The Mazahua language (Central Mazahua: Jñatrjo, [ɲ̥atrjo]) is an Oto-Pamean language spoken in the central states of Mexico by the ethnic group that is widely known as the Mazahua but calls itself the Hñatho. It is a Mesoamerican language and has many of the traits of the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area. In 2003, along with some 62 other indigenous languages, it was recognised by a statutory law of Mexico (General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples)[2] as an official language in the Federal District and the other administrative divisions in which it is spoken, and on an equal footing with Spanish. The largest concentration of Mazahua is found in the municipality of San Felipe del Progreso, State of México, near Toluca.
| Mazahua | |
|---|---|
| Jñatjo (Toluca Mazahua) Jñatrjo (Central Mazahua) | |
| Region | Mexico: State of Mexico, Toluca |
| Ethnicity | Mazahua |
Native speakers | 150,000 (2020 census)[1] |
Oto-Manguean
| |
| Official status | |
| Regulated by | Secretaría de Educación Pública |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:mmc – Toluca Mazahuamaz – Central Mazahua |
| Glottolog | maza1293 |
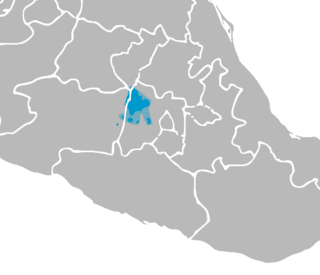 Extent of the Mazahua language in Mexico | |
 The Mazahua language, number 4 (darker blue), northwest | |
The closest relatives of the Mazahua language are Otomi, Matlatzinca, and Ocuilteco/Tlahuica languages, which together with Mazahua form the Otomian subgroup of the Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family.
Mazahua is a tonal language and distinguishes high, low, and falling tones on all syllables except the final syllable of a word whose stress is predictable.
Mazahua's most distinctive feature is its abnormally-large phoneme inventory, around sixty phonemes, or twice the number in English. There are eight vowel phonemes, seven contrastive nasal vowels, and as many as forty-five consonants.
Amongst them are ejectives, implosives and contrastive voiceless sonorants. Along with Sindhi and Tukang Besi, Mazahua is a rare case of a language with true implosives that is far from regions where implosives are commonly encountered. It is also one of the few languages with ejective fricatives.[3]
Mazahua-language programming is carried by the CDI's radio station XETUMI-AM, broadcasting from Tuxpan, Michoacán.
Phonology
editConsonants
edit| Bilabial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | lab. | ||||||
| Nasal | glott. | m̰ | n̰ | ɲ̰ | |||
| voiceless | m̥ | n̥ | ɲ̥ | ||||
| plain | m | n | ɲ | ||||
| Plosive | implosive | ɓ | ɗ | ||||
| ejective | tʼ | kʼ | kʼʷ | ||||
| aspirated | pʰ | tʰ | kʰ | kʷʰ | |||
| tenuis | p | t | k | kʷ | ʔ | ||
| voiced | ɡ | ɡʷ | |||||
| Affricate | ejective | tsʼ | tʃʼ | ||||
| aspirated | tsʰ | tʃʰ | |||||
| tenuis | ts | tʃ | |||||
| Fricative | ejective | sʼ | |||||
| aspirated | sʰ | ||||||
| tenuis | s | ʃ | h | ||||
| voiced | z | ʒ | ɣ | ||||
| Semivowel | glott. | j̰ | w̰ | ||||
| voiceless | j̊ | w̥ | |||||
| plain | j | w | |||||
| Liquid | lateral | l | |||||
| trill | r | ||||||
Oral vowels
edit| Front | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | oral | i | u |
| nasal | ĩ | ũ | |
| Close-mid | oral | e | o |
| nasal | ẽ | õ | |
| Mid | ə | ||
| Open-mid | oral | ɛ | ɔ |
| nasal | ɛ̃ | ɔ̃ | |
| Open | oral | a | |
| nasal | ã | ||
Orthography
editThe orthography is based on the Spanish alphabet, with additional rules to account for the large phonetic inventory of Mazahua:
- A diagonal strikethrough indicates a reduced vowel (these letters were added to Unicode in 2016)[4]
- Underline indicates a nasal vowel[5]
- An apostrophe indicates an ejective consonant or glottalic consonant
- The letter j after a consonant indicates an aspirated consonant
- The letter u after a consonant indicates labialization[6]
| Grapheme | Phoneme |
|---|---|
| a | [a] |
| ⱥ | [ə] |
| a̱ | [ã] |
| b | [ɓ] |
| c | [k] |
| cꞌ | [kʼ] |
| cj | [kʰ] |
| cu | [kʷ] |
| cꞌu | [kʷʼ] |
| cju | [kʷʰ] |
| ch | [tʃ] |
| chꞌ | [tʃʼ] |
| chj | [tʃʰ] |
| d | [ɗ] |
| dy | [dz] |
| e | [e] |
| ɇ | [ɛ] |
| e̱ | [ɛ̃]/[ẽ] |
| g | [ɡ] |
| gu | [ɡʷ] |
| hu | [w] |
| ꞌhu | [w̰] |
| i | [i] |
| i̱ | [ĩ] |
| j | [j]/[h] |
| jꞌ | [j̰] |
| jm | [m̥] |
| jn | [n̥] |
| jñ | [ɲ̥] |
| ju | [w̥] |
| jy | [j̊] |
| l | [l] |
| m | [m] |
| mꞌ | [m̰] |
| n | [n] |
| nꞌ | [n̰] |
| ñ | [ɲ] |
| ñꞌ | [ɲ̰] |
| o | [o] |
| ø | [ɔ] |
| o̱ | [õ]/[ɔ̃] |
| p | [p] |
| pj | [pʰ] |
| r | [r] |
| s | [s] |
| sꞌ | [sʼ] |
| sj | [sʰ] |
| t | [t] |
| tꞌ | [tʼ] |
| tj | [tʰ] |
| ts | [ts] |
| tsꞌ | [tsʼ] |
| tsj | [tsʰ] |
| u | [u] |
| ꞹ | [ɨ] |
| u̱ | [ũ] |
| x | [ʃ] |
| z | [z] |
| zh | [ʒ] |
| ꞌ | [ʔ] |
Sample text
editThe following the first Article of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) into Mazahua:
Texe yo nte̱ꞌe̱ chjetrjoji, angezeji ximi xoꞌoji ñeje kꞌinchiji, nesta ra ngara na joꞌo kꞌo dyaja e nte̱ꞌe̱. |
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood. |
References
edit- ^ INALI (2012) México: Lenguas indígenas nacionales
- ^ "Ley General de Derechos Lingüísticos de los Pueblos Indígenas" [General Law of the Linguistic Rights of Indigenous peoples] (in Spanish). 13 March 2003. Archived from the original on 8 February 2007.
- ^ Ian Maddieson (with a chapter contributed by Sandra Ferrari Disner); Patterns of sounds; Cambridge University Press, 1984. ISBN 0-521-26536-3
- ^ "Proposal to encode two Latin characters for Mazahua" (PDF). Unicode. 22 January 2016. Retrieved 12 March 2024.
- ^ Ferguson, Carol (19 February 2005). God's Mimic: The Biography of Hazel Page. Trafford Publishing. ISBN 9781412044288 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Mazahua language, alphabet and pronunciation". www.omniglot.com.
Sources
edit- Knapp Ring, Michael Herbert, Fonología del mazahua, Tesis de licenciatura, ENAH, México, 1996
- Michael Knapp, 2002 “Elementos de dialectología Mazahua" In Del Cora Al Maya Yucateco: Estudios Linguisticos Sobre Algunas Lenguas Indigenas Mexicanas Paulette Levy (Ed.), Universidad Nacional Autonoma De Mexico