The line of Gennari (also called the "band" or "stria" of Gennari) is a band of myelinated axons that runs parallel to the surface of the cerebral cortex on the banks of the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. This formation is visible to the naked eye as a white strip running through the cortical grey matter, and is the reason the V1 in primates is also referred to as the "striate cortex." The line of Gennari is due to dense axonal input from the thalamus to layer IV of visual cortex. It is the name given to the enlarged external band of Baillarger. The structure is named for its discoverer, Francesco Gennari, who first observed it in 1776 as a medical student at the University of Parma.[1] He described it in a book which he published in 1782.[2] Although non-primate species have areas that are designated primary visual cortex, some (if not all) lack a stria of Gennari.[3]
| Line of Gennari | |
|---|---|
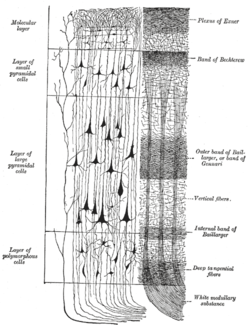 Cerebral cortex. To the left, the groups of cells; to the right, the systems of fibers. Quite to the left of the figure a sensory nerve fiber is shown. | |
 Micrograph showing the visual cortex (predominantly pink). The blue, horizontal band in the lower half of the image are the bands of Baillarger/the line of Gennari. Subcortical white matter (predominantly blue) is seen at the very bottom of the image. LFB stain. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | stria occipitalis laminae granularis internae isocorticis |
| NeuroNames | 2118 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Vicq d’Azyr published the stripes in Traité d'anatomie (1786), and for a while it was known as the stripe of Vicq d’Azyr.[4]
See also
editExternal links
editReferences
edit- ^ Glickstein, Mitchell; Rizzolatti, Giacomo (1984-12-01). "Francesco Gennari and the structure of the cerebral cortex". Trends in Neurosciences. 7 (12): 464–467. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(84)80255-6. ISSN 0166-2236. S2CID 53168851.
- ^ F. Gennari. De Peculiari Structura Cerebri Parma Ex Regio Typographeo, 1782.
- ^ Zilles and Wree. Isocortex in Paxinos (Ed.) The Rat Nervous System, 1985.
- ^ Glickstein, Mitchell; Rizzolatti, Giacomo (December 1984). "Francesco Gennari and the structure of the cerebral cortex". Trends in Neurosciences. 7 (12): 464–467. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(84)80255-6.