Cholestane is a saturated tetracyclic triterpene. This 27-carbon biomarker is produced by diagenesis of cholesterol and is one of the most abundant biomarkers in the rock record.[2] Presence of cholestane, its derivatives and related chemical compounds in environmental samples is commonly interpreted as an indicator of animal life and/or traces of O2, as animals are known for exclusively producing cholesterol, and thus has been used to draw evolutionary relationships between ancient organisms of unknown phylogenetic origin and modern metazoan taxa.[3] Cholesterol is made in low abundance by other organisms (e.g., rhodophytes, land plants), but because these other organisms produce a variety of sterols it cannot be used as a conclusive indicator of any one taxon.[4][5] It is often found in analysis of organic compounds in petroleum.

| |
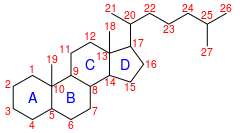 IUPAC numbering[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cholestane
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bR,9aS,9bS,11aR)-9a,11a-Dimethyl-1-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.496 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H48 | |
| Molar mass | 372.681 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.911 g/ml |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Background
editCholestane is a saturated C-27 animal biomarker often found in petroleum deposits. It is a diagenetic product of cholesterol, which is an organic molecule made primarily by animals and make up ~30% of animal cell membranes[citation needed]. Cholesterol is responsible for membrane rigidity and fluidity, as well as intracellular transport, cell signaling and nerve conduction.[6] In humans, it is also the precursor for hormones (i.e., estrogen, testosterone). It is synthesized via squalene and naturally assumes a specific stereochemical orientation (3β-ol, 5α (H), 14α (H), 17α (H), 20R). This stereochemical orientation is typically maintained throughout diagenetic processes, but cholestane can be found in the fossil record with many stereochemical configurations.
Biomarker
editCholestane in the fossil record is often interpreted as an indicator (biomarker) of ancient animal life and is often used by geochemists and geobiologists to reconstruct animal evolution (particularly in the Precambrian Earth history; e.g., Ediacaran,[3] Cryogenian and Proterozoic in general[7][8]). Molecular oxygen is required to produce cholesterol;[9] thus, the presence of cholestane suggests some trace of oxygen in the paleoenvironment. Cholestane is not exclusively derived from diagenesis of animal-derived steroid molecules; cholestane may also be associated with the presence of e.g., rhodophytes and embryophytes,[10][5] although the abundance of such non-metaozan cholestane is unknown. Embryophytes generally produce a variety of sterols, which are collectively known as phytosterols,[11] and cholesterol remains a minor component. In contrast, bacteria produce other cyclic triterpenoids such as hopanoids and their diagenetic products hopanes are utilized as bacterial biomarkers.
Natural preservation in fossils
editCholesterol has 256 stereoisomers, but only one of them is formed naturally in production of cholesterol (3β-ol, 5α (H), 14α (H), 17α (H), 20R) and is therefore the primary stereoisomer of interest for cholestane measurements. Deviations from this stereochemistry often reflects diagenesis, thermal maturation and preservation bias.
Diagenesis typically leads to the loss of functional groups and double bonds in organic molecules. For cholestane specifically, diagenesis of cholesterol to cholestane produces a molecule that is fully saturated compared to its steroid counterpart. This process occurs without the loss or gain of carbon atoms and therefore can serve as an indicator of the original steroid produced by the organism in the environment.[12]
Thermal alteration can also cause loss of the alkane side-chain at C17.[13] An experiment demonstrated that over 4 weeks at 300 °C, cholestane underwent 17% decomposition of its alkane side chain. In contrast, the polycyclic structure (C1-17) is very thermally stable. Diagenetic processes can also cause methyl shifts and aromatization.
Stereochemical alteration
editAdditional diagenetic processes can further alter the cholestane molecule. For instance, cholestane is susceptible to stereochemical shifts over time from its natural isomer. These changes can be the effect of thermal or microbial alteration. Thermal alteration can cause changes in stereochemistry at both the C20 chiral center, as well as the hydrogen atoms. The ratio of R/S stereoisomers is typically reported as a measure of “thermal maturity”.[14] In contrast, conversion of the hydrogen atom at the C5 position from α to β configuration reflects anaerobic microbial activity,[3] and can be understood through isotope labeling experiments on controlled microbe experiments metabolizing the steroid of interest.[15][16] One study demonstrated that there are two reactions that can produce loss of the cholesterol double bond—(1) direct reduction of double bond or (2) production of ketone prior to reduction of double bond—resulting in distinct isomerization of the hydrogen atom at the C5 position.[15] The C14 and C17α hydrogen atoms are more stable and undergo changes to β configuration in much lower abundances than the 5 hydrogen atom.
Measurement techniques
editGC/MS
editCholestane can be extracted from samples and measured on the GC/MS to quantify relative abundance to other organic compounds. This measurement is done by extraction of the steranes into a non-polar solvent (e.g., dichloromethane or chloroform) and purified into a “saturates” fraction using silica gel column gas chromatography. Cholestane isomers will elute from the column based on molecular weight and various stereochemistry, which makes traditional mass spectrometry challenging due to close co-elution of isomers. Alternatively, one can measure cholestane using GC/MS/MS experiments which target the m/z fragment 217 (from molecular ion 372). This specific method first looks for the 372 molecular ion of cholestane, and then fragments that molecular ion further to its m/z 217 fragment in order to improve identification of specific isomers.
δ13C isotope ratios
editδ13C values of cholestane reflect the carbon isotope composition of the animals that created the original cholesterol molecules. Animal carbon isotope composition is typically understood to be a function of their diet;[17] therefore, carbon isotope composition of cholestane would reflect this original diet value as well. δ13C values can be measured using a gas chromatograph coupled to an IRMS.
More generally, steranes can be used as an indicator of environmental shifts. A study has presented δ13C values of steranes versus hopanes and used it to propose changes in the photic zone over the course of the Miocene, as changes in the isotope value must be either a result of dissolved inorganic carbon within the water or biological isotope fractionation.[14]
Case studies
editEarly life biomarkers
editPresence of cholestane does not necessarily indicate presence of animals, but is often used in conjunction with other biomarkers to note the rise of distinct taxa in the fossil record; with regard to this, a study measured relative abundance in cholestane versus other triterpenoid biomarkers to demonstrate the rise of algae during the Neoproterozoic.[7][18]
Tracing the actual origins of cholestane within the fossil record is challenging, as most of the rocks from that time period are heavily metamorphosed and thus potential biomarkers are thermally altered.[citation needed] A study linked the source of cholestane to a specific Ediacaran fossil (Dickinsonia) to provide constraints to the taxonomic classification of Ediacaran biota as evolutionary preludes to metazoan life.[3] Cholestane is not a specific marker for animals though and is found in most eukaryotic lineages.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ The Nomenclature of Steroids Archived 2011-05-14 at the Wayback Machine, IUPAC
- ^ Peters, Kenneth E. (Kenneth Eric), 1950- (2007). The biomarker guide. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521039987. OCLC 1015511618.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e Bobrovskiy, Ilya; Hope, Janet M.; Ivantsov, Andrey; Nettersheim, Benjamin J.; Hallmann, Christian; Brocks, Jochen J. (2018-09-20). "Ancient steroids establish the Ediacaran fossil Dickinsonia as one of the earliest animals". Science. 361 (6408): 1246–1249. Bibcode:2018Sci...361.1246B. doi:10.1126/science.aat7228. hdl:1885/230014. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 30237355.
- ^ Combaut, Georges; Saenger, Peter (April 1984). "Sterols of the amansieae (rhodomelaceae: Rhodophyta)". Phytochemistry. 23 (4): 781–782. Bibcode:1984PChem..23..781C. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(00)85025-6. ISSN 0031-9422.
- ^ a b Sonawane, Prashant D.; Pollier, Jacob; Panda, Sayantan; Szymanski, Jedrzej; Massalha, Hassan; Yona, Meital; Unger, Tamar; Malitsky, Sergey; Arendt, Philipp; Pauwels, Laurens; Almekias-Siegl, Efrat (2016-12-22). "Plant cholesterol biosynthetic pathway overlaps with phytosterol metabolism". Nature Plants. 3 (1): 16205. doi:10.1038/nplants.2016.205. ISSN 2055-0278. PMID 28005066. S2CID 5518449.
- ^ Life : the science of biology. Sadava, David E. (9th ed.). Sunderland, Mass.: Sinauer Associates. 2011. ISBN 978-1429219624. OCLC 368046231.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b Brocks, Jochen J.; Jarrett, Amber J. M.; Sirantoine, Eva; Hallmann, Christian; Hoshino, Yosuke; Liyanage, Tharika (August 2017). "The rise of algae in Cryogenian oceans and the emergence of animals". Nature. 548 (7669): 578–581. Bibcode:2017Natur.548..578B. doi:10.1038/nature23457. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 28813409. S2CID 205258987.
- ^ Summons, Roger E; Brassell, Simon C; Eglinton, Geoffrey; Evans, Evan; Horodyski, Robert J; Robinson, Neil; Ward, David M (November 1988). "Distinctive hydrocarbon biomarkers from fossiliferous sediment of the Late Proterozoic Walcott Member, Chuar Group, Grand Canyon, Arizona". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 52 (11): 2625–2637. Bibcode:1988GeCoA..52.2625S. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(88)90031-2. ISSN 0016-7037.
- ^ Mehta, Sweety (2013-09-17). "Biosynthesis and Regulation of Cholesterol (with Animation) | Animations". PharmaXChange.info. Retrieved 2019-06-04.
- ^ Summons, Roger E.; Erwin, Douglas H. (2018-09-20). "Chemical clues to the earliest animal fossils". Science. 361 (6408): 1198–1199. Bibcode:2018Sci...361.1198S. doi:10.1126/science.aau9710. hdl:1721.1/134716.2. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 30237342. S2CID 52306517.
- ^ Darnet, Sylvain; Blary, Aurélien; Chevalier, Quentin; Schaller, Hubert (2021). "Phytosterol Profiles, Genomes and Enzymes – An Overview". Frontiers in Plant Science. 12: 878. doi:10.3389/fpls.2021.665206. ISSN 1664-462X. PMC 8172173. PMID 34093623.
- ^ Grantham, P.J.; Wakefield, L.L. (January 1988). "Variations in the sterane carbon number distributions of marine source rock derived crude oils through geological time". Organic Geochemistry. 12 (1): 61–73. Bibcode:1988OrGeo..12...61G. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(88)90115-5. ISSN 0146-6380.
- ^ Mango, Frank D. (January 1990). "The origin of light cycloalkanes in petroleum". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 54 (1): 23–27. Bibcode:1990GeCoA..54...23M. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(90)90191-m. ISSN 0016-7037.
- ^ a b Schoell, M.; Schouten, S.; Damste, J. S. S.; de Leeuw, J. W.; Summons, R. E. (1994-02-25). "A Molecular Organic Carbon Isotope Record of Miocene Climate Changes". Science. 263 (5150): 1122–1125. Bibcode:1994Sci...263.1122S. doi:10.1126/science.263.5150.1122. hdl:1874/4185. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17831625. S2CID 40960698.
- ^ a b Mermoud, F.; Wünsche, L.; Clerc, O.; Gülaçar, F.O.; Buchs, A. (January 1984). "Steroidal ketones in the early diagenetic transformations of Δ5 sterols in different types of sediments". Organic Geochemistry. 6: 25–29. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(84)90023-8. ISSN 0146-6380.
- ^ Taylor, Craig D.; Smith, Steven O.; Gagosian, Robert B. (November 1981). "Use of microbial enrichments for the study of the anaerobic degradation of cholesterol". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 45 (11): 2161–2168. Bibcode:1981GeCoA..45.2161T. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(81)90068-5. ISSN 0016-7037.
- ^ Hayes, John M. (2001-12-31), "3. Fractionation of Carbon and Hydrogen Isotopes in Biosynthetic Processes", Stable Isotope Geochemistry, De Gruyter, pp. 225–278, doi:10.1515/9781501508745-006, ISBN 9781501508745
- ^ Hoshino, Yosuke; Poshibaeva, Aleksandra; Meredith, William; Snape, Colin; Poshibaev, Vladimir; Versteegh, Gerard J. M.; Kuznetsov, Nikolay; Leider, Arne; van Maldegem, Lennart; Neumann, Mareike; Naeher, Sebastian (2017). "Cryogenian evolution of stigmasteroid biosynthesis". Science Advances. 3 (9): e1700887. Bibcode:2017SciA....3E0887H. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1700887. PMC 5606710. PMID 28948220.
External links
edit- Cholestanes at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)