Schmidtler's smooth newt (Lissotriton schmidtleri) is a newt species found from northwestern Greece and southeast Bulgaria over East Thrace across the Bosphorus to northwest Anatolia.[1][4][5]: 234 Its range borders that of the smooth newt (L. vulgaris), the Greek smooth newt (L. graecus) and Kosswig's smooth newt (L. kosswigi) to the north, west, and east, respectively.[4]
| Schmidtler's smooth newt | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male during breeding season[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Urodela |
| Family: | Salamandridae |
| Genus: | Lissotriton |
| Species: | L. schmidtleri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lissotriton schmidtleri | |
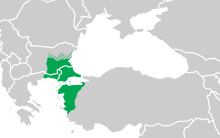
| |
| range in the Balkans and in Anatolia; hatching indicates unclear contact zones with L. graecus and L. vulgaris | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
| |
Christopher Raxworthy described the species in 1988 as Triturus vulgaris schmidtleri, a subspecies of the smooth newt.[2] After genetic data had suggested the smooth newt was a complex of distinct lineages, Pabijan and colleagues recognised Schmidtler's smooth newt as distinct species in 2017.[6] This was followed by subsequent authors.[3][4]
The species differs from other species in the smooth newt species complex mainly in the male secondary characters during breeding season.[4] It is overall very similar to the smooth newt but rather small, with males reaching 5–7 cm (2.0–2.8 in) length. The dorsal crest reaches 2 mm or more in height and is denticulated. The tail end is elongated but does not have a filament as in the neighbouring Kosswig's smooth newt. The body is slightly square-shaped but has no dorso-lateral folds. Toe flaps are only weakly developed.[2][5]: 234
Paedomorphic adults have been reported for Schmidtler's smooth newt.[7]
The species's conservation status has not yet been evaluated separately from the smooth newt by the IUCN. Since its range is much smaller than that of the smooth newt species complex as a whole, it is likely to be more vulnerable than previously estimated.[1][4]
References
edit- ^ a b c Wielstra, B.; Bozkurt, E.; Olgun, K. (2015). "The distribution and taxonomy of Lissotriton newts in Turkey (Amphibia, Salamandridae)". ZooKeys (484): 11–23. doi:10.3897/zookeys.484.8869. ISSN 1313-2970. PMC 4361781. PMID 25829839.
- ^ a b c Raxworthy, C.J. (1988). "A description and study of a new dwarf sub-species of smooth newt, Triturus vulgaris, from western Anatolia, Turkey". Journal of Zoology. 215 (4): 753–763. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1988.tb02409.x. ISSN 0952-8369.
- ^ a b Frost, D.R. (2020). "Lissotriton schmidtleri (Raxworthy, 1988)". Amphibian Species of the World: An Online Reference. Version 6.1. New York, USA: American Museum of Natural History. doi:10.5531/db.vz.0001. Archived from the original on 25 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Wielstra, B.; Canestrelli, D.; Cvijanović, M.; et al. (2018). "The distributions of the six species constituting the smooth newt species complex (Lissotriton vulgaris sensu lato and L. montandoni) – an addition to the New Atlas of Amphibians and Reptiles of Europe" (PDF). Amphibia-Reptilia. 39 (2): 252–259. doi:10.1163/15685381-17000128. S2CID 4941926. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 April 2019.
- ^ a b Sparreboom, M. (2014). Salamanders of the Old World: The Salamanders of Europe, Asia and Northern Africa. Zeist, The Netherlands: KNNV Publishing. doi:10.1163/9789004285620. ISBN 9789004285620.
- ^ Pabijan, M.; Zieliński, P.; Dudek, K.; Stuglik, M. & Babik, W. (2017). "Isolation and gene flow in a speciation continuum in newts". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 116: 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2017.08.003. ISSN 1055-7903. PMID 28797693.
- ^ Bozkurt, E.; Tural, M.; Ulutaş, G. & Olgun, K. (2016). "Two New Paedomorphic Population Records of the Smooth Newt, Lissotriton vulgaris schmidtleri (Raxworthy, 1988) (Urodela, Salamandridae), from Western Turkey". Russian Journal of Herpetology. 23: 158–162. doi:10.30906/1026-2296-2016-23-2-158-162 (inactive 31 January 2024).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2024 (link)