the top it would have been wide enough for a walkway with a narrow protective parapet on the outer edge and with hoop-like crenellations.[164] The term Cyclopean was derived by the latter Greeks of the Classical era who believed that only the mythical giants, the Cyclopes, could have constructed such megalithic structures.[162] On the other hand, cut stone masonry is used only in and around gateways. Another typical feature of Mycenaean megalithic construction was the use of a relieving triangle above a lintel block—an opening, often triangular, designed to reduce the weight over the lintel. The space was filled with some lighter stone.[164]
Cyclopean fortifications were typical of Mycenaean walls, especially at the citadels of Mycenae, Tiryns, Argos, Crisa and Athens, while smaller boulders are found in Midea and large limestone slabs are found at Gla.[164] In the Mycenaean settlements found in Epirus and Cyprus, Cyclopean-style walls are also present,[165][166] as well as in western Anatolia.[167] Besides the citadels, isolated forts were also erected on various strategic locations. The fortification systems also incorporated technical refinements such as secret cisterns, galleries, sally ports and projecting bastions for the protection of gateways.[162] On the other hand, the palace of Pylos, although a major center of power, paradoxically appears to have been left without any defensive walls.[168]
Other architectural features
editMycenaean domestic architecture originates mainly from earlier Middle Helladic traditions (c. 2000–1650 BC) both in shape, as well as in location of settlement. The observed uniformity in domestic architecture came probably as a result of a shared past among the communities of the Greek mainland rather than as a consequence of cultural expansion of the Mycenaean Koine.[50] Moreover, varying sizes of mudbricks were used in the construction of buildings.[156]
Contrary to popular belief, some Mycenaean representative buildings already featured roofs made of fired tiles, as in Gla and Midea.[169]
Warfare
editThe military nature of the Mycenaean Greeks is evident from the numerous weapons unearthed, the use of warrior and combat representations in contemporary art, and the preserved Greek Linear B records.[170][171] The Mycenaeans invested in the development of military infrastructure, with military production and logistics being supervised directly from the palatial centers.[171][172] According to the Linear B records in the palace of Pylos, every rural community (the damos) was obliged to supply a certain number of men who had to serve in the army. Similar service was also performed by the aristocracy.[173]
Mycenaean armies were initially based on heavy infantry, equipped with spears, large shields and on some occasions, armor.[174] Later in the 13th century BC, Mycenaean warfare underwent major changes both in tactics and weaponry and armed units became more uniform and flexible, while weapons became smaller and lighter.[171] The spear remained the main weapon among Mycenaean warriors, while the sword played a secondary role in combat.[175] Other offensive weapons used were bows, maces, axes, slings and javelins.[175][176] The precise role and contribution of chariots on the battlefield is a matter of dispute due to the lack of sufficient evidence.[177] It appears that chariots were initially used as fighting vehicles during the 16th to 14th centuries BC, while later, in the 13th century BC, their role was limited to battlefield transport.[178]
The boar's tusk helmet was the most identifiable piece of Mycenaean armor in use from the beginning to the collapse of Mycenaean culture. It is also known from several depictions in contemporary art in Greece and the Mediterranean.[179][180] A representative piece of Mycenaean armor is the Dendra panoply (c. 1450–1400 BC) which consisted of a cuirass of a complete set of armor made up of several elements of bronze.[181] In general, most features of the later hoplite panoply of classical Greek antiquity, were already known to Mycenaean Greece.[182] "Figure-of-eight" shields were the most common type of Mycenaean shields.[183] During the Late Mycenaean period, smaller types of shields were adopted, either of completely circular shape, or almost circular with a part cut out from their lower edge.[184]
Art and pottery
editMost of the finest Mycenaean art comes under the immediate suspicion of either being Minoan art actually imported from Crete, or produced on the mainland by Cretan or Cretan-trained artists. This is less true of pottery, although the (very untypical) Mycenaean palace amphora with octopus (NAMA 6725) clearly derives directly from the Minoan "Marine Style", and it ceases to be the case after about 1350 BC. Some works appear to have subjects adjusted to warlike Mycenaean tastes, although the distinctively Minoan subject of bull-leaping also appears. The production of luxury art for, and probably often in, the Minoan palaces was already a well-established tradition when Mycenaean elites became customers, and was perhaps more integrated into Minoan religion and culture than it ever became in Mycenaean Greece.[185]
Metalwork
editSeveral important pieces in gold and other metals come from the Gold grave goods at Grave Circles A and B at Mycenae, including the Mask of Agamemnon, Silver Siege Rhyton, Bulls-head rhyton, and gold Nestor's Cup. The chemical compositions of the silver objects indicate that the silver was sourced from several locations.[186] The Theseus Ring, found in Athens, is one of the finest of a number of gold signet rings with tiny multi-figure scenes of high quality, many from the princely Grave Circles A and B at Mycenae. These tend to be regarded as Cretan, as do the carved gemstones also found in elite graves. Though they collected them, the Mycenaean elite did not apparently use Minoan seals for authenticating anything, but treated them as ornaments, at least one prince wearing a collection around his wrists, like modern charm bracelets. Sinclair Hood believed that at the time of the Vaphio burial (c. 1500–1450) "it was broadly speaking possible to classify the finer seals as being of Cretan, the more crudely engraved of mainland manufacture", but that "this criterion no longer applies after the mainland conquest of Crete c. 1450".[187]
Vessels
editDuring the Late Mycenaean period (1400–1200 BC), Mycenaean vessels/pottery exhibited similarities spanning a significant area of the Eastern Mediterranean (i.e., from the Levant to Sicily) and possibly reflecting a form of economic and political union centered at Mycenae.[188] However, the Minoan pottery of Crete during this time remained distinct indicating a degree of autonomy on the island.[188] The Mycenaean Greeks produced in large quantities a variety of diversely-styled vessels such as stirrup jars, large bowls, alabastron, krater and stemmed cups (or kylikes) resembling champagne glasses.[188]
Stirrup jars (Linear B: ka-ra-re-u, khlareus; "oil vessel"), specifically, were first invented on the island of Crete during the 16th century BC and used widely by the Mycenaeans from 1400 BC onward for transporting and storing wine and oil; the jars were usually pear-shaped or globular. As for stemmed cups (or kylikes), they evolved from Ephyraean goblets and a large quantity was discovered at a site called the "Potter's Shop" located in Zygouries. Mycenaean drinking vessels such as the stemmed cups contained single decorative motifs such as a shell, an octopus or a flower painted on the side facing away from the drinker.[188] The Mycenaean Greeks also painted entire scenes (called "Pictorial Style") on their vessels depicting warriors, chariots, horses and deities reminiscent of events described in Homer's Iliad.[189] Other items developed by the Mycenaeans include clay lamps,[190] as well as metallic vessels such as bronze tripod cauldrons (or basins).[191] A few examples of vessels in faience and ivory are also known.[192]
Figures and figurines
editThe Mycenaean period has not yielded sculpture of any great size. The statuary of the period consists for the most part of small terracotta figurines found at almost every Mycenaean site in mainland Greece—in tombs, in settlement debris, and occasionally in cult contexts (Tiryns, Agios Konstantinos on Methana). The majority of these figurines are female and anthropomorphic or zoomorphic.
The female figurines can be subdivided into three groups, which were popular at different periods: the Psi and phi type figurines, and the Tau-type. The earliest are the Phi-type, which look like the Greek letter Phi (their arms give the upper body a rounded shape). The Psi-type looks like the letter Psi (these have outstretched upraised arms). The latest (12th century BC) are the Tau-type; these figurines look like the Greek letter Tau (with folded arms at right angles to the body). Most figurines wear a large polos.[193] They are painted with stripes or zigzags in the same manner as the contemporary pottery and presumably made by the same potters. Their purpose is uncertain, but they may have served as both votive objects and toys: some are found in children's graves but the vast majority of fragments are from domestic rubbish deposits.[194]
The presence of many of these figurines on sites where worship took place in the Archaic and Classical periods (approximately 200 below the sanctuary of Athena at Delphi, others at the temple of Aphaea on Aegina, at the sanctuary of Apollo Maleatas above Epidauros and at Amyclae near Sparta), suggests both that many were indeed religious in nature, perhaps as votives, but also that later places of worship may well have first been used in the Mycenaean period.[195]
Larger male, female or bovine terracotta wheelmade figures are much rarer. An important group was found in the Temple at Mycenae together with coiled clay snakes,[196] while others have been found at Tiryns and in the East and West Shrines at Phylakopi on the island of Melos.[197]
Frescoes
editThe painting of the Mycenaean age was much influenced by that of Minoan painting, and was probably at least initially by Cretan painters. Their style gradually drifts away from that of Crete, and in late periods greatly reduces in quality. Fragments of wall paintings have been found in or around the palaces (Pylos, Mycenae, Tiryns) and in domestic contexts (Zygouries).[198] The largest complete wall painting depicting three female figures, probably goddesses, was found in the so-called "cult center" at Mycenae.[199] Various subjects are represented: hunting, bull leaping (tauromachy), battle scenes, processions, etc. Some scenes may be part of mythological narratives, but if so their meaning eludes us. Other frescoes include geometric or stylised motifs, also used on painted pottery (see above).[citation needed]
Burial practices
editThe usual form of burial during this period was inhumation (burial in the earth, covered by dirt and stones).[200] The earliest Mycenaean burials were mostly in individual graves in the form of a pit or a stone-lined cist and offerings were limited to pottery and occasional items of jewellery.[201] Groups of pit or cist graves containing elite members of the community were sometimes covered by a tumulus (mound) in the manner established since the Middle Helladic.[202] It has been argued that this form dates back to the Kurgan culture;[203] however, Mycenaean burials are in actuality an indigenous development of mainland Greece with the Shaft Graves housing native rulers.[204] Pit and cist graves remained in use for single burials throughout the Mycenaean period alongside more elaborate family graves.[205] The shaft graves at Mycenae within Grave Circles A and B belonging to the same period represent an alternative manner of grouping elite burials. Next to the deceased were found full sets of weapons, ornate staffs as well as gold and silver cups and other valuable objects which point to their social rank.[206]
Beginning also in the Late Helladic period are to be seen communal tombs of rectangular form. Nevertheless, it is difficult to establish whether the different forms of burial represent a social hierarchization, as was formerly thought, with the "tholos" being the tombs of the elite rulers, the individual tombs those of the leisure class, and the communal tombs those of the people. Cremations increased in number over the course of the period, becoming quite numerous in the last phase of the Mycenaean era.[207] The tholos was introduced during the early 15th century BC as the new and more imposing form of elite burial.[208] The most impressive tombs of the Mycenaean era are the monumental royal tombs of Mycenae, undoubtedly intended for the royal family of the city. The most famous is the Treasury of Atreus, a tholos. A total of nine of such tholos tombs are found in the region of Mycenae, while six of them belong to a single period (Late Helladic IIA, c. 1400–1300 BC).[209] It has been argued that different dynasties or factions may have competed through conspicuous burial.[210]
Cuisine
editWith respect to Mycenaean cuisine, skewer trays were discovered in Gla, Mycenae, and Pylos.[211] The so-called "souvlaki trays" (or portable grills) used by the Mycenaean Greeks were rectangular ceramic pans that sat underneath skewers of meat.[211] It is not clear whether these trays would have been placed directly over a fire or if the pans would have held hot coals like a portable barbecue pit.[211][212]
Writing
editIn c. 1600 BC, the Mycenaean Greeks borrowed from the Minoan civilization its syllabic writing system (i.e., Linear A) and developed their own syllabic script known as Linear B.[213] The Linear B script was utilized by the Mycenaean palaces in Greece for administrative purposes where economic transactions were recorded on clay tablets and some pottery in the Mycenaean dialect of the Greek language.[213] The Linear B tablets were first discovered in Crete by English archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans c. 1900 and later deciphered by English architect and cryptographer Michael Ventris in 1952.[214][215] Ventris's discovery of an archaic Greek dialect in the Linear B tablets demonstrated that Mycenaean Greek was "the oldest known Greek dialect, elements of which survived in Homer's language as a result of a long oral tradition of epic poetry."[213] The written records of every Mycenaean region were similar but the scribes sometimes used words that were probably part of their local dialect. The existence of a common language is probably explained by their shared bureaucratic system and writing script.[216]
Legacy
editIn the 8th century BC, after the end of the so-called Greek Dark Ages, Greece emerged with a network of myths and legends, the greatest of all being that of the Trojan Epic Cycle.[217] In general, the Greeks of Classical antiquity idealized the Mycenaean period as a glorious period of heroes, closeness of the gods and material wealth.[218] The legends of Homer's Epics were especially and generally accepted as part of the Greek past and it was not until the 19th century that scholars began to question Homer's historicity.[217] At this time, German archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann undertook the first modern archaeological excavations in Greece at the site of Mycenae in 1876.[219] Thus, Schliemann set out to prove the historical accuracy of the Iliad by identifying the places described by Homer.[217]
As part of the Mycenaean heritage that survived, the names of the gods and goddesses of Mycenaean Greece became major figures of the Olympian Pantheon of later antiquity.[220] Moreover, the language of the Mycenaeans offers the first written evidence of Greek,[221] while a significant part of the Mycenaean vocabulary can also be found in modern English.[222]
The Mycenaean Greeks were also pioneers in the field of engineering, launching large-scale projects unmatched in Europe until the Roman period, such as fortifications, bridges, culverts, aqueducts, dams and roads suitable for wheeled traffic. They also made several architectural innovations, such as the relieving triangle.[223] They were also responsible for transmitting a wide range of arts and crafts, especially of Minoan origin. The Mycenaean civilization was in general more advanced compared to the Late Bronze Age cultures of the rest of Europe.[224] Several Mycenaean attributes and achievements were borrowed or held in high regard in later periods, so it would be no exaggeration to consider Mycenaean Greece as a cradle of civilization.[223]
There are scholars who identify the Sea Peoples who migrated to the Near East as Mycenaean Greeks.[225][226] In a 2020 study by Polish historian Łukasz Niesiołowski-Spanò, a group of people known from the Bible – the Levites – were linguistically identified with the Greek term *la-wo (in later Greek laoi) – "the people" or "armed men".[227] Niesiołowski-Spanò concluded that the Levites were a group of Mycenaean Greek mercenaries who managed to settle down in Canaan and integrate with the local population, preserving their own group name.[227]
Genetic and anthropometric studies
editA cephalometric analysis by Argyropoulos et al. (1989) published in The Angle Orthodontist showed remarkable similarity in craniofacial morphology between ancient Greeks (including Mycenaeans) and modern Greeks, suggesting a close affinity, and that the Greek ethnic group remained stable in its cephalic and facial morphology for the last 4,000 years.[228]
A craniofacial morphological study by Papagrigorakis et al. (2014) published in Anthropologischer Anzeiger also indicated craniological similarities between modern Greeks and ancient Greeks (including Mycenaeans), indicating continuity.[229]
In an archaeogenetic study published in Nature, Lazaridis et al. (2017) found that Minoans and Mycenaean Greeks were genetically highly similar, but not identical; modern Greeks resembled the Mycenaeans, but with some additional dilution of the early Neolithic ancestry. Furthermore, proposed migrations by Egyptian or Phoenician colonists was not discernible in their data, thus "rejecting the hypothesis that the cultures of the Aegean were seeded by migrants from the old civilizations of these regions." The FST between the sampled Bronze Age populations and present-day West Eurasians was estimated, finding that Mycenaean Greeks and Minoans were least differentiated from the populations of modern Greece, Cyprus, Albania, and Italy.[230][231][232][233]
A genetic study by Clemente et al. (2021) found that in the Early Bronze Age, the populations of the Minoan, Helladic, and Cycladic civilizations in the Aegean, were genetically homogeneous. In contrast, during the Middle Bronze Age, this population was more differentiated; probably due to gene flow from a Yamnaya-related population from the Pontic–Caspian steppe. This is corroborated by sequenced genomes of Middle Bronze Age individuals from northern Greece, who had a much higher proportion of steppe-related ancestry; the timing of this gene flow was estimated at 2,300 BCE, and is consistent with the dominant linguistic theories explaining the emergence of the Proto-Greek language. Present-day Greeks share about 90% of their ancestry with them, suggesting continuity between the two time periods. In the case of Mycenaeans however, this steppe-related ancestry was diluted. The ancestry of the Mycenaeans could be explained via a 2-way admixture model of such MBA individuals in northern Greece, and either an EBA Aegean or MBA Minoan population.[234]
A study by Lazaridis et al. (2022) analysed 21 new Mycenaean samples and one new Minoan sample, along with previously published samples. The study found that Mycenaeans were differentiated from Minoans by an influx of western steppe (Yamnaya-like) ancestry, with Mycenaean samples having approximately 8.6±2% steppe/Yamnaya-like ancestry on average, comprising 4.3±1% Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) ancestry on average and an approximately matching amount of Caucasus hunter-gatherer ancestry (4.3±1% on average), though some of the Mycenaeans lacked steppe ancestry altogether.[235][236] Individual Mycenaean samples from mainland Greece had proportions of EHG ancestry ranging from 0% up to 19±7% at Kastrouli, or 12±2% at the Palace of Nestor.[237][238] Another Mycenaean individual from Crete, dating from c. 1370 – c. 1340 BC (Crete Armenoi) had 24±6% EHG ancestry.[238] The remaining (non steppe-related) Mycenaean ancestry was similar to that of the Minoans and the Early Bronze Age population of mainland Greece, and elite Mycenaean samples (from the Palace of Nestor at Pylos and its environs) did not differ from the general population in terms of their average ancestral composition.[238] According to Lazaridis et al. these results strongly support the hypothesis that Mycenaeans were the outcome of admixture between descendants of Yamnaya-like steppe migrants and a Minoan-like population,[235] with steppe migrants considered to be Indo-European speakers and progenitors of the Greek language.[236] Minoans were predominantly of Early European Farmer ancestry (74±3% on average), with additional Caucasus Hunter-Gatherer ancestry (18.2±1.2% on average). Lazaridis et al. also identified Levant Pre-Pottery Neolithic ancestry in some Minoan and Mycenaean individuals.[238]
In a comment on the study by Lazaridis et al. (2022), Paul Heggarty of the Max Planck Institute expressed doubts regarding the connection between the "small contribution in Mycenaean Greece" of the "ancestral mix of Yamnaya culture" and the steppe as the "earliest, original source" of Indo-European languages.[239]
A study by Skourtanioti et al. (2023) generated genome-wide data from 95 Bronze Age individuals from mainland Greece and the Aegean, which was analysed in the context of all previously published samples from the region.[240] Mycenaean (Late Bronze Age) individuals were found to deviate from Early Bronze Age individuals in the direction of Central and Eastern European Bronze Age populations, due to having western steppe-related ancestry not found in the earlier samples. The potential source of this ancestry included related groups from Serbia (Early Bronze Age), Croatia (Middle Bronze Age), Italy (Early and Middle Bronze Age), 'Western Steppe Eneolithic-Bronze Age', and 'Germany Corded Ware'; the latter two were found to be the most adequate sources, but "at the moment it is not possible to more closely identify the region(s) from where this genetic affinity was derived." Using 'Germany Corded Ware' as a source proxy, it was estimated that Mycenaeans from the southern Greek mainland had 22.3% steppe-related ancestry on average, whereas Late Bronze Age individuals from nearby islands and the Cyclades had slightly lower amounts of this ancestry, and one individual from the island of Salamis had none; in Crete, samples dating from the 17th to the 16th centuries BC had minimal or no such steppe-related ancestry, whereas later samples dating from c. 1300 BC varied from 0% to approximately 40% steppe-related ancestry.[241] This influx of steppe-related ancestry was related to Mycenaean domination of the island from the 15th century BC onwards, and was possibly also due in part to later migrations from more distant areas such as Italy.[242]
| Date | Location | Sex | mtDNA[a] | Y-DNA[b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 1700 – c. 1450 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | T2b | CT |
| c. 1700 – c. 1200 BC | Apatheia Galatas, Peloponnese | Male | X2 | J2a1 |
| c. 1700 – c. 1200 BC | Apatheia Galatas, Peloponnese | Female | X2 | – |
| c. 1626 – c. 1518 BC | Mygdalia, Achaea, Peloponnese | Female | H26b | – |
| c. 1626 – c. 1508 BC | Lazarides, Aegina | Female | T1a5 | – |
| c. 1613 – c. 1503 BC | Proskynas, Phthiotis | Male | ? | J |
| c. 1612 – c. 1452 BC | Mygdalia, Achaea, Peloponnese | Male | T1a4 | J2b2a1 |
| c. 1611 – c. 1457 BC | Mygdalia, Achaea, Peloponnese | Male | K1a | J2b2a1 |
| c. 1611 – c. 1452 BC | Mygdalia, Achaea, Peloponnese | Male | K1a | J2b2a1 |
| c. 1610 – c. 1448 BC | Kolikrepi-Spata, Attica | Female | T2c1+146 | – |
| c. 1609 – c. 1446 BC | Mygdalia, Achaea, Peloponnese | Male | U8b1a2b | G2a2a1 |
| c. 1596 – c. 1438 BC | Mygdalia, Achaea, Peloponnese | Female | U3c | – |
| c. 1520 – c. 1440 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Male | ? | F |
| c. 1516 – c. 1436 BC | Kolikrepi-Spata, Attica | Female | HV | – |
| c. 1505 – c. 1429 BC | Kolikrepi-Spata, Attica | Female | HV0a | – |
| c. 1504 – c. 1425 BC | Mygdalia, Achaea, Peloponnese | Male | U8b1a2b | J2b2a1 |
| c. 1500 BC | Aidonia, Corinthia, Peloponnese | Male | R0a1a | C1a2 |
| c. 1500 BC | Aidonia, Corinthia, Peloponnese | Female | K1a2c | – |
| c. 1497 – c. 1316 BC | Kolikrepi-Spata, Attica | Male | H5 | J2a1a2b2a2b2~ |
| c. 1440 – c. 1299 BC | Tiryns, Argolid, Peloponnese | Male | W1h1 | J2a1a1a2 |
| c. 1429 – c. 1293 BC | Glyka Nera, Attica | Male | ? | R1b1a1b |
| c. 1424 – c. 1293 BC | Lazarides, Aegina | Male | H | G2a |
| c. 1421 – c. 1313 BC | Glyka Nera, Attica | Male | U3c | J2a1a |
| c. 1416 – c. 1280 BC | Peristeria Tryfilia, Peloponnese | Female | H | – |
| c. 1411 – c. 1262 BC | Agia Kyriaki, Salamis | Female | X2d | – |
| c. 1410 – c. 1360 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Female | J1c1 | – |
| c. 1403 – c. 1233 BC | Lazarides, Aegina | Female | K2a2a | – |
| c. 1403 – c. 1229 BC | Tiryns, Argolid, Peloponnese | Male | H13a2a | J2a |
| c. 1400 – c. 1300 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | H41a | – |
| c. 1400 – c. 1300 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | K1a+195 | J2a1a1a2 |
| c. 1400 – c. 1300 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | N1a1b | – |
| c. 1400 – c. 1300 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | ? | G2 |
| c. 1400 – c. 1300 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | H4a1 | – |
| c. 1397 – c. 1222 BC | Kastrouli-Desfina, Phokis | Female | K1a2 | – |
| c. 1394 – c. 1222 BC | Tiryns, Argolid, Peloponnese | Female | V | – |
| c. 1386 – c. 1217 BC | Kastrouli-Desfina, Phokis | Male | H2 | G2a2b |
| c. 1382 – c. 1134 BC | Kastrouli-Desfina, Phokis | Male | W1 | J2a1a2b2a2b2~ |
| c. 1375 BC | Aidonia, Corinthia, Peloponnese | Female | U5a1d2b | – |
| c. 1375 – c. 1200 BC | Aidonia, Corinthia, Peloponnese | Male | N1b1a2 | J2a |
| c. 1375 – c. 1200 BC | Aidonia, Corinthia, Peloponnese | Male | N1b1a2 | J2a2~ |
| c. 1375 – c. 1200 BC | Aidonia, Corinthia, Peloponnese | Male | ? | R1b1a1b |
| c. 1371 – c. 1123 BC | Kastrouli-Desfina, Phokis | Male | K2b | G |
| c. 1367 – c. 1112 BC | Kastrouli-Desfina, Phokis | Female | U3b1b | – |
| c. 1360 – c. 1295 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Male | H7 | G |
| c. 1360 – c. 1295 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Male | ? | G2a2a1a2a1a1 |
| c. 1360 – c. 1295 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Female | J1c+16261 | – |
| c. 1360 – c. 1070 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Female | K1c1 | – |
| c. 1350 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | W1h1 | – |
| c. 1350 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | ? | CT |
| c. 1350 – c. 1150 BC | Kastrouli-Desfina, Phokis | Male | T2c1d1 | G2a2b2b1a1a2 |
| c. 1350 – c. 1150 BC | Kastrouli-Desfina, Phokis | Female | U3b | – |
| c. 1350 – c. 1150 BC | Kastrouli-Desfina, Phokis | Female | U3b1 | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | H7c | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | H4a1 | E1b1b1a1b |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | H1bm | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | HV1a'b'c | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | H | J2a/J2a1a~ |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | J2b1 | R1b1a1b |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | K1a4b1 | J2a1a1a2 |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | N1'5 | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1250 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | HV1 | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | H1 | G2a2b2a |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | H1e | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | H1 | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | H1az | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | W6 | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | HV4a1+16291 | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | X2 | J2a |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Female | H1m | – |
| c. 1300 – c. 1200 BC | Chania, Crete | Male | J2b1 | G2a |
| c. 1200 – c. 1070 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Male | N1a1a1a3 | R1b1a1b2a |
| c. 1200 – c. 1070 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Male | ? | R1b1a1b |
| c. 1200 – c. 1070 BC | Palace of Nestor, Messenia, Peloponnese | Male | X | R1b1a1b |
| c. 1175 – c. 1150 BC | Koukounaries, Paros | Female | H5a2 | – |
| c. 1175 – c. 1150 BC | Koukounaries, Paros | Male | U1a1a | J1/J1b |
| c. 1175 – c. 1150 BC | Koukounaries, Paros | Female | J2b1b1 | – |
| c. 1175 – c. 1150 BC | Koukounaries, Paros | Female | H+16291 | – |
See also
editReferences
editCitations
edit- ^ a b c d e f g Knodell 2021, Table 1, pp. 7, 65.
- ^ a b c d e f g Lazaridis et al. 2017, Supplementary Information: pp. 2–3
- ^ a b c d e f Fields 2004, pp. 10–11.
- ^ "Mycenaean Civilization". World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
- ^ Hammond 1976, p. 139: "Moreover, in this area a small tholos-tomb with Mycenaean pottery of III B style and a Mycenaean acropolis have been reported at Kiperi near Parga, and another Mycenaean acropolis lay above the Oracle of the Dead on the hill called Xylokastro"; Tandy 2001, p. xii (Fig. 1); p. 2: "The strongest evidence for Mycenaean presence in Epirus is found in the coastal zone of the lower Acheron River, which in antiquity emptied into a bay on the Ionian coast known from ancient sources as Glykys Limin (Figure 2-A)."
- ^ Hatzopoulos 2011, p. 53: "There is one illusion that ought to be first dispelled—that Mt Olympus and the Kambounian mountains constituted an impassable barrier between Thessaly and Macedonia. In fact recent archaeological discoveries have established that already in the second millennium bc the Mycenaean world extended well beyond Thessaly and included at least the southern part of Macedonia. Abundant Mycenaean pottery, both imported and locally produced, weapons, pins, brooches and syllabic script have been found in tombs of Orestis, Elimeia and Pieria"; Borza 1992, p. 64: "The existence of a Late Bronze Age Mycenaean settlement in the Petra not only confirms its importance as a route from an early period, but also extends the limits of Mycenaean settlement to the Macedonian frontier."
- ^ a b Castleden 2005, p. 192.
- ^ van Wijngaarden 2002, Part III: Cyprus, pp. 125–202.
- ^ van Wijngaarden 2002, Part II: The Levant, pp. 31–124; Bietak & Czerny 2007, Sigrid Deger-Jalkotzy, "Mycenaeans and Philistines in the Levant", pp. 501–629.
- ^ Peruzzi 1980; van Wijngaarden 2002, Part IV: The Central Mediterranean, pp. 203–260.
- ^ Morris 1996, "Greece: Dark Age Greece", pp. 253–256.
- ^ The extent to which Homer attempted to or succeeded in recreating a "Mycenaean" setting is examined in Moses I. Finley, The World of Odysseus, 1954.
- ^ "The Bronze Age on the Greek Mainland: Early Bronze Age – Early Helladic I". Athens: Foundation of the Hellenic World. 1999–2000.
- ^ Chadwick 1976, p. 617.
- ^ Latacz 2004, pp. 159, 165, 208–209.
- ^ Latacz 2004, pp. 159, 165.
- ^ Beckwith 2009, p. 43.
- ^ a b Latacz 2004, p. 120.
- ^ Latacz 2004, p. 138.
- ^ Hajnal & Posch 2009, pp. 1–2.
- ^ a b Kelder 2010, pp. 46–47.
- ^ Kelder 2010, pp. 37–38; Latacz 2004, p. 159.
- ^ a b Beckman, Bryce & Cline 2012, p. 4.
- ^ Latacz 2004, p. 123.
- ^ Bryce 2005, p. 58.
- ^ Latacz 2004, p. 122.
- ^ Bryce 2005, p. 357.
- ^ Burns 2010, p. 92: "The most famous object from Shaft Grave V, if not all of Mycenaean Greece, is the gold mask popularly known as the 'mask of Agamemnon'."
- ^ Sergent 1982, p. 672.
- ^ Wright 2008, p. 230: "Scholars during much of the twentieth century CE argued for a break between the Early and Middle Bronze Ages, theorizing in particular the arrival of Indo-European speaking peoples at this time. Research in the past thirty years, though, shows that despite destruction and abandonment of some settlements after EH II and EH III, the transition between these periods shows many signs of continuity [...] Furthermore, the succeeding transition between EH III and MH I seems to have been less abrupt than previously thought, with evidence of continuity in some of the ceramics and lithic traditions at Lerna [...] Likewise, it was thought through the 1970s that the shaft graves at Mycenae announced a dramatic cultural change beginning in LH I (with some scholars even arguing that Indo-European Greek speakers arrived at this time), but this view no longer prevails. We often cannot distinguish MH III from LH I, and frequently refer to assemblages as MH III/LH I, because the society that was developing into what we commonly refer to as Mycenaean civilization had deep roots in the indigenous Middle Helladic cultural forms [...]"
- ^ a b Dickinson 1977, pp. 32, 53, 107–108; Dickinson 1999, pp. 97–107.
- ^ Littauer & Crouwel 1996, p. 299: "The Shaft Graves of Mycenae themselves do not mark a new dynasty imposed from outside, as Drews and other scholars would have it; nor do they represent a sudden clear break with the Middle Helladic past. The tombs indicate the rise of vigorous local chieftains who became a warrior élite."
- ^ a b c d Schofield 2006, p. 31.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 51.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 48.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 32.
- ^ Dickinson 1977, pp. 53, 107; Littauer & Crouwel 1996, pp. 297–305.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 67.
- ^ Schofield 2006, pp. 64–68.
- ^ Higgins, Reynold Alleyne (1997). Minoan and Mycenaean art. World of art (New rev. ed.). London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-20303-3.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 97; Schofield 2006, p. 55.
- ^ Tartaron 2013, p. 28.
- ^ a b c Schofield 2006, pp. 71–72.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 75.
- ^ a b c Kelder 2010, p. 8.
- ^ Tartaron 2013, p. 21.
- ^ Kelder 2010, pp. 50, 52.
- ^ a b Bryce 2005, p. 361.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 194: "The Mycenaean colonies in Anatolia were emphatically confined to a narrow coastal strip in the west. There were community-colonies at Ephesus, Iasos and Miletus, but they had little effect on the interior..."
- ^ a b Kelder 2010, p. 107.
- ^ Kelder 2010, pp. 108–109.
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 11; Fields 2004, p. 53.
- ^ a b c Beckman, Bryce & Cline 2012, p. 6.
- ^ Kelder 2010, pp. 119–120.
- ^ Bryce 2005, p. 59; Kelder 2010, p. 23.
- ^ Bryce 2005, pp. 129, 368.
- ^ Bryce 2005, p. 193.
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 26.
- ^ Bryce 2005, p. 58; Kelder 2010, pp. 119–120.
- ^ Bryce 2005, p. 224.
- ^ a b Kelder 2010, p. 27.
- ^ Bryce 2005, pp. 361, 364.
- ^ Bryce 2005, p. 290.
- ^ a b Kelder 2010, p. 34.
- ^ Millek, Jesse (2023). Destruction and Its Impact on Ancient Societies at the End of the Bronze Age. Lockwood Press. pp. 74–75, 139–142. ISBN 9781948488846.
- ^ a b Cline 2014, p. 130.
- ^ a b Castleden 2005, p. 219.
- ^ a b c d e f g Freeman 2014, p. 126.
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 33.
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 32.
- ^ Tartaron 2013, p. 20.
- ^ Hinzen, Klaus-G.; Maran, Joseph; Hinojosa-Prieto, Hector; Damm-Meinhardt, Ursula; Reamer, Sharon K.; Tzislakis, Jana; Kemna, Kilian; Schweppe, Gregor; Fleischer, Claus; Demakopoulou, Katie (27 March 2018). "Reassessing the Mycenaean Earthquake Hypothesis: Results of the HERACLES Project from Tiryns and Midea, Greece". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 108 (3A): 1046–1070. Bibcode:2018BuSSA.108.1046H. doi:10.1785/0120170348. ISSN 0037-1106.
- ^ Millek 2023, pp. 147–156.
- ^ Cline 2014, p. 129.
- ^ a b Tartaron 2013, p. 18.
- ^ Salavoura, Eleni (2021). "New opportunities in turbulent times: Attica in the 12th c. BC". EAA 2021, Widening Horizons, 8–11 September, Kiel.
- ^ Zeman, Piotr (2021). "Differing trajectories of collapse in the Late Bronze Age Argolid: Mycenae and Tiryns from 1250 BC to 1100 BC". EAA 2021, Widening Horizons, 8–11 September, Kiel.
- ^ Mylonas 1966, pp. 227–228.
- ^ Mylonas 1966, pp. 231–232.
- ^ Drews 1993, p. 49.
- ^ a b Tartaron 2013, p. 19.
- ^ Alexakha 2016, pp. 164–169.
- ^ Freeman 2014, p. 127.
- ^ a b Kelder 2010, p. 9.
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 97.
- ^ Kelder 2010, pp. 8–9.
- ^ Kelder 2010, pp. 45, 86, 107.
- ^ Kelder 2010, pp. 86–87.
- ^ Thomas 1995, p. 350.
- ^ a b c d e Chadwick 1976, Chapter 5: Social Structure and Administrative System, pp. 69–83.
- ^ a b Kelder 2010, p. 11.
- ^ Fields 2004, p. 57.
- ^ Chadwick 1976, pp. 71–72.
- ^ δῆμος. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; An Intermediate Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- ^ δοῦλος. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project
- ^ Olsen 2014, p. 7.
- ^ a b c Cline 2012, p. 145.
- ^ Cline 2012, p. 242.
- ^ a b Budin 2009, p. 94.
- ^ Chadwick 1976, p. 152.
- ^ Olsen 2014, p. 6.
- ^ Budin 2009, p. 96.
- ^ Tartaron 2013, p. 24.
- ^ a b c Kelder 2010, p. 116.
- ^ Gilstrap, William; Day, Peter; Kaza, Konstantina; Kardamaki, Elina (9 May 2013). Pottery Production at the Late Mycenaean site of Alimos, Attica. Materials and Industries in the Mycenaean World: Current Approaches to the Study of Materials and Industries in Prehistoric Greece, University of Nottingham, 9–10 May 2013 (PDF). Nottingham, UK. pp. 13–14.
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 117.
- ^ a b c Cline 2007, p. 200.
- ^ Stubbings 1951, IV: Mycenaean II Pottery in Syria and Palestine; V: Mycenaean III Pottery in Syria and Palestine.
- ^ Petrie 1894.
- ^ Cline 2012, pp. 300, 387, 787.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 107: "Huge quantities of olive oil were produced and it must have been a major source of wealth. The simple fact that southern Greece is far more suitable climatically for olive production may explain why the Mycenaean civilization made far greater advances in the south than in the north. The oil had a variety of uses, in cooking, as a dressing, as soap, as lamp oil, and as a base for manufacturing unguents."
- ^ Tartaron 2013, p. 29; Kling 1989; Nikolaou 1973; International Archaeological Symposium 1973.
- ^ Cline 2007, p. 197.
- ^ Cline 2007, p. 196.
- ^ Boston University – The Historical Society.
- ^ Tartaron 2013, p. 22; Feuer 2004, pp. 155–157; Balmuth & Tykot 1998, "The Mycenaeans in Sardinia", p. 400; Runnels & Murray 2001, p. 15.
- ^ Ridgway 1992, p. 4; Taylour 1958; Fisher 1998; Runnels & Murray 2001, p. 15; Vianello 2005, "Eastern Sicily and the Aeolian Islands", p. 51; Feuer 2004, pp. 155–157; van Wijngaarden 2002, Part IV: The Central Mediterranean, pp. 203–260.
- ^ de la Cruz 1988, pp. 77–92; Ridgway 1992, p. 3; Runnels & Murray 2001, p. 15.
- ^ Castleden 2005.
- ^ "Amber object bearing Linear B symbols" (in German). Freising. 1999. Archived from the original on 30 August 2016. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- ^ Budin 2009, p. 53: "One of the most extraordinary examples of the extent of Mycenaean influence was the Pelynt Dagger, a fragment of a Late Helladic III sword, which has come to light in the tomb of a Wessex chieftain in southern England!"
- ^ Feuer 2004, p. 259.
- ^ "Ancient Drug Trade Unearthed". CBS News. 7 August 2002. Retrieved 19 January 2021.
- ^ "Traces of opiates found in ancient Cypriot vessel". University of York. 3 October 2018. Retrieved 19 January 2021.
- ^ Cockburn, Harry (3 October 2018). "Bronze Age saw flourishing drug trade, opium discovered in ancient vase reveals". Independent. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 19 January 2021.
- ^ a b Kelder 2010, p. 115.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 146.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 157.
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 114.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 144.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 160.
- ^ Paul, Adams John (10 January 2010). "Mycenaean Divinities". Northridge, CA: California State University. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ^ a b c Castleden 2005, p. 143.
- ^ Nilsson 1940.
- ^ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 500–504; Chadwick 1976, p. 88: "Pa-ja-wo suggested Homeric Paieon, which earlier would have been Paiawon, later Paidn, an alternative name of Apollo, if not again a separate god."
- ^ a b c Chadwick 1976, p. 95
- ^ Chadwick 1976, pp. 95, 99.
- ^ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 565–568.
- ^ Chadwick 1976, p. 99.
- ^ Chadwick & Baumbach 1963, p. 176f.
- ^ Kn V 52 (text 208 in Ventris and Chadwick); Chadwick 1976, p. 88.
- ^ a b Mylonas 1966, p. 159.
- ^ Chadwick 1976, pp. 92–93.
- ^ Mylonas 1966, p. 159: "Wa-na-ssoi, wa-na-ka-te, (to the two queens and the king). Wanax is best suited to Poseidon, the special divinity of Pylos. The identity of the two divinities addressed as wanassoi, is uncertain."
- ^ Chadwick 1976, p. 76.
- ^ a b Whittaker von Hofsten 2007, pp. 3–18.
- ^ Hughes-Brock 1999, pp. 277–296.
- ^ Stocker & Davis 2017, pp. 588–589.
- ^ Evans 1930, pp. 502, 691.
- ^ a b Billigmeier & Turner 1981, pp. 3–20.
- ^ a b Olsen 2015, pp. 107–138.
- ^ Olsen 2014.
- ^ a b c Fields 2004, p. 19
- ^ Cline 2012, p. 485
- ^ Ταράντου, Σοφία (28 April 2009). "Βρήκαν μυκηναϊκό ανάκτορο". Ethnos.gr. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g Kelder 2010, p. 109
- ^ Fields 2004, p. 21
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 110
- ^ Fields 2004, p. 20.
- ^ Fields 2004, p. 45
- ^ Fields 2004, p. 46
- ^ a b c d Fields 2004, p. 10.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 78.
- ^ a b c Fields 2004, p. 11.
- ^ Tandy 2001, p. 20: "In LH IBBB (ca. 1310-1190), Mycenaean material culture spread widely throughout coastal and inland Epirus; in this period Mycenaean engagement in Epirus was strongest, both quantitatively and qualitatively. Though the Kiperi tholos may have gone out of use early in LH IIIB, the Cyclopean wall found there, as well as those at Ephyra, Kastriza, and Ayia Eleni, cannot have been built (and probably after) LH IIIB."
- ^ Iacovou 2013, p. 610. Iacovou quotes Vassos Karageorghis who states that "The introduction of 'Cyclopean'-type walls at the very beginning of the LC IIIA period at Enkomi, Kition, Sinda and Maa-Palaeokastron was due to the arrival of Mycenaean settlers in Cyprus."
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 127.
- ^ Fields 2004, p. 44.
- ^ Wikander 1990, p. 288; Shear 2000, p. 134.
- ^ Cline 2012, p. 305.
- ^ a b c Cline 2012, p. 313.
- ^ Palaima 1999, pp. 367–368.
- ^ D'Amato & Salimbeti 2011, p. 10.
- ^ Howard 2011, p. 7.
- ^ a b Howard 2011, p. 50.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 306; D'Amato & Salimbeti 2011, p. 13.
- ^ Howard 2011, p. 63.
- ^ Fields 2004, p. 22.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 119.
- ^ D'Amato & Salimbeti 2011, p. 23.
- ^ D'Amato & Salimbeti 2011, p. 27.
- ^ Kagan & Viggiano 2013, p. 36: "In fact, most of the essential items of the "hoplite panoply" were known to Mycenaean Greece, including the metallic helmet and the single thrusting spear."
- ^ D'Amato & Salimbeti 2011, p. 20.
- ^ Cline 2012, p. 312; Schofield 2006, p. 123.
- ^ Hood 1978, pp. 17–18, 23–24.
- ^ Wood, J. R.; Hsu, Y-T.; Bell, C. (2021). "Sending Laurion Back to the Future: Bronze Age Silver and the Source of Confusion". Internet Archaeology. 56 (9). doi:10.11141/ia.56.9. S2CID 236973111.
- ^ Hood 1978, pp. 227–228 (p. 228 quoted).
- ^ a b c d Castleden 2005, p. 135.
- ^ Castleden 2005, pp. 135–137: "Large kraters decorated in Pictorial Style are found almost exclusively in Cyprus, and for a long time it was naturally assumed that they were manufactured there, but a few examples have been found on the Greek mainland, mostly near Mycenae, and it has now been established that they were all manufactured at workshops close to Mycenae, probably at Berbati just to the east of the city, where there are the right clay sources. The ware was probably specifically made for export to Cyprus, where they were used as centerpieces for drinking ceremonies. The decoration appears to have been painted on at high speed and the effect is sometimes crude, Reynold Higgins calls it 'barbarous', which is a fair description, but the scenes showing warriors, horses and chariots can still tell us much about everyday life in Mycenaean Greece, and as much again about Mycenaean religious beliefs and mythology. One krater from Enkomi in Cyprus shows a charioteer with his groom riding along, perhaps into battle, while a long-robed god, Zeus perhaps, stands in his way holding the scales of destiny that will decide his fate. It is an archetypal scene reminiscent of several in the Iliad, where the gods are shown intervening in battle and deciding the outcome."
- ^ Furumark 1941, p. 78: "There are two types of Mycenaean lamps. One of these (type 321) has a broad horizontal lip with two opposite depressions for wicks. This type is the clay version of a Minoan stone lamp, known in many examples both from Crete and from the Mainland. The other (type 321 a) has one wick-spout and a handle at the opposite side."
- ^ Castleden 2005, pp. 56, 166.
- ^ Schofield 2006, p. 107.
- ^ French 1971, pp. 101–187.
- ^ See account of their use in K.A. and Diana Wardle "The Child's Cache at Assiros, Macedonia", in Sally Crawford and Gillian Shepherd (eds): Children, Childhood and Society: Institute for Archaeology and Antiquity Interdisciplinary Studies (Volume I) Oxford: Archaeopress, 2007.
- ^ Hägg & Marinatos 1981, Robin Hägg, "Official and Popular Cults in Mycenaean Greece", pp. 35–39
- ^ Moore, Taylour & French 1999
- ^ Renfrew, Mountjoy & Macfarlane 1985
- ^ Hood 1978, pp. 77–83; Immerwahr 1990.
- ^ Taylour 1969, pp. 91–97; Taylour 1970, pp. 270–280.
- ^ Cavanagh & Mee 1998.
- ^ Taylour, French & Wardle 2007; Alden 2000.
- ^ Pelon 1976.
- ^ Hammond 1967, p. 90.
- ^ Dickinson 1977, pp. 33–34, 53, 59–60.
- ^ Lewartowski 2000.
- ^ Dickinson 1977, pp. 53, 107; Anthony 2007, p. 48.
- ^ Papadimitriou 2001.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 97.
- ^ Kelder 2010, p. 95.
- ^ Graziado 1991, pp. 403–440.
- ^ a b c Hruby 2017, "Souvlaki trays", pp. 23–25.
- ^ Gannon, Megan (8 January 2014). "Ancient Greeks Used Portable Grills at Their Picnics". Live Science. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ a b c "Linear A and Linear B". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- ^ "Sir Arthur Evans". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- ^ "Michael Ventris". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- ^ Gschnitzer, Fritz; Chaniotis, Angelos (May 2012). Ιστορία της Αρχαίας Ελληνικής Κοινωνίας (in Greek). National Bank of Greece Cultural Foundation. p. 43. ISBN 9789602504802.
- ^ a b c Castleden 2005, p. 2.
- ^ Hansen 2004, p. 7.
- ^ Sansone 2004, "Greece in the Bronze Age", pp. 7–8.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 235.
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 228.
- ^ Vallance, Richard (2015). "Did you Know you Speak Mycenaean Greek? You do!". academia.edu. Retrieved 30 March 2016.
Whether we realize it or not, not only are tens of thousands of English words direct derivatives of ancient Greek, but some are derived even from Mycenaean Greek, which makes them very ancient indeed!
- ^ a b Castleden 2005, p. 231
- ^ Castleden 2005, p. 230.
- ^ Niesiołowski-Spano, Łukasz (2016). Goliath's Legacy. Philistines and Hebrews in Biblical Times. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag.
- ^ Yasur-Landau, Asaf (2010). The Philistines and Aegean Migration at the End of the Late Bronze Age. Cambridge: CUP.
- ^ a b Niesiołowski-Spano, Łukasz (2020). "The Levites,*ra-wo,λᾶός/λαοί–A new proposal for lexical and historical relationship". Biblica. 101, 3 (3): 444–452. doi:10.2143/BIB.101.3.3288731.
- ^ Argyropoulos, E.; Sassouni, V.; Xeniotou, A. (1989). "A comparative cephalometric investigation of the Greek craniofacial pattern through 4,000 years". The Angle Orthodontist. 59 (3): 195–204. ISSN 0003-3219. PMID 2672905.
- ^ Papagrigorakis, Manolis J.; Kousoulis, Antonis A.; Synodinos, Philippos N. (1 June 2014). "Craniofacial morphology in ancient and modern Greeks through 4,000 years". Anthropologischer Anzeiger. 71 (3): 237–257. doi:10.1127/0003-5548/2014/0277. ISSN 0003-5548. PMID 25065118.
- ^ a b Lazaridis et al. 2017
- ^ "Ancient DNA analysis reveals Minoan and Mycenaean origins". phys.org. Retrieved 28 July 2021.
- ^ Gibbons, Ann (2 August 2017). "The Greeks really do have near-mythical origins, ancient DNA reveals". Science Magazine. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ Gannon, Megan (3 August 2017). "More than Myth: Ancient DNA Reveals Roots of 1st Greek Civilizations". LiveScience. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ Clemente et al. 2021
- ^ a b Lazaridis 2022a
- ^ a b Lazaridis et al. 2022b
- ^ Lazaridis 2022a, Fig. 1D
- ^ a b c d Lazaridis et al. 2022b, pp. 1–13, Supplementary Materials: pp. 233–241
- ^ Heggarty, Paul (2022). "Redefining Indo European Origins? [eLetter comment on Lazaridis et al. 2022 in Science: 'The genetic history of the Southern Arc: A bridge between West Asia and Europe']". Science.
- ^ Skourtanioti et al. 2023
- ^ Skourtanioti et al. 2023: "We found various sources ranging from East Europe, to Central and South Europe adequately fitting most models for the LBA Aegean groups. The smaller and heterogeneous sample of BA Bulgarian individuals or BA Sicily did not fit. Models with Serbia (EBA), Croatia (MBA) and Italy (EMBA) were adequate most of the time, while those with 'W. Eurasian Steppe En-BA' (En, Eneolithic) or some Central European source (for example, Germany LN-EBA 'Corded Ware') were adequate for all groups at the P ≥ 0.01 cutoff. Therefore, at the moment it is not possible to more closely identify the region(s) from where this genetic affinity was derived. Among the groups of the southern mainland, the estimated coefficients of the WES-related ancestry are overlapping (±1 s.e.) and average to 22.3% (Fig. 4a) ... Fig. 4 ... a, Estimated mean coefficient (coeff.) (±1 s.e.) of additional ancestry (WES-related) using as proxy a BA Central European population ('Germany LN-EBA Corded Ware'). ..."
- ^ Skourtanioti et al. 2023: "However, two-way models with all of the above sources as well as 'Mainland MLBA' fit the allele frequencies of all the LBA individuals from Crete ('Crete LBA'). This also applied when we modelled the two clusters from LBA Crete separately (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Table 9) but for the Crete LBA (group C) with high WES ancestry (individuals XAN030, KRO008, KRO009 and published Armenoi), just one source from 'Mainland MLBA' became adequate. ... A more direct demographic connection can be proposed regarding the LBA Cretan and Greek mainland populations. Following an horizon of destructions targeting palatial centres and elite symbols in Crete (Late Minoan IB), material culture, funerary architecture and burial practices are believed to express innovations with features traditionally ascribed to the Mycenaean culture. On these grounds, an invasion of the island by people from the Greek mainland (around fifteenth century BC) has been proposed but remains highly contested. While unable to settle this debate decisively, the genetic analyses demonstrate that Cretan populations at larger port cities biologically mixed with populations coming to the island during the course of a few centuries. The presence of individuals with some of the highest Western Eurasian Steppe-related ancestry proportions within the Late Bronze Age Aegean (Crete LBA group C), despite fitting with a scenario that the Greek mainland was the only source of incoming people, could also suggest that populations from more distant areas (for example, Italy) contributed to the Crete LBA transition, a possibility that is supported in the material culture as well."
- ^ Lazaridis et al. 2022b, Supplementary Materials: Data S1
- ^ Skourtanioti et al. 2023, Supplementary information: pp. 11–31, 39–61, Supplementary Table 2
Sources
edit- Alden, Maureen Joan (2000). Well Built Mycenae (Volume 7): The Prehistoric Cemetery – pre-Mycenaean and Early Mycenaean Graves. Oxford: Oxbow Books. ISBN 978-1-84-217018-2.
- Alexakha, Andrey (2016). "A Model of Social Progress". The Journal of European Economic History. 3: 137–209.
- Aydar, Erkan; ÇİNer, Attila; Ersoy, Orkun; ÉCochard, Emilie; Fouache, Eric G. (2021). "Volcanic ash and tsunami record of the Minoan Late Bronze Age Eruption (Santorini) in a distal setting, southwestern Turkey". Journal of Quaternary Science. 36 (4): 586–597. Bibcode:2021JQS....36..586A. doi:10.1002/jqs.3314. S2CID 235554972.
- Beckwith, Christopher I. (2009). Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present. Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-13589-2.
- Billigmeier, Jon-Christian; Turner, Judy A. (1981). "The socio-economic roles of women in Mycenaean Greece: A brief survey from evidence of the Linear B tablets". Women's Studies. 8 (1–2): 3–20. doi:10.1080/00497878.1981.9978529.
- Burns, Bryan E. (2010). Mycenaean Greece, Mediterranean Commerce and the Formation of Identity (1st ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521119542.
- D'Amato, Raphaelo; Salimbeti, Andrea (2011). Bronze Age Greek Warrior 1600–1100 BC. illustrated by Giuseppe Rava. Oxford, UK: Osprey Pub Co. ISBN 9781849081955.
- Balmuth, Miriam S.; Tykot, Robert H. (1998). Studies in Sardinian Archaeology, Volume 5. Ann Arbor, MI: Oxbow Books. ISBN 9781900188821.
- Bietak, Manfred; Czerny, Ernst (2007). The synchronisation of civilisations in the Eastern Mediterranean in the second millennium B.C. III : proceedings of the SCIEM 2000—2nd EuroConference, Vienna, 28th of May-1st of June 2003. Wien: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften. ISBN 978-3-7001-3527-2.
- Beckman, Gary M.; Bryce, Trevor R.; Cline, Eric H. (2012). "Writings from the Ancient World: The Ahhiyawa Texts" (PDF). Writings from the Ancient World. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature. ISSN 1570-7008.
- Borza, Eugene N. (1992). In the Shadow of Olympus: The Emergence of Macedon. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-00880-6.
- Bryce, Trevor (2005). The Kingdom of the Hittites (New ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199279081.
- Budin, Stephanie Lynn (2009) [2004]. The Ancient Greeks: An Introduction. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-537984-6.
- Castleden, Rodney (2005). The Mycenaeans. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-36336-5.
- Cavanagh, William G.; Mee, Christopher (1998). A Private Place: Death in Prehistoric Greece [SIMA 125]. Jonsered: Paul Aströms Förlag. ISBN 978-9-17-081178-4.
- Chadwick, John; Baumbach, Lydia (1963). "The Mycenaean Greek Vocabulary". Glotta. 41 (3/4): 157–271.
- Chadwick, John (1976). The Mycenaean World. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-29037-1.
- Clemente, Florian; Unterländer, Martina; Dolgova, Olga; Amorim, Carlos Eduardo G.; et al. (13 May 2021). "The genomic history of the Aegean palatial civilizations". Cell. 184 (10): 2565–2586.e21. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.039. ISSN 0092-8674. PMC 8127963. PMID 33930288.
- Cline, Eric H. (2007). "Rethinking Mycenaean International Trade with Egypt and the Near East". In Galaty, M.; Parkinson, W. (eds.). Rethinking Mycenaean Palaces II: Revised and Expanded Edition. Los Angeles, CA: Cotsen Institute of Archaeology. pp. 190–200.
- Cline, Eric H., ed. (2012). The Oxford Handbook of the Bronze Age Aegean. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-987360-9.
- Cline, Eric H. (2014). 1177 B.C. The Year Civilization Collapsed. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-40-084998-7.
- Coleman, John E. (2000). "An Archaeological Scenario for the "Coming of the Greeks" ca. 3200 B.C." The Journal of Indo-European Studies. 28 (1–2): 101–153.
- de la Cruz, José Clemente Martín (1988). "Mykenische Keramik aus Bronzezeitlichen Siedlungsschichten von Montoro am Guadalquivir". Madrider Mitteilungen (29): 77–92.
- Dickinson, Oliver (1977). The Origins of Mycenaean Civilization. Götenberg: Paul Aströms Förlag.
- Dickinson, Oliver (December 1999). "Invasion, Migration and the Shaft Graves". Bulletin of the Institute of Classical Studies. 43 (1): 97–107. doi:10.1111/j.2041-5370.1999.tb00480.x.
- Dickinson, Oliver (2006). The Aegean from Bronze Age to Iron Age: Continuity and Change between the Twelfth and Eighth Centuries BC. New York, NY: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-20-396836-9.
- Drews, Robert (1993). The End of the Bronze Age. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-69-102591-9.
- Evans, Arthur J. (1930). The Palace of Minos: A Comparative Account of the Successive Stages of the Early Cretan Civilization as Illustred by the Discoveries at Knossos (Band 3): The Great Transitional Age in the Northern and Eastern Sections of the Palace. London: Macmillan. doi:10.11588/DIGLIT.811.
- Feuer, Bryan Avery (2004). Mycenaean Civilization: An Annotated Bibliography through 2002. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company, Inc. ISBN 978-0-78-641748-3.
- Fields, Nic; illustrated by Donato Spedaliere (2004). Mycenaean Citadels c. 1350–1200 BC (3rd ed.). Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 9781841767628.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Fields, Nic; illustrated by Brian Delf (2006). Bronze Age War Chariots. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 9781841769448.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Finley, Moses I. (1954). The World of Odysseus. New York, NY: New York Review Books. ISBN 978-1-59-017017-5.
- Fisher, Elizabeth A. (1998). The Mycenaeans and Apulia. An Examination of Aegean Bronze Age Contacts with Apulia in Eastern Magna Grecia. Jonsered, Sweden: Astrom.
- Freeman, Charles (2014). Egypt, Greece and Rome: Civilizations of the Ancient Mediterranean (3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199651924.
- French, Elizabeth (1971). "The Development of Mycenaean Terracotta Figurines". The Annual of the British School at Athens. 66: 101–187. doi:10.1017/S0068245400019146. ISSN 0068-2454. JSTOR 30103231. S2CID 194064357.
- Furumark, Arne (1941). The Mycenaean Pottery: Analysis and Classification. Stockholm: Victor Pettersons Bokindustriaktiebolag.
- Graziado, Giampaolo (July 1991). "The Process of Social Stratification at Mycenae in the Shaft Grave Period: A Comparative Examination of the Evidence". American Journal of Archaeology. 95 (3): 403–440. doi:10.2307/505489. JSTOR 505489. S2CID 191350824.
- Hägg, Robin; Marinatos, Nannó (1981). Sanctuaries and Cults in the Aegean Bronze Age: Proceedings of the First International Symposium at the Swedish Institute in Athens, 12–13 May, 1980. Stockholm: Svenska Institutet i Athen. ISBN 978-9-18-508643-6.
- Hajnal, Ivo; Posch, Claudia (2009). "Graeco-Anatolian Contacts in the Mycenaean Period". Sprachwissenschaft Innsbruck Institut für Sprachen und Literaturen. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
- Hammond, Nicholas G.L. (1967). "Tumulus Burial in Albania, the Grave Circles of Mycenae, and the Indo-Europeans". Annual of the British School at Athens. 62: 77–105. doi:10.1017/S006824540001409X. S2CID 163130464.
- Hammond, Nicholas G.L. (1976). Migrations and Invasions in Greece and Adjacent Areas. Park Ridge, NJ: Noyes Press. ISBN 978-0-8155-5047-1.
- Hansen, William F. (2004). Handbook of Classical Mythology. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57-607226-4.
- Hatzopoulos, Miltiades (2011). "Macedonians and other Greeks". In Fox, Robin Lane (ed.). Brill's Companion to Ancient Macedon: Studies in the Archaeology and History of Macedon, 650 BC – 300 AD. BRILL. ISBN 978-90-04-20650-2.
- Hood, Sinclair (1978). The Arts in Prehistoric Greece. Harmondsworth: Penguin (Penguin/Yale History of Art). ISBN 0140561420.
- Howard, Dan (2011). Bronze Age Military Equipment. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Military. ISBN 9781848842939.
- Hruby, Julie (2017). "3 Finding haute cuisine: Identifying shifts in food styles from cooking vessels". In Hruby, Julie; Trusty, Debra (eds.). From Cooking Vessels to Cultural Practices in the Late Bronze Age Aegean. Oxford and Philadelphia: Oxbow Books. pp. 15–26. ISBN 9781785706325.
- Hughes-Brock, Helen (1999). "Mycenaean Beads: Gender and Social Contexts". Oxford Journal of Archaeology. 18 (3): 277–296. doi:10.1111/1468-0092.00084.
- Iacovou, Maria (2013). "Chapter Twenty-Two Aegean-Style Material Culture in Late Cypriot III: Minimal Evidence, Maximum Interpretation". In Killebrew, Ann E.; Lehmann, Gunnar (eds.). The Philistines and other "Sea Peoples" in Text and Archaeology. Atlanta, GA: Society of Biblical Literature. pp. 585–618. ISBN 978-1-58-983721-8.
- Immerwahr, Sara A. (1990). Aegean Painting in the Bronze Age. University Park: Pennsylvania State University Press. ISBN 978-0-27-100628-4.
- Kagan, Donald; Viggiano, Gregory F. (2013). Men of Bronze: Hoplite Warfare in Ancient Greece. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9781400846306.
- Kelder, Jorrit M. (2010). "The Kingdom of Mycenae: A Great Kingdom in the Late Bronze Age Aegean". CDL Press. Bethesda, MD. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- Kling, Barbara (1989). Mycenaean IIIC:1b and Related Pottery in Cyprus. Lund: P. Aströms Förlag. ISBN 978-9-18-609893-3.
- Knodell, Alex R. (2021). Societies in Transition in Early Greece: An Archaeological History. Oakland, CA: University of California Press. doi:10.1525/luminos.101. ISBN 978-0-520-38054-7.
- Latacz, Joachim (2004). Troy and Homer: Towards a Solution of an Old Mystery. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199263080.
- Lazaridis, Iosif; Mittnik, Alissa; Patterson, Nick; Mallick, Swapan; Rohland, Nadin; Pfrengle, Saskia; Furtwängler, Anja; Peltzer, Alexander; Posth, Cosimo; Vasilakis, Andonis; McGeorge, P. J. P.; Konsolaki-Yannopoulou, Eleni; Korres, George; Martlew, Holley; Michalodimitrakis, Manolis; Özsait, Mehmet; Özsait, Nesrin; Papathanasiou, Anastasia; Richards, Michael; Roodenberg, Songül Alpaslan; Tzedakis, Yannis; Arnott, Robert; Fernandes, Daniel M.; Hughey, Jeffery R.; Lotakis, Dimitra M.; Navas, Patrick A.; Maniatis, Yannis; Stamatoyannopoulos, John A.; Stewardson, Kristin; Stockhammer, Philipp; Pinhasi, Ron; Reich, David; Krause, Johannes; Stamatoyannopoulos, George (2017). "Genetic origins of the Minoans and Mycenaeans". Nature. 548 (7666): 214–218. Bibcode:2017Natur.548..214L. doi:10.1038/nature23310. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 5565772. PMID 28783727.
- Lazaridis, Iosif; et al. (2022a). "A genetic probe into the ancient and medieval history of Southern Europe and West Asia". Science. 377 (6609): 940–951. Bibcode:2022Sci...377..940L. doi:10.1126/science.abq0755. PMC 10019558. PMID 36007020.
- Lazaridis, Iosif; Alpaslan-Roodenberg, Songül; Acar, Ayşe; Açıkkol, Ayşen; et al. (2022b). "The genetic history of the Southern Arc: A bridge between West Asia and Europe". Science. 377 (6609): eabm4247. doi:10.1126/science.abm4247. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 10064553. PMID 36007055. S2CID 251843620.
- Skourtanioti, Eirini; Ringbauer, Harald; Gnecchi Ruscone, Guido Alberto; Bianco, Raffaela Angelina; et al. (16 January 2023). "Ancient DNA reveals admixture history and endogamy in the prehistoric Aegean". Nature Ecology and Evolution. 7 (2): 290–303. doi:10.1038/s41559-022-01952-3. ISSN 2397-334X. PMC 9911347. PMID 36646948. S2CID 255941038.
- Lewartowski, Kazimierz (2000). Late Helladic Simple Graves: A Study of Mycenaean Burial Customs (BAR International Series 878). Oxford: Archaeopress. ISBN 978-1-84-171079-2.
- Littauer, M.A.; Crouwel, J.H. (1996). "Robert Drews and the Role of Chariotry in Bronze Age Greece". Oxford Journal of Archaeology. 15 (3): 297–305. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0092.1996.tb00087.x. S2CID 154807613.
- Moore, A.D.; Taylour, W.D.; French, Elizabeth Bayard (1999). Well Built Mycenae (Volume 10): The Temple Complex. Warminster, England: Aris & Phillips. ISBN 978-1-84-217000-7.
- Morris, Ian (1996). "Greece: Dark Age Greece". In Fagan, Brian M. (ed.). The Oxford Companion to Archaeology. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 253–256. ISBN 9780195076189.
- Mylonas, George Emmanuel (1961). Eleusis and the Eleusinian Mysteries. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Mylonas, George Emmanuel (1966). Mycenae and the Mycenaean Age. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691035239.
- Nikolaou, Kyriakos (1973). The First Myceneans in Cyprus. Nicosia: Department of Antiquities, Cyprus.
- Nilsson, Martin Persson (1940). Greek Popular Religion. New York: Columbia University Press.
- Nilsson, Martin Persson (1967). Geschichte der Griechischen Religion (3rd ed.). Munich: C.H. Beck Verlag.
- Olsen, Barbara A. (2015). "The Worlds of Penelope: Women in the Mycenaean and Homeric Economies". Arethusa. 48 (2): 107–138. doi:10.1353/are.2015.0007. S2CID 161197955.
- Olsen, Barbara A. (2014). Women in Mycenaean Greece: The Linear B Tablets from Pylos and Knossos. Hoboken, NJ: Taylor and Francis. ISBN 978-1-31-774795-6.
- Palaima, Tom (1999). "Mycenaean Militarism from a Textual Perspective" (PDF). Polemos: Warfare in the Aegean Bronze Age (Aegaeum). 19: 367–378. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- Papadimitriou, Nikolas (2001). Built Chamber Tombs of Middle and Late Bronze Age Date in Mainland Greece and the Islands (BAR International Series 925). Oxford: John and Erica Hedges Ltd. and Archaeopress. ISBN 978-1-84-171170-6.
- Pelon, Olivier (1976). Tholoi, Tumuli et Cercles Funéraires. Paris: Diffusion de Boccard. ISBN 9782869583702.
- Peruzzi, Emilio (1980). Mycenaeans in Early Latium. Rome: Edizioni dell'Ateneo & Bizzarri.
- Petrie, Sir William Matthew Flinders (1894). Tell el-Amarna. London: Methuen & Co.
- Renfrew, Colin; Mountjoy, Penelope A.; Macfarlane, Callum (1985). The Archaeology of Cult: The Sanctuary at Phylakopi. London: British School of Archaeology at Athens. ISBN 978-0-50-096021-9.
- Ridgway, David (1992). The First Western Greeks. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-52-142164-5.
- Runnels, Curtis Neil; Murray, Priscilla (2001). Greece before History: An Archaeological Companion and Guide. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-4050-0.
- Rutter, Jeremy B. (1996). "Prehistoric Archaeology of the Aegean". Trustees of Dartmouth College and the Foundation of the Hellenic World. Archived from the original on 1 January 2009. Retrieved 15 April 2021.
- Sansone, David (2004). Ancient Greek Civilization. Malden (Massachusetts), Oxford (United Kingdom), Carlton (Victoria, Australia): Blackwell Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-0-631-23236-0.
- Sergent, Bernard (1982). "Penser — et mal penser — les Indo-Européens1 (Note critique)". Annales. Histoire, Sciences Sociales. 37 (4): 669–681. doi:10.3406/ahess.1982.282879. ISSN 0395-2649. S2CID 162244841.
- Shear, Ione Mylonas (January 2000). "Excavations on the Acropolis of Midea: Results of the Greek–Swedish Excavations under the Direction of Katie Demakopoulou and Paul Åström". American Journal of Archaeology. 104 (1): 133–134. doi:10.2307/506802. JSTOR 506802.
- Schofield, Louise (2006). The Mycenaeans. Los Angeles, CA: J. Paul Getty Museum. ISBN 9780892368679.
- Stocker, Sharon R.; Davis, Jack L. (2017). "The Combat Agate from the Grave of the Griffin Warrior at Pylos". Hesperia: The Journal of the American School of Classical Studies at Athens. 86 (4): 583–605. doi:10.2972/hesperia.86.4.0583. JSTOR 10.2972/hesperia.86.4.0583. S2CID 165510271.
- Stubbings, Frank H. (1951). Mycenaean Pottery from the Levant. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Tandy, David W. (2001). Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy. Montréal, Québec, Canada: Black Rose Books Limited. ISBN 978-1-55164-188-1.
- Tartaron, Thomas F. (2013). Maritime Networks in the Mycenaean World. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107067134.
- Taylour, Lord William; French, Elizabeth Bayard; Wardle, K.A. (2007). Well Built Mycenae (Volume 13): The Helleno-British Excavations within the Citadel at Mycenae 1959–1969. Warminster, England: Aris & Phillips. ISBN 978-1-84-217295-7.
- Taylour, Lord William (1969). "Mycenae, 1968". Antiquity. 43 (170): 91–97. doi:10.1017/S0003598X00040187. S2CID 246044998.
- Taylour, Lord William (1970). "New Light on Mycenaean Religion". Antiquity. 44 (176): 270–280. doi:10.1017/S0003598X00041740. S2CID 163471174.
- Taylour, Lord William (1958). Mycenaean Pottery in Italy and Adjacent Areas. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Thomas, Carol G. (1995). "The Components of Political Identity in Mycenaean Greece" (PDF). Aegaeum. 12: 349–354. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 September 2013.
- van Wijngaarden, Geert Jan (2002). Use and Appreciation of Mycenaean Pottery in the Levant, Cyprus and Italy (1600–1200 BC). Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press. ISBN 978-9-05-356482-0.
- Vianello, Andrea (2005). Late Bronze Age Mycenaean and Italic Products in the West Mediterranean: A Social and Economic Analysis. Oxford: Archaeopress. ISBN 978-1-84-171875-0.
- Wardle, K.A.; Wardle, Diana (1997). Cities of Legend: The Mycenaean World. London: Bristol Classical Press. ISBN 978-1-85-399355-8.
- Whittaker von Hofsten, Helène (2007). "Reflections on the Social Status of Mycenaean Women". In Lovén, Lena Larsson; Strömberg, Agneta (eds.). Public Roles and Personal Status Men and Women in Antiquity. Sävedalen: Paul Åströms Förlag. pp. 3–18. ISBN 9789170812378.
- Wikander, Örjan (January–March 1990). "Archaic Roof Tiles the First Generations". Hesperia. 59 (1): 285–290. JSTOR 148143.
- Wright, James Clinton (2008). "Early Mycenaean Greece". In Shelmerdine, Cynthia W. (ed.). The Cambridge Companion to the Aegean Bronze Age. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 230–257. doi:10.1017/CCOL9780521814447.011. ISBN 9781139001892.
- Wood J. R., Hsu, Y-T and Bell, C. 2021 Sending Laurion Back to the Future: Bronze Age Silver and the Source of Confusion, Internet Archaeology 56. https://doi.org/10.11141/ia.56.9
- Acts of the International Archeaological Symposium: "The Mycenaeans in the Eastern Mediterranean", Nicosia 27th March-2nd April, 1972. Ministry of Communications and Works, Department of Antiquities. 1973.
Further reading
edit- Anthony, David W. (2007). The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-05887-0.
- Barlow, Jane Atwood; Bolger, Diane L.; Kling, Barbara (1991). Cypriot Ceramics: Reading the Prehistoric Record. Philadelphia, PA: University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. ISBN 978-0-92-417110-9.
- Boehm, Isabelle; Müller-Celka, Sylvie, eds. (2010). Espace civil, espace religieux en Égée durant la période mycénienne. Approches épigraphique, linguistique et archéologique. Actes des journées d'archéologie et de philologie mycéniennes, Lyon, 1er février et 1er mars 2007 (in French). Vol. 54. Lyon: Maison de l'Orient et de la Méditerranée Jean Pouilloux. ISBN 978-2-35668-012-9.
- Burkert, Walter (1987) [1985]. Greek Religion: Archaic and Classical. Oxford and Malden: Blackwell Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-11-872499-6.
- De Fidio, Pia (1990). "Potere politico et funzione del sacro nella società micenee". Mélanges Pierre Lévêque. 4: 151–171.
- Doumas, Christos (1980). Thera and the Aegean World II: Papers Presented at the Second International Scientific Congress, Santorini, Greece, August 1978. London: Thera and the Aegean World. ISBN 978-0-95-061332-1.
- French, Elizabeth Bayard (2002). Mycenae: Agamemnon's Capital. Stroud: Tempus. ISBN 978-0-7524-1951-0.
- Gitin, Seymour; Mazar, Amihay; Stern, Ephraim; Dothan, Trude Krakauer (1998). Mediterranean Peoples in Transition: Thirteenth to Early Tenth Centuries BCE. Jerusalem: Israel Exploration Society. ISBN 978-9-65-221036-4.
- Güterbock, Hans G. (April 1983). "The Hittites and the Aegean World: Part 1. The Ahhiyawa Problem Reconsidered". American Journal of Archaeology. 87 (2): 133–138. doi:10.2307/504928. JSTOR 504928. S2CID 191376388.
- Güterbock, Hans G. (June 1984). "Hittites and Akhaeans: A New Look". Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society. 128 (2): 114–122.
- Hagg, Robin; Wells, Berit (1978). Opuscula Atheniensia XII. Lund: Paul Astroms Forlag. ISBN 978-9-18-508612-2.
- Podzuweit, Christian (1982). "Die mykenische Welt und Troja". In Hänsel, B. (ed.). Südosteuropa zwischen 1600 und 1000 V. Chr (in German). Berlin: Moreland Editions. pp. 65–88.
- Higgins, Reynold Alleyne (1997). Minoan and Mycenaean Art. London and New York: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-50-020303-3.
- Hooker, J.T. (1976). Mycenaean Greece. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul. ISBN 9780710083791.
- Huxley, G.L. (1960). Achaeans and Greeks. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press.
- Mellink, Machteld J. (April 1983). "The Hittites and the Aegean World: Part 2. Archaeological Comments on Ahhiyawa-Achaians in Western Anatolia". American Journal of Archaeology. 87 (2): 138–141. doi:10.2307/504929. JSTOR 504929. S2CID 194070218.
- Mountjoy, Penelope A. (1986). Mycenaean Decorated Pottery: A Guide to Identification (Studies in Mediterranean Archaeology 73). Göteborg: Paul Aströms Forlag. ISBN 978-9-18-609832-2.
- Nur, Amos; Cline, Eric (2000). "Poseidon's Horses: Plate Tectonics and Earthquake Storms in the Late Bronze Age Aegean and Eastern Mediterranean" (PDF). Journal of Archaeological Science. 27 (1): 43–63. Bibcode:2000JArSc..27...43N. doi:10.1006/jasc.1999.0431. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2006.
- Preziosi, Donald; Hitchcock, Louise A. (1999). Aegean Art and Architecture. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-284208-4.
- Robertson, Martin (1959). Les Grands siècles de la peinture: La peinture Grecque. Genève-Paris: Skira.
- Rodríguez, Juan Piquero (2017). "Estudios sobre el léxico micénico: notas sobre la naturaleza y funciones del ra-wa-ke-ta". In de la Villa, Jesús; Rey, Emma Falque; Castro, José Francisco González; Jiménez, María José Muñoz (eds.). Conuentus Classicorum: temas y formas del Mundo Clásico (in Spanish). Vol. 1. Sociedad Española de Estudios Clásicos. pp. 355–364. ISBN 978-84-697-8214-9.
- Skeat, T.C. (1934). The Dorians in Archaeology. London: de la More Press.
- Taylour, Lord William (1990) [1964]. The Mycenaeans. London: Thames & Hudson Limited. ISBN 978-0-50-027586-3.
- Vermeule, Emily; Karageorghis, Vassos (1982). Mycenaean Pictorial Vase Painting. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-67-459650-4.
- Vermeule, Emily Townsend (March 1960). "The Fall of the Mycenaean Empire". Archaeology. 13 (1): 66–76. JSTOR 41663738.
- Weiss, Barry (June 1982). "The Decline of Late Bronze Age Civilization as a Possible Response to Climatic Change". Climatic Change. 4 (2): 173–198. Bibcode:1982ClCh....4..173W. doi:10.1007/bf00140587. ISSN 0165-0009. S2CID 154059624.
External links
edit- Godart, Louis (2013) [January 1997]. "Les citadelles mycéniennes" (in French). Clio.
- Hemingway, Seán; Hemingway, Colette (2000–2013). "Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History: Mycenaean Civilization". The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
- Horejs, Barbara; Pavúk, Peter, eds. (2007). "The Aegeo-Balkan Prehistory Project". The Aegeo-Balkan Prehistory Team.
- Rutter, Jeremy B. "Prehistoric Archeology of the Aegean". Hanover, NH: Dartmouth College. Archived from the original on 1 January 2009. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- Salimbetti, Andrea (September 2015). "The Greek Age of Bronze".
- "The Mycenaeans and Italy: The Archaeological and Archaeometric Ceramic Evidence". University of Glasgow School of Humanities. Archived from the original on 27 September 2013. Retrieved 26 September 2013.
- Wright, James C. (2002). "The Nemea Valley Archaeological Project: Internet Edition". Bryn Mawr College Department of Classical and Near Eastern Archaeology. Archived from the original on 31 March 2007. Retrieved 2 December 2005.